Glomus
Glomus is a genus of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, and all species form symbiotic relationships with plant roots. Glomus is the largest genus of AM fungi, with ca. 85 species described, but is currently defined as non-monophyletic.
How common are glomus tumors in young adults?
Abnormal growth of a glomus body results in Glomus Tumors. Glomus Tumors usually occur in people 20 to 50 years of age but are more frequent in young adults. More common in women, 70% of Glomus Tumors present in the hand with the clear majority occurring underneath the nail bed. Most of the nodules are solitary but can occur in clusters.
Where do glomus tumors occur in the body?
Benign tumors of glomus bodies can occur within the middle ear or at other sites: the temporal bone and neck, or within the jugular vein (the large vein in the upper neck which drains the head toward the heart). Glomus tumors of the middle ear are more common than glomus tumors of the jugular vein.
What is the size of a benign glomus tumor?
The tumor is the translucent oblate spheroid in the center of the incision, approximate horizontal dimension is 4 millimeters. Surgical excision is the preferred treatment for benign glomus tumors.
What is the prognosis of glomus tumors?
Malignant glomus tumors, or glomangiosarcomas, are extremely rare and usually represent a locally infiltrative malignancy. However, metastases do occur and are usually fatal. Cancerous glomus tumors are exceedingly rare.

How rare is a glomus tumor?
The glomus tumor is a rare benign neoplasm that arises from the neuroarterial structure called a glomus body1, which accounts for 1 % to 4.5 % of tumors in the hand.
Where are glomus tumors most commonly found?
In the head and neck, glomus tumor tissue is found in the jugular bulb, middle ear, and carotid artery. Of these sites, tumors are most common in the jugular bulb, which is a region of the jugular vein positioned immediately below the middle ear.
How common are glomus tumors ear?
Glomus tumours are fairly rare with an incidence of around 1 per 1 million[4]. They are usually hypervascular tumours that arise within the jugular foramen of the temporal bone[1-4]. They characteristically present with conductive hearing loss and a pulsatile tinnitus as demonstrated in our case.
How do you know if you have a glomus tumor?
MRI or CT Imaging Glomus tumors are usually diagnosed with MRI or CT scans. These scans also help identify additional glomus tumors that may be present.
How painful are glomus tumors?
Glomus tumors are painful subungual lesions. They produce a throbbing or lancinating local discomfort, cold-sensitivity, and severe pain following minor trauma. The diagnosis is confirmed by histology, but the clinical diagnosis is highly suggestive. Complete excision will usually relieve pain.
Do glomus tumors spread?
Malignant glomus tumor, or glomangiosarcoma, is a very rare mesenchymal neoplasm that, when seen, occurs in visceral organs. Despite having histologic features of malignancy, these tumors usually do not metastasize. However, when metastasis occurs, this disease is often fatal.
Can a glomus tumor burst?
Additionally, subungual glomus tumors have been reported to rupture and have also been reported to result in various nail changes, including color change, erythronychia, splitting, and thickening of the nail bed.
Is a glomus tumor cancerous?
Glomus tumors, or paragangliomas, are slow-growing, usually benign tumors in the carotid arteries (major blood vessels in your neck), the middle ear or the area below the middle ear (jugular bulb). Glomus tumors are most often benign; however, they can cause significant damage to surrounding tissues as they grow.
How do you get rid of a glomus tumor?
How are Glomus Tumors treated? Surgical excision of the tumor is the only treatment modality. During a 15-minute outpatient procedure the nail is removed, an incision is made into the nail bed exposing the tumor, and the tumor is removed.
Do glomus tumors show on MRI?
Glomus tumors are often evaluated with MRI, which has a positive predictive value of 97%.
Why do glomus tumors hurt?
The classic history of glomus tumour is excruciating paroxysmal pain, severe point tenderness, and cold sensitivity. The mechanism of pain may be attributed to contraction of myofilaments in response to temperature changes, leading to an increase in intracapsular pressure.
What causes glomus tumor in finger?
When exposed to cold temperatures, the glomus body moves blood away from the skins surface to reduce heat loss. While they are located all over the body, glomus apparati are found in higher concentrations in the fingers and toes. Abnormal growth of a glomus body results in Glomus Tumors.
What causes glomus Tumours?
The cause of a glomus jugulare tumor is unknown. In most cases, there are no known risk factors. Glomus tumors have been associated with changes (mutations) in a gene responsible for the enzyme succinate dehydrogenase (SDHD).
