Einstein’s Explanation of the Photoelectric Effect
- The strength of the photoelectric current depends upon the intensity of incident radiation, and it should be higher than the threshold frequency.
- The reverse stopping potential was the photo-current stop. ...
- Photoelectric current does not occur if the frequency of the incident radiation is below the threshold frequency. ...
Which theory best explains the photoelectric effect?
Which theory best explains the photoelectric effect? In 1905, Einstein found the photoelectric effect on the basis of quantum theory. According to Einstein, when a photon of energy hν falls on the metal surface it transfers all its energy to the electron of the metal and the electron is emitted out from the metal surface.
Did Einstein perform experiments?
What made Einstein’s reputation was one of the most important experiments in 20th-century science: a challenging, incredibly precise observation of a solar eclipse that proved his general theory of relativity for the first time.
Who is credited with explaining the photoelectric effect?
The photoelectric effect was discovered by German physicist Heinrich Rudolf Hertz in 1887. Einstein explained this effect in 1905.He performed the experiment and observe the result and published the paper.
How did Einstein contribute to the atomic theory?
Einstein's biggest contribution to the Atomic Theory was that he was able to fully prove through usage of evidence that atoms did indeed exist, and he was also able to demonstrate that electrons could leave metal through usage of light.

What is photoelectric effect How did Einstein explain it by the Planck's quantum theory?
In 1905 Einstein extended Planck's hypothesis to explain the photoelectric effect, which is the emission of electrons by a metal surface when it is irradiated by light or more-energetic photons.
Did Einstein discover the photoelectric effect?
Despite the popularity of Einstein's theories of relativity and his musings on black holes, Einstein's Nobel Prize in physics was actually awarded for his discovery of the photoelectric effect. This discovery revolutionized our understanding of the world around us.
Who explained how the photoelectric effect works?
The photoelectric effect was discovered in 1887 by the German physicist Heinrich Rudolf Hertz. In connection with work on radio waves, Hertz observed that, when ultraviolet light shines on two metal electrodes with a voltage applied across them, the light changes the voltage at which sparking takes place.
When did Einstein discover photoelectric effect?
1905Einstein explained the phenomenon in the year 1905. According to Einstein, light is made up of little packets, at first called quanta and later photons. When a photon hits the electrons it gives electrons enough energy to escape from the surface of the metal. This explains the behaviour of light striking the metal.
How did Einstein prove that light was a particle?
(If light were a wave, strong light should cause photoelectrons to fly out with great power.) Another puzzling matter is how photoelectrons multiply when strong light is applied. Einstein explained the photoelectric effect by saying that "light itself is a particle," and for this he received the Nobel Prize in Physics.
How did Einstein win the Nobel Prize for photoelectric effect?
The Nobel Prize in Physics 1921 was awarded to Albert Einstein "for his services to Theoretical Physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect."
What is law of photoelectric effect?
(i) There is a definite cut off value of frequency below which electrons cannot be ejected by any substance. (ii) Number of emitted electrons are directly proportional to the intensity of light incident. (iii) Kinetic energy of emitted electrons depends on the frequency of incident light on substance.
Who discovered electron?
J J Thomson discovered electron.
What is the threshold frequency?
Threshold frequency is defined as the minimum frequency that is required for the radiation such that photoelectric effect is produced.
Which metals exhibit photoelectric effect?
Alkali metal is usually used for exhibiting photoelectric effect. Metals such as copper and sodium are the examples of metals that exhibit photoele...
What type of light is needed to cause the photoelectric effect?
Ultraviolet light is the type of light that is needed to cause the photoelectric effect.
What are the applications of photoelectric effect?
The applications of photoelectric effect are electric eye in door openers, light meters in photography, photostatic copying, and solar panels.
Einstein's Explanation Of Photoelectric Effect - A Complete Guide
The best approach to understand the photoelectric effect is through Line Spectrum of the atom .
Einstein's Photoelectric Effect - Introduction, Equation and Theory
The energy conversion in photoelectric cells takes place from optical to electrical .
1. How can photoelectric effect be understood ?
Auger electrons are emitted when the electron beam that hits the surface creates electron holes in the lower shell, which are filled with electrons...
2. How does the conversion of energy in photoelectric cells takes place ?
Let us consider a ping pong ball inside a bucket. If we hit the ball with other small-sized balls from outside, it can increase the vibration of th...
3. What causes the Auger effect ?
The direct application of the Photoelectric effect is in photocells and solar cells. The Photoelectric effect gave rise to the quantum revolution....
4. Explain the work function of the Photoelectric Effect?
5. What are the applications of the Photoelectric Effect ?
What is Einstein's theory of photoelectric effect?
Einstein Theory of Photoelectric Effect. Einstein's idea about light was revolutionary and magnificent. He gave an efficient method of irradiation. Light has some tiny group of particles known as photons. These particles consist of higher energy, which is also called the quantum of radiation.
What did Albert Einstein do?
He has contributed his work in the field of general relativity, black holes, photoelectric effect, and many more. In 1921, Einstein was awarded the Nobel Prize in physics for the discovery of the photoelectric effect.
