Are there lakes and waterfalls at Joshua Tree National Park?
Joshua Tree National Park is an American national park in southeastern California, east of Los Angeles and near Palm Springs. ... there is so much more to Tennessee than meets the eye. There are not only spectacular lakes and rivers, but many more waterfalls to explore than you may realize. Luckily, all of these sites are well preserved by ...
Can you stay in Joshua Tree National Park?
Re: staying overnight in joshua tree park Only camping is allowed inside the park. There is no national park lodge inside the park -- no hotel, no food inside the park. The main Visitor Center for this national park is at the park headquarters located in the town of Twentynine Palms.
What is the best hike in Joshua Tree National Park?
Top trails ( 125)
- Ryan Mountain Trail. Ryan Mountain is one of the most popular destinations in Joshua Tree! ...
- Arch Rock Trail. Length: 1.4 mi • Est. ...
- Barker Dam Trail. Length: 1.1 mi • Est. ...
- Hidden Valley Nature Trail. ...
- Lost Palms Oasis Trail. ...
- Skull Rock Nature Trail. ...
- Fortynine Palms Oasis Trail. ...
- Cholla Cactus Garden Trail. ...
- Split Rock Loop Trail. ...
- Mastodon Peak Loop Trail. ...
Are there hot springs in Joshua Tree?
There are hiking and exploring trails, bouldering and rock climbing in Joshua Tree National Park. Azure Palm Hot Springs is less than 45 minutes away. Azure Palm Hot Springs offers hiking and exploring, mineral springs soaking in the evenings, and evening massages at the end of the day. Is There Anywhere To Swim In Joshua Tree?

What is so special about Joshua tree?
Joshua Trees are an incredibly unusual looking tree, in part because they're not actually a tree at all! They're a plant belonging to the Yucca genus that happens to resemble the size and growth pattern of a tree.
Is a Joshua tree actually a tree?
Joshua trees aren't actually trees—they're succulents, a type of plant that stores water. In their dry ecosystems, however, they are considered trees of the desert.
Why do Joshua trees only grow in Joshua tree?
They Only Grow at Certain Altitudes Here some more facts about the Joshua tree: they only grow at elevations between 400 and 1800m (1300-5900 ft). They prefer these higher elevations where the climate is cooler. You'll find them mostly on slopes, ridges and flat-topped hills of the desert.
What did natives call Joshua trees?
Southern Paiute called the Joshua tree sovarampi. Cahuilla Indians referred to it as humwichawa and the Western Shoshone knew it simply as umpu. For thousands of years many Indian groups embraced the tree as a spiritual reference and valued resource.
What's the meaning of the Joshua Tree?
"The name Joshua tree was given by a group of Mormon settlers who crossed the Mojave Desert in the mid-19th century. The tree's unique shape reminded them of a Biblical story in which Joshua reaches his hands up to the sky in prayer."
What is the biblical story of the Joshua Tree?
The name "Joshua tree" is commonly said to have been given by a group of Mormon settlers crossing the Mojave Desert in the mid-19th century: The tree's role in guiding them through the desert combined with its unique shape reminded them of a biblical story in which Joshua keeps his hands reached out for an extended ...
Where is the 1000 year old Joshua tree?
Tehachapi, CA (93561)
What indigenous land is Joshua tree on?
Joshua Tree National Park and the surrounding area is home to many different indigenous tribes including the Serrano, Chemehuevi, Mojave Cahuilla, and Mojave.
Can a Joshua tree survive in the desert?
Rigid leaves covered by a waxy surface help the Joshua tree survive in the desert by being able to resist wilting and water loss. Its widespread roots are about 3 feet deep.
Why is 29 Palms called 29 Palms?
The area was then generally known as Palms Springs. Legend says that these gold miners first used the name of Twentynine