How could a bacteriophage be used to clone a gene?
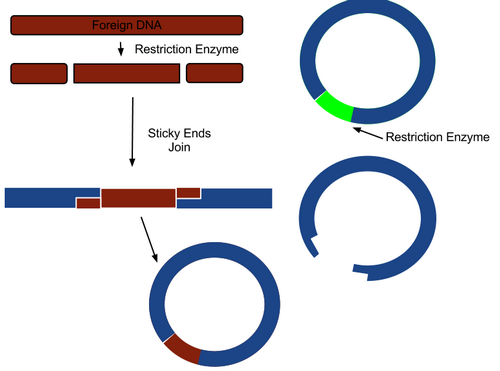
- Cut open the plasmid and "paste" in the gene. This process relies on restriction enzymes (which cut DNA) and DNA ligase (which joins DNA).
- Insert the plasmid into bacteria.
- Grow up lots of plasmid-carrying bacteria and use them as "factories" to make the protein.
What are the bacteriophages used for cloning?
Jun 16, 2020 · How could a bacteriophage be used to clone a gene? The bacteriophages used for cloning are the phage λ and M13 phage. In replacement vectors, the cleavage sites flank a region containing genes not essential for the lytic cycle, and this region may be deleted and replaced by the DNA insert in the cloning process, and a larger sized DNA of 8–24 kb may be inserted.
What can I do with the cloning of genes?
Dec 17, 2020 · Bacteriophages as cloning vectors. The most commonly used bacteriophage vectors are those based on phage Lambda (X) (Figure 12.8). The genome of X is 48.5kb in length; it was the first genome to have its entire sequence determined (1982). As drawn conventionally, the genome is linear, and contains 46 genes.
What does it mean to clone a gene?
Bacteriophage lambda as a cloning vector Extensive research has been directed toward the development of multipurpose lambda vectors for cloning ever since the potential of using coliphage lambda as a cloning vector was recognized in the late 1970s. An understanding of the intrinsic molecular organization and of the genetic events which det …
What are bacteriophages and how do they work?
Oct 08, 2017 · Just as too big a genome cannot be packaged , neither can one that is too small (< 37kb); consequently, constructs lacking an insert will not result in the formation of plaques. Another naturally occurring bacteriophage of E. coli that has been adapted for use as a cloning vector is phage M13. This is a single-stranded phage that for part of its replication cycle inside …

How is bacteriophage used as a cloning vector?
How are bacteriophage used in genetic engineering?
Can bacteriophages be used for gene therapy?
How do you clone a gene from bacteria?
- DNA. ...
- Bacterial plasmids are cut with the same restriction enzyme.
- The gene-sized DNA and cut. ...
- The recombinant plasmids are transferred into bacteria using electroporation or heat shock.
- The bacteria is plated out and allowed to grow into colonies. ...
- The.
How phages can be used in biotechnology?
Why bacteriophage is suitable subject for research in genetics?
Why is bacteriophage used as a vector?
What are the applications uses of bacteriophages?
Are bacteriophages used in CRISPR?
How do you clone mRNA?
Which is used in gene cloning?
What is gene cloning and why do we need to clone a gene?
Is Bacteriophage Lambda a cloning vector?
Bacteriophage lambda as a cloning vector. Extensive research has been directed toward the development of multipurpose lambda vectors for cloning ever since the potential of using coliphage lambda as a cloning vector was recognized in the late 1970s.
How can recombinant phages be differentiated from parental phages?
In most cases, the recombinants can be differentiated from the parental phages by their altered phenotype. Libraries constructed in lambda vectors are screened easily with antibody or nucleic acid probes since several thousand clones can be plated on a single petri dish.
When was Lambda used as a cloning vector?
Extensive research has been directed toward the development of multipurpose lambda vectors for cloning ever since the potential of using coliphage lambda as a cloning vector was recognized in the late 1970s. An understanding of the intrinsic molecular organization and of the genetic events which determine lysis or lysogeny in lambda has allowed ...
What is cloning of genes?
Cloning of genes provided for the first time, large quantities of specific DNA fragments, in other words genes, especially of higher organisms. These DNA fragments can be used as probe and permit, by hybridization, the detection and dosage of the correspond ing mRNAs in cells which are at different stages of their development or placed in diverse physiological conditions.
Can you clone a gene from a eucaryotic gene?
But if one wants to clone a eucaryotic gene, it is often preferable to clone first the DNA copy (cDNA) of the mRNA corresponding to the gene sought. The size of these cDNAs is indeed generally much smaller than that of their genomic counterpart due to the absence of introns.
What are the methods of cloning?
Methods of Cloning, 2. Cloning of a Specific Gene, 3. Cloning of a Specific Gene, 4. Expression of Cloned Genes, 5. Cloning of Genes in Eucaryotic Cells and 6. Precautions to be taken during Experiments of Genetic Recombination.
How many base pairs of DNA can be inserted into an E. coli plasmid?
It must be noted that there is no minimal size for the heterologous DNA inserted in a plasmid, and that this size can reach at least 40 x 10 6 daltons, i.e. about 60 000 base pairs (= 60 kb).
Does insertion of foreign DNA affect the number of plasmid molecules present in the cell?
Moreover, the insertion of foreign DNA in plasmids of the Col series does not affect the number of plasmid molecules which can be present in the cell, so that the heterologous DNA inserted will be present also at the concentration of several copies in the transformed bacterial cell.
How many kb is a bacteriophage?
The DNA of the bacteriophage (47 000 base pairs = 47 kb) is often used as cloning vector because it offers some advantages over the bacterial plasmids. About 15 kb of the central part of the genome of this phage are not essential for its survival and can be replaced by heterologous DNA to be cloned.
Can tryptophan be cloned?
It was thus possible to clone the genes of the tryptophan operon, or the gene of the ligase of E.coli, starting from DNA fragments resulting from the hydrolysis of the whole chromosome of E.coli.

Vectors For Gene Cloning: Plasmids and Bacteriophage
Plasmids
Size and Copy Number
Conjugation and Compatibility
Types of Plasmids
Bacteriophage
- Bacteriophages are a group of viruses that used bacterial cells as host and reproduce by infecting bacterial cells. Like all other viruses bacteriophages are also consisting of a protein coat that provides protection to the genome. Most of the phages are DNA viruses that code for several genes responsible for virus replication. A major problem of u...
Lytic and Lysogenic Phages
Genetic Organization of Lambda DNA
Linear and Circular Forms of Lambda DNA
M-13: Filamentous Phage