Why do glomus tumors hurt?
The classic history of glomus tumour is excruciating paroxysmal pain, severe point tenderness, and cold sensitivity. The mechanism of pain may be attributed to contraction of myofilaments in response to temperature changes, leading to an increase in intracapsular pressure.
What is glomus tumor in the ear?
Glomus tumors, or paragangliomas, are slow-growing, usually benign tumors in the carotid arteries (major blood vessels in your neck), the middle ear or the area below the middle ear (jugular bulb). Glomus tumors are most often benign; however, they can cause significant damage to surrounding tissues as they grow.
What is a glomus tumor?
Glomus tumors (also called paragangliomas) are a rare, slow-growing, and usually benign type of skull base tumor that often develop near the inner ear. Without treatment, they can harm surrounding tissue, damage nerves, and cause other serious problems. Duke’s skull base tumor experts collaborate to diagnose your tumor and offer a range of the most effective and advanced therapies available. Our goal is to treat the tumor while minimizing any injury to the surrounding structures.
How to diagnose a glomus tumor?
Glomus tumors are usually diagnosed with MRI or CT scans. These scans also help identify additional glomus tumors that may be present.
What are the symptoms of a glomus tumor?
One of the most common symptoms of glomus tumors is hearing your heartbeat in your ears, which doctors call pulsatile tinnitus. Other symptoms include hearing loss, voice changes, and problems with swallowing.
What is the treatment for a tumor?
Radiation oncologists use radiation treatments and stereotactic radiation therapy to target the tumor and shrink it. Radiation may be recommended before surgery, after surgery, or alone.
Where is Glomus tympanicum located?
Glomus tympanicum, located in the middle ear. These are usually very small.
How to embolize a tumor?
If your tumor is large, you may need an endovascular procedure a few days before surgery to embolize -- cut off the blood supply to -- the tumor. During this minimally invasive procedure, a surgeon makes a small incision and inserts a thin catheter into a major artery (usually in the groin). The catheter is threaded to the tumor site. Then, through the catheter, your surgeon uses tiny tools to block key blood vessels that feed the tumor.
How small is a glomus tumor?
In very early cases, glomus tumors can be as small as 2 to 3 mm. and appear as a red ball behind an intact tympanic membrane (eardrum). As glomus tumors expand, they begin to fill the middle ear. Some glomus tumors of the middle ear start by growing from the floor of the ear upward.
What is a glomus tumor?
Glomus Tumors (Tympanicum Jugulare) Glomus tumors are the most common benign tumors of the middle ear. They arise from glomus bodies. Glomus bodies are tiny, normal structures in the middle ear which serve as baro receptors. These baro receptors sense and help to regulate the oxygen pressure in the middle ear and mastoid.
How to treat glomus tympanicum?
Many glomus tympanicum tumors can now be approached through the ear canal by elevating the eardrum and then destroying the tumor completely with an Argon or CO2 laser versus more radical surgeries performed in the past.
What is the best test for glomus tumors?
If, however, there is erosion of the floor of the middle ear and jugular blub, CT scaning will provide the information. An MRI (Magentic Resonance Imaging) is also useful. However, a more useful test for glomus tumors is today’s MRA (Magentic Resonance Angiography).
What imaging studies are needed to determine the extent of a glomus tumor?
Imaging studies, including a CT scanning, MRI scanning and MR angiography, should be obtained to determine the limits and extent of any glomus tumors. It is necessary to differentiate between a glomus tumor limited to the middle ear, and a glomus tumor arising from the jugular vein. At the time of initial examination of the ear, the two may be indistinguishable. They are classified by area and degree of involvement. The classifications are:
How long before surgery to remove glomus jugulare tumor?
This procedure is usually performed 24 hours before surgery, greatly reducing the blood supply to the tumor. With embolization of large glomus jugulare tumors, transfusion is not usually necessary. Thus the procedure can be performed with greater safety.
Where do glomus tumors occur?
Glomus tumors are similar to chemodectomas, blood vessel tumors occurring in bodies similar to the glomus body. These tumors can occur along the carotid artery, the major arterial blood supply to the brain. They can also occur along other important portions of the blood supply in the neck and throat.
Where is the glomus tumor located?
Glomus tumors, or paragangliomas, are slow-growing, usually benign tumors in the carotid arteries (major blood vessels in your neck), the middle ear or the area below the middle ear (jugular bulb).