What happens when electrons are imparted with a threshold frequency?
When electrons are imparted with a threshold frequency (v0), they acquire enough energy to eject out of the surface.
What happens when a metal surface is irradiated with light of sufficient energy?
According to the Photoelectric effect, when a metal surface is irradiated with light of sufficient energy, it causes the electrons of the metal to eject out. So let us try to understand what the explanation behind the Photoelectric effect is. The electrons present inside the atoms of the metal surface gain energy and start vibrating ...
What happens when a photoelectron comes out of a metallic surface?
When the photoelectron comes out of the metallic surface, it will be converted to purely kinetic energy as there is no electric field outside the surface. The quantum energy imparted by the photons is partly used by the electron to overcome the molecular attraction of the surface.
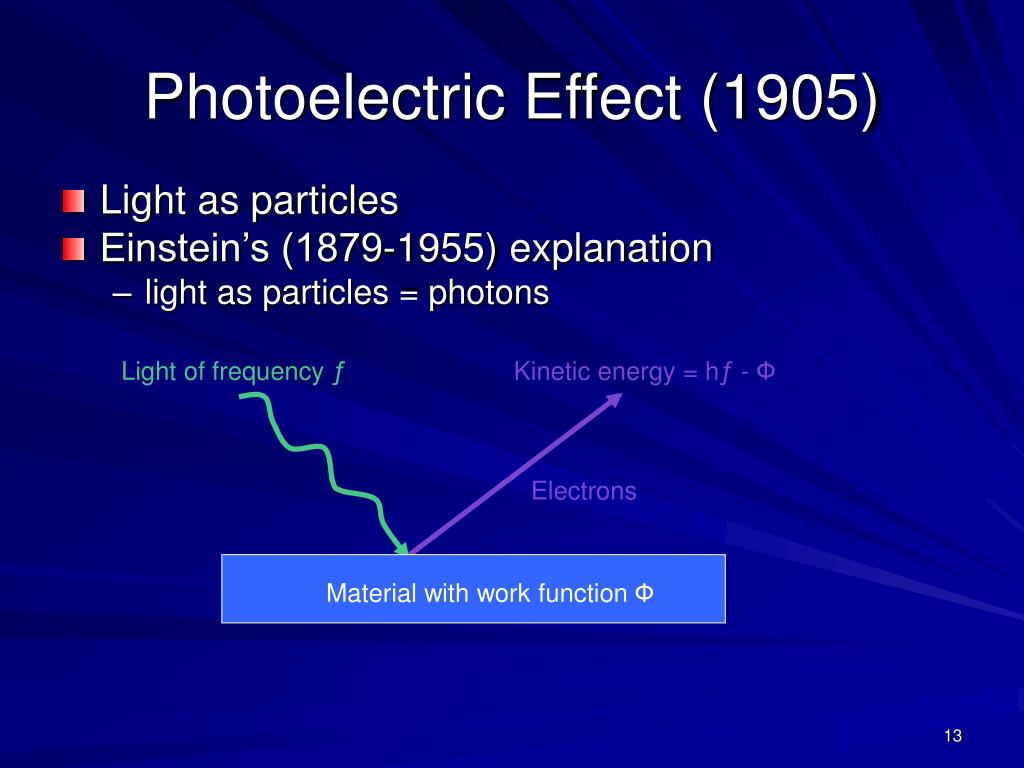
What is the kinetic energy of a photoelectron?
So, the kinetic energy of a photoelectron is = (energy imparted by photon) - (energy used to come out of the surface). This energy is constant for a surface, and it is denoted by Φ. This is called the work function of a surface and is constant for a given material. Thus the equation is given as,
What is the particle of light called?
A particle of light is called a photo. When a photon collides with electrons, it imparts the sum of its energy to it, gaining which the electron ejects out of the surface. The remaining energy of the photon forms a free negative charge called photoelectron.
Who discovered the photoelectric effect?
Brian Greene discusses the key formula in the photoelectric effect, an insight that helped launch the quantum revolution. This video is an episode in his Daily Equation series. In 1905 Einstein extended Planck’s hypothesis to explain the photoelectric effect, which is the emission of electrons by a metal surface when it is irradiated by light ...
What is the photoelectric effect?
In 1905 Einstein extended Planck’s hypothesis to explain the photoelectric effect, which is the emission of electrons by a metal surface when it is irradiated by light or more-energetic photons. The kinetic energy of the emitted electrons depends on the frequency ν of the radiation, not on its intensity; for a given metal, ...
What is the spectra of light emitted by gaseous atoms?
The spectra of light emitted by gaseous atoms had been studied extensively since the mid-19th century. It was found that radiation from gaseous atoms at low pressure consists of a set of discrete wavelengths. This is quite unlike the radiation from a solid, which is distributed over a continuous range of wavelengths.
What is the force on the electron?
The force on the electron (the analogue of the gravitational force between the Sun and a planet) is the electrostatic attraction between the positively charged nucleus and the negatively charged electron.
Which physicist proposed the theory that electrons move in circular orbits?
