
What is the difference between external and internal resorption?
Although external resorption is more common, it is often misdiagnosed as internal resorption. An inflammatory process occurring within the pulp tissue, internal resorption ultimately leads to dentin loss. 1 While the exact process is not fully understood, two histological characteristics are common.
What is internal resorption of a tooth?
Internal resorption affects the inside of a tooth. It’s much less common than external resorption and most often affects men. It’s also more common in people who have teeth that have received extensive oral surgery, such as tooth transplantation.
What is internal resorption and how is it diagnosed?
Internal resorption (IR) is a rare, insidious, resorptive pathological process, beginning in the pulpal space and extending into the surrounding dentin. Its diagnosis and management have been a challenge to dental practitioners. Due to its insidious pathology, internal resorption can progress to a great extent before its detection.
What is the prevalence of internal root resorption?
4. Clinical Characteristics Internal resorption is usually asymptomatic and approximately only 2% shows clinical signs [27]. It is more frequently observed in males than females [28]. Haapasalo suggested a prevalence of 0.01%–1% for internal root resorption occurring due to inflammatory causes [5].
Is tooth resorption rare?
Because it is not damaging the internal tissue, a root canal will not treat the problem. Depending on the severity of the external resorption, extraction may or may not be necessary. Don't start to worry about your teeth resorbing just yet though! Tooth resorption overall is pretty rare.
How common is resorption?
Tooth resorption is present in 5 to 10% of the general population who has never been subjected to orthodontic treatment. It has been considered the major cause of tooth loss; however, considerable confusion remains with regards to diagnosis of the different types of tooth resorption.
How do you treat internal tooth resorption?
Root canal treatment remains the treatment of choice of internal root resorption as it removes the granulation tissue and blood supply of the clastic cells. Internal root resorption presents specific difficulties in instrumentation and filling.
Can internal tooth resorption be stopped?
Internal resorption progression can be stopped with early root canal therapy, but a “wait and see” approach may be taken for external resorption.
How fast does root resorption occur?
ERR can advance rapidly, such that an entire root surface may be resorbed within just a few months if left untreated. ERR also affects teeth with chronic apical periodontitis. One of the most common causes for apical RR is overzealous orthodontic tooth movement.
Why has my child's tooth gone pink?
A quick side note: loose baby teeth might turn pink. This happens a lot. Basically, as the root of the tooth resorbs (dissolves away), that resorption can continue into the crown of a tooth that has been waiting a long time to come out. A pink tooth is likely pretty hollow, and may fracture into two or more pieces.
Is tooth resorption common?
What exactly is root resorption? Although it may sound frightening and rare, it's actually a fairly common affliction that occurs naturally due to an oral injury or irritation.
Is tooth resorption genetic?
Tooth resorptions are not hereditary.
Can internal resorption spread to other teeth?
A tooth being resorbed is actually eaten away, either by cells inside the pulp or outside the root. Because the growing cells shouldn't be, resorption is a little like cancer. Only a little bit though. That's because root resorption never spreads, not even to the tooth next to it.
Can you reverse tooth resorption?
External resorption that can be cured requires treatment that entails removal of the tissue invading the root of your tooth, chemical treatment of the debrided root surface to prevent recurrence followed by replacement of the lost root structure with some kind of restorative material.
Why does internal resorption happen?
Internal resorption is the result of an inflamed pulp and the clastic precursor cells recruiting through the blood vessels.
How common is root resorption with Invisalign?
Conclusions: Orthodontic treatment with Invisalign® aligners could lead to RR. However, its incidence resulted to be very similar to that described for orthodontic light forces, with an average percentage of RR < 10% of the original root length.
What is internal resorption?
Internal. Internal resorption affects the inside of a tooth. It’s much less common than external resorption and most often affects men. It’s also more common in people who have teeth that have received extensive oral surgery, such as tooth transplantation.
What is resorption in dental?
Bottom line. Share on Pinterest. Resorption is the term for a common type of dental injury or irritation that causes a loss of a part or parts of a tooth. Resorption can affect many parts of a tooth, including: interior pulp. cementum, which covers the root. dentin, which is the second-hardest tissue underneath enamel.
Why do teeth resorb?
External resorption is often caused by injuries to the mouth and teeth that cause swelling and loss of bone and tissue on and around a tooth. Such injuries may occur from prolonged use of orthodontic appliances such as braces, or from tooth grinding or tooth bleaching.
How do you know if your tooth is resorption?