How to diagnose glomus tumor?
First, you’ll meet with your doctor for a physical exam and to discuss your symptoms. Then your doctor may order imaging tests, such as an MRI, CT scan or angiogram.
What are the symptoms of a glomus tumor?
Paraganglioma symptoms depend on where the tumor is located. A tumor in the carotid arteries (carotid body tumor) can cause: A mass in the neck. Hoarseness.
What is the best treatment for a glomus tumor?
Your team may recommend a combination of treatments for glomus tumors, including surgery and radiation.
How common are glomus tumors?
Glomus Tumors usually occur in people 20 to 50 years of age but are more frequent in young adults. More common in women, 70% of Glomus Tumors present in the hand with the clear majority occurring underneath the nail bed. Most of the nodules are solitary but can occur in clusters. Glomus Tumors represent 1 to 5% of all soft tissue tumors in ...
What are Glomus Tumors?
A Glomus Tumor is rare, usually benign, soft tissue neoplasm. The glomus apparatus (or glomus body) is a part of the dermal layer of the skin and is thought to aid in temperature regulation. When exposed to cold temperatures, the glomus body moves blood away from the skins surface to reduce heat loss. While they are located all over the body, glomus apparati are found in higher concentrations in the fingers and toes. Abnormal growth of a glomus body results in Glomus Tumors.
What are the symptoms of Glomus Tumors?
These lesions are usually quite small, less than 7mm in diameter. They can be extremely painful, are sensitive to temperature change, and tender on palpation. The pain is often worse at night and can be relieved by applying a tourniquet. The mass can cause the nail bed to grow irregularly with ridging possible.
How are Glomus Tumors diagnosed?
Glomus Tumors often require a specialist for accurate diagnosis. Upon examination the mass may appear as a bluish lesion under the nail or in the fingertip pulp. There may be an abnormal ridge in the nail, swelling at the tip and the nodule will be tender to touch. X-rays may show deformity or erosion in the distal phalanx if the mass is long standing, otherwise the films may appear normal. MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is the gold standard for diagnosis.
How can Dr. Knight help you with a glomus tumor?
When it comes to this rare and complex finger tumor, it is important to find a surgeon who is well-versed in their treatment and who has seen many cases. Dr. Knight is one such surgeon, and he will bring his expertise to bear in your case, which will, no doubt, lead to a quick diagnosis after a long period of pain that has been difficult to diagnose.
What percentage of glomus tumors are solitary?
Most of the nodules are solitary but can occur in clusters. Glomus Tumors represent 1 to 5% of all soft tissue tumors in the hand and fingers.
Do you have to have surgery to remove a glomus tumor?
Do I have to have surgery to get rid of a glomus tumor?#N#Unfortunately, due to the nature of glomus tumors and what they are made of, as well as where they are and how they are connected to the body’s surrounding tissues, surgery is the only viable option when it comes to having them removed. In the case of fingers, where they most commonly occur on hands, it is very important that the doctor carefully outline the area of the tumor so that the incision is done precisely and carefully, and the surrounding tissues are not excised in addition to the body of the tumor. Complete removal of the glomus body is key to making sure that the tumor doesn’t recur.
Where are glomus tumors located?
Most malignant glomus tumors are located in deep/visceral sites, but can arise in superficial sites
What are the symptoms of glomus tumor?
Patients with glomus tumors frequently report a history of symptoms of pulsatile tinnitus, hearing loss, aural fullness, and not uncommonly, cranial nerve dysfunction such as facial paresis, dysphasia, or hoarseness. Patients should be questioned regarding symptoms including tachycardia, palpitations, headaches, pallor, excessive perspiration, nausea, and problems of control of blood pressure, all of which are related to excess catecholamine secretion by the tumor. A complete otologic and head and neck examination is required. The tympanic membrane and middle ear space are inspected for tumor. When tumor is in the middle ear, a red mass is noted behind the tympanic membrane, and pulsation can be observed under high magnification (Fig. 125-1 ). The patient should be evaluated for evidence of weakness or dysfunction of cranial nerves VII, VIII, IX, X, XI, and XII. Both sides of the neck are palpated for mass lesions in the jugulodigastric and carotid bifurcation areas. Audiometry should be performed to determine the presence of a conductive, mixed, or sensorineural hearing loss.
What is the lining of glomangioma?