Bohr’s theory, which assumed that electrons moved in circular orbits, was extended by the German physicist Arnold Sommerfeld and others to include elliptic orbits and other refinements. Attempts were made to apply the theory to more complicated systems than the hydrogen atom.
Who proposed the wave hypothesis?
De Broglie ’s wave hypothesis. Faced with evidence that electromagnetic radiation has both particle and wave characteristics, Louis-Victor de Broglie of France suggested a great unifying hypothesis in 1924. De Broglie proposed that matter has wave as well as particle properties.
Who discovered that X-rays scatter from electrons as if they are particles?
In 1922 the American physicist Arthur Holly Compton showed that X-rays scatter from electrons as if they are particles. Compton performed a series of experiments on the scattering of monochromatic, high-energy X-rays by graphite.
What is the photoelectric effect?
The photoelectric effect is a direct consequence of the particle nature of EM radiation. The photoelectric effect is a direct consequence of the wave nature of EM radiation. The photoelectric effect is a direct consequence of both the wave and particle nature of EM radiation.
How do photovoltaic cells work?
Unlike electric eyes, which trip a mechanism when current is lost, photovoltaic cells utilize semiconductors to directly transfer the electrons released through the photoelectric effect into a directed current. The energy from this current can then be converted for storage, or immediately used in an electric process.
What is the kinetic energy of an ejected electron?
The kinetic energy KE of an ejected electron equals the photon energy minus the binding energy BE of the electron in the specific material. An individual photon can give all of its energy to an electron. The photon’s energy is partly used to break the electron away from the material.
What is the way in which the frequency and intensity of the incoming radiation affect the ejected electrons?
The manner in which the frequency and intensity of the incoming radiation affect the ejected electrons strongly suggests that electromagnetic radiation is quantized. This event, called the photoelectric effect, is strong evidence for the existence of photons.
What is the effect of light on a material?
When light strikes certain materials, it can eject electrons from them. This is called the photoelectric effect, meaning that light ( photo) produces electricity. One common use of the photoelectric effect is in light meters, such as those that adjust the automatic iris in various types of cameras.
How much energy does DNA break?
A DNA molecule can be broken with about 1 eV of energy, for example, and typical atomic and molecular energies are on the order of eV, so that the photon in this example could have biological effects, such as sunburn. The ejected electron has rather low energy, and it would not travel far, except in a vacuum.
What is an example of a photovoltaic cell?
Figure 21.9 A solar cell is an example of a photovoltaic cell. As light strikes the cell, the cell absorbs the energy of the photons. If this energy exceeds the binding energy of the electrons, then electrons will be forced to move in the cell, thereby producing a current.
What was Albert Einstein's contribution to the world?
While he certainly made significant contributions to all of those topics during his lifetime, Albert Einstein was perhaps even more well known in his time for his work to understand the photoelectric effect. In fact, when he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1921, the honor was stated to be “for his services to Theoretical Physics, ...
What is Einstein's legacy?
Einstein's Legacy: The Photoelectric Effect. Despite the popularity of Einstein's theories of relativity and his musings on black holes, Einstein's Nobel Prize in physics was actually awarded for his discovery of the photoelectric effect . This discovery revolutionized our understanding of the world around us.
Why is Einstein's discovery important?
This discovery is so important—and Nobel Prize worthy—because Einstein suggested for the first time that light is both a wave and a particle. This phenomenon, known as the wave-particle duality of light, is fundamental to all of quantum mechanics and has influenced the development of electron microscopes and solar cells.
Who is the author of the Einstein podcast?
ABOUT THE AUTHOR (S) Sabrina Stierwalt, PhD, is an astrophysicist at Occidental College and the host of the Everyday Einstein podcast on Quick and Dirty Tips.
What happens when light hits a metal?
When light with energy above a certain threshold hits a metal surface, an electron that was previously bound to the metal is knocked loose. Each particle of light, called a photon, collides with an electron and uses some of its energy to dislodge it from the metal.
What was the photoelectric effect?
The photoelectric effect posed a significant challenge to the study of optics in the latter portion of the 1800s. It challenged the classical wave theory of light, which was the prevailing theory of the time. It was the solution to this physics dilemma that catapulted Einstein into prominence in the physics community, ...
What is the energy of a photon?
Building on Max Planck 's blackbody radiation theory, Einstein proposed that radiation energy is not continuously distributed over the wavefront, but is instead localized in small bundles (later called photons ). The photon's energy would be associated with its frequency ( ν ), through a proportionality constant known as Planck's constant ( h ), or alternately, using the wavelength ( λ) and the speed of light ( c ):
What is the term for the light that emits electrons?
Electrons emitted in this fashion are called photoelectrons (although they are still just electrons). This is depicted in the image to the right.
Is light a particle or a wave?
Though no one could deny that light behaved as a wave, after Einstein's first paper, it was undeniable that it was also a particle. Cite this Article.
Does the intensity of the light source affect the kinetic energy of the photoelectrons?
The intensity of the light source had no effect on the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons. Below a certain frequency, the photoelectric effect does not occur at all. There is no significant delay (less than 10 -9 s) between the light source activation and the emission of the first photoelectrons.