Tooth resorption doesn’t always present a clear set of symptoms. In many cases, a person may not notice tooth resorption for years. However, as resorption worsens, symptoms often develop. symptoms of resorption. pain stemming from the root, crown, or inside of a tooth. dark or pinkish discoloration.
What is the treatment for dental resorption?
Treatment for dental resorption is focused on preserving any remaining parts of a tooth that have begun to experience loss.
Can resorption cause permanent teeth to be damaged?
Resorption can cause long-term damage to permanent teeth. But in primary teeth, or baby teeth, resorption is a normal part of the dental development process. As a child grows, the roots of their baby teeth undergo resorption to make way for permanent teeth.
Is tooth resorption internal or external?
Tooth resorption is classified internally and externally, depending on where the loss of tooth occurs. External resorption is often easier to see than internal resorption because it commonly occurs on the outer surface of a tooth.
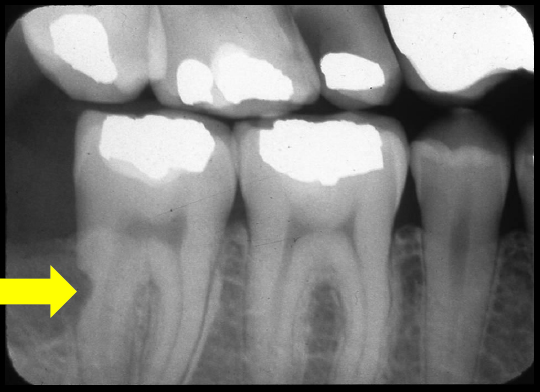
RADIOGRAPHIC DIAGNOSTICS
Radiographically, a uniform, semicircular radiolucent area contiguous with the pulp is a sign of internal resorption (Figure 1). In order to distinguish this from external resorption that may be on the facial or lingual surface of the root, an additional, angulated radiograph (shift-shot X-ray) can be helpful.
CLINICAL TREATMENT
Treatment for internal resorption includes root canal therapy, followed by restoration. Considering that vital pulp tissue is necessary for resorption, root canal therapy will stop the resorption. 5 The chemical cleaning aspect of root canal therapy typically involves using various concentrations of sodium hypochlorite.
What Causes Tooth Resorption?
There are numerous causes of resorption, but the most common occurs after a trauma or dental surgery.
What are the Symptoms of Tooth Resorption?
Most people are completely unaware that they have tooth resorption until it becomes a severe condition.
How to Manage Tooth Resorption
Tooth resorption is managed by preserving the parts of the tooth that are affected.
When to See a Doctor
You should visit your dentist at least twice a year. You’ll receive a professional cleaning, a comprehensive dental examination, a thorough head and neck exam, and any necessary x-rays.
How to Prevent Resorption of Teeth
The best way to prevent any tooth injury or damage is to protect them. You can do this by brushing and flossing regularly and maintaining a healthy diet to avoid tooth decay.
Resources
American Association of Endodontists. Glossary of Endodontic Terms, 10th edition.
How many people have root resorption?
Root resorption normally affects 5 to 10% of the general population who have never undergone any type of orthodontic treatment. It is considered among the most common causes of tooth loss in people across the world.
What causes external inflammatory resorption?
External inflammatory resorption is normally caused by a prolonged trauma of the tooth ultimately resulting in pathological resorption. Some of the most common causes of this type of resorption include the drying of the root surface after a trauma, previous surgery, injury to the periodontal ligament (PDL), pressure, or complete exposure of the dentine tubules.
What is resorption on X-rays?
Resorption that extends to the roots of the tooth can be visualized in an X-ray report as a flattening of the root tips as well as a reduction in their length. Root resorption can occur in a number of ways. External resorption is further classified into several types:
What is external root resorption?
This problem is more common than internal resorption and can affect any external part of the tooth. When it begins with the cementum around the root, it may be called external root resorption. External resorption may appear on the outer surface of the tooth in the form of deep chips or holes.
What is tooth resorption?
What is tooth resorption? In short, it happens when some of the body's cells start eating away at part of the tooth structure. If your dentist has told you that you have tooth or root resorption you likely have a lot of questions:
Why do teeth resorb?
The most common cause of external resorption is an injury to the teeth and mouth that leads to swelling and loss of tissue and bone surrounding the affected teeth. Such injuries normally occur due to trauma, tooth grinding, using different orthodontic appliances like braces for a long time, or tooth bleaching.
Where does resorption occur?
According to the American Association of Endodontists, resorption can occur internally, in the tooth pulp, or externally, affecting the enamel or cementum , the latter being more common. Occasionally, external root resorption may occur alongside internal resorption. Tooth resorption often begins on the external surface of ...