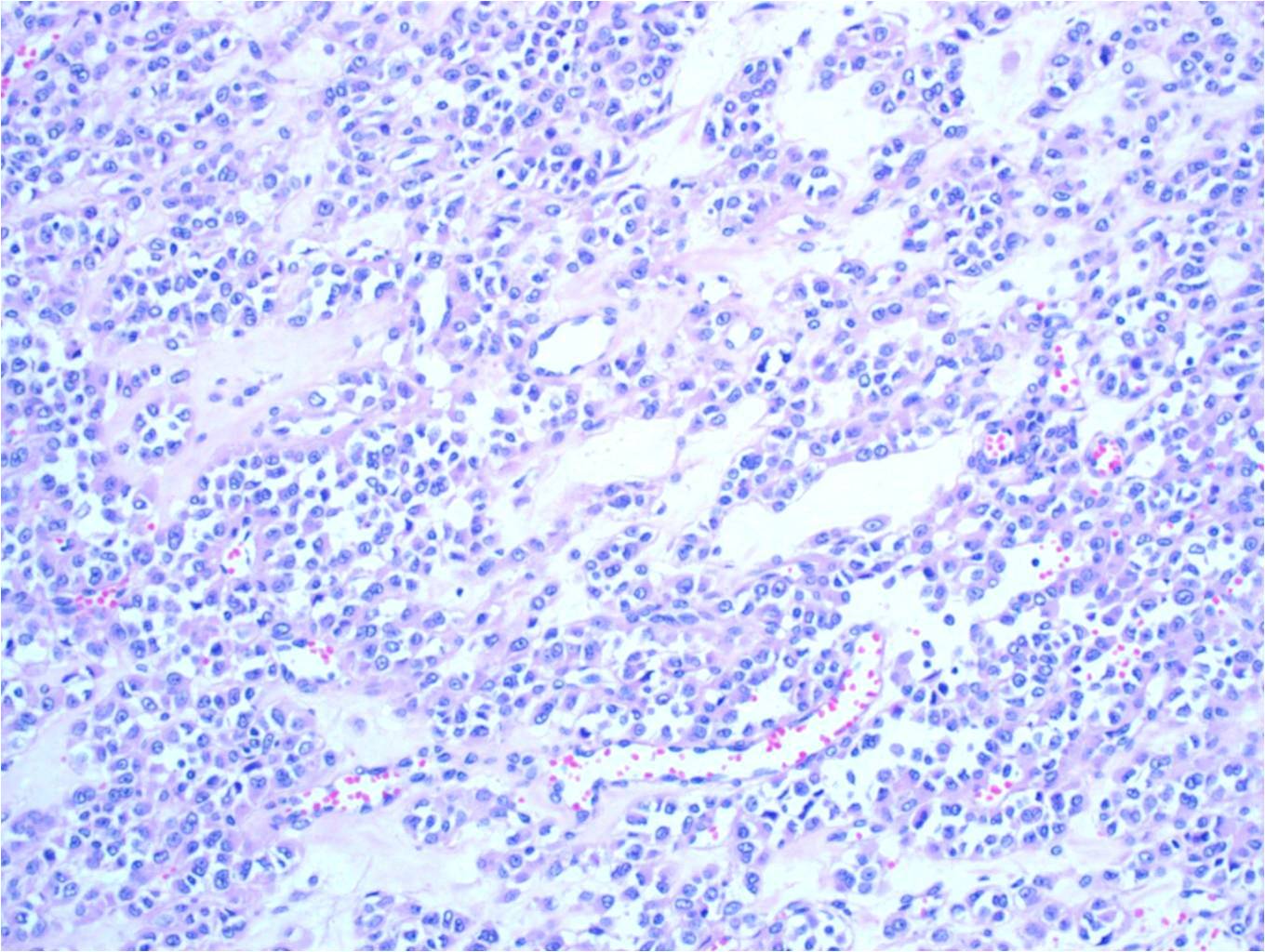
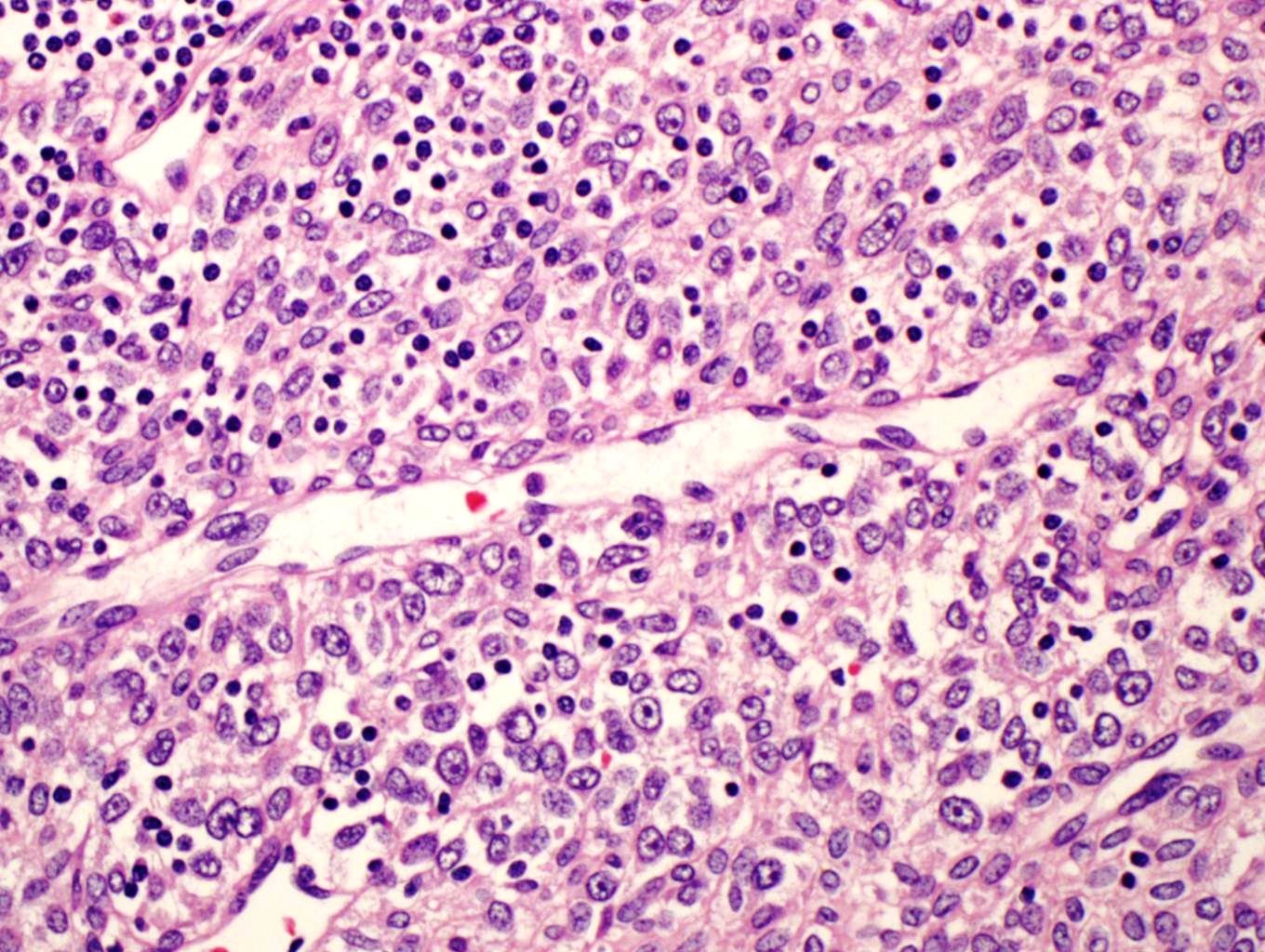
The large dilated spaces of glomangioma are always lined by arrays of neoplastic glomus cells ; however, this lining can vary widely in thickness from field to field.
What are glomus cells?
Composed of uniform, round to ovoid cells with bland nuclear features, light ly eosinophilic cytoplasm, and well-demarcated cell borders (so-called glomus cells)
What is a glomangiomyoma?
Glomangiomyoma is a variant of GT that features a smooth muscle component in addition to areas of otherwise conventional-appearing GT or glomangioma. Note the small areas of rounded glomus cells .
Is a pulmonary glomus tumor homogeneous?
Pulmonary glomus tumor shows a solid homogeneous proliferation composed of rather small cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm. Note the absence of mitotic activity.
Is a glomus tumor compressed?
Glomus tumor is shown obliterating normal lung parenchyma; however, pulmonary airway is not involved by the tumor, which appears compressed by the tumor.
How often do glomus tumors occur?
Solitary glomus tumors are more frequent in adults than in others. Multiple glomus tumors develop 11–15 years earlier than single lesions; about one third of the cases of multiple tumors occur in those younger than 20 years. Congenital glomus tumors are rare; they are plaguelike in appearance and are considered a variant of multiple glomus tumors.
Where are glomus tumors found?
Glomus tumors are usually solitary and small lesions. The vast majority are found in the hand, wrist, foot, and under the fingernails. They are often painful, and the pain is reproduced when the lesion is placed in cold water. Multiple tumors are less likely to be painful.
What are the criteria for glomus tumor diagnosis?
Criteria for the diagnosis of malignancy in glomus tumors are: Tumor size of more than 2 centimeters and subfascial or visceral location. Atypical mitotic figures. Marked nuclear atypia and any level of mitotic activity. Pericytes of Zimmerman.
What is the size of a glomus tumor?
The tumor is the translucent oblate spheroid in the center of the incision, approximate horizontal dimension is 4 millimeters. Surgical excision is the preferred treatment for benign glomus tumors.
Where does a malignant glomus tumor come from?
Another report of a malignant glomus tumor ( glomangiosarcoma) with metastases from the skin. A malignant glomus tumor one arose from the kidneys.
What is glomangioma inherited?
Familial glomangiomas have been associated with a variety of deletions in the GLMN ( glomulin) gene, and are inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, with incomplete penetrance.
Is a glomus tumor benign?
The majority of glomus tumors are benign, but they can also show malignant features. Glomus tumors were first described by Hoyer in 1877 while the first complete clinical description was given by Masson in 1924. Histologically, glomus tumors are made up of an afferent arteriole, anastomotic vessel, and collecting venule.
What is a glomus tumour?
A glomus tumour is a nodule that arises from glomus cells in the arterial portion of the glomus body, or the Sucquet-Hoyer canal. The tumour is usually found on the nail bed or palm of a young adult and can be extremely painful, particularly following change in temperature or pressure.
How is a glomus tumour diagnosed?
Glomus tumour may be suspected clinically, as it is typically a solitary, painful, 1–2 cm reddish-blue papule or nodule on or around a nail bed. It usually undergoes biopsy . The histology of a glomus tumour reveals solid sheets of glomus cells around small blood vessels. Immunohistochemical studies may be helpful in diagnosis.
Can a glomus be excised?
Solitary glomus tumours can be surgically excised.
Imaging Studies of Glomus Tumors
Embolization of Glomus Jugulare Tumors: Blocking Blood Supply
- Before routine embolization, blocking the blood supply of glomus tumors, was used. Large amounts of blood were lost during surgery. In recent years, with the perfection of new techniques used by the radiologist, feeding vessels to the tumor can be selectively found and blocked during angiography. Tiny balls of microscopic biocompatiable sponge are injected into the tumor. This …
Preoperative Assessment of Glomus Tumors
- Once the ear surgeon has determined the classification of glomus tumor, a careful evaluation of the x-ray results must be made in order to make certain there are no tumors associated with other blood vessels. Glomus tumors are similar to chemodectomas, blood vessel tumors occurring in bodies similar to the glomus body. These tumors can occur along the carotid artery, the major ar…
Surgery of The Glomus Tympanicum
- The size and the extent of the glomus tumor determine the procedure needed. Examination of the eardrum helps the ear surgeon to estimate the size of the tumor. In very early cases, glomus tumors can be as small as 2 to 3 mm. and appear as a red ball behind an intact tympanic membrane (eardrum). As glomus tumors expand, they begin to fill the middle...
Invasion of The Jugular Vein
- If the tumor appears to have invaded the jugular vein, then control of the blood vessels of the neck may be necessary with a separate incision in the neck before the tumor can be completely removed. This is the exception in glomus tumors which arise from the middle ear and mastoid, but the usual situation in glomus jugular tumors. Ic. Invasion of the Brain If the glomus tumor co…
Summary
- Using this team approach, the removal of glomus tumors has become a more successful procedure in terms of sparing vital cranial nerves. In addition, blood loss has been brought to a minimum and most patients do not require transfusion.
Alternative Treatments
- Radiation Glomus tumors are not highly radiosensitive (sensitive to the radiation therapy’s x-rays). However, in older patients, or those who should not undergo surgery, radiation therapy may help to arrest the growth of a glomus tumor. In the younger patient, complete surgical removal of the tumor after embolization is the preferred method of treatment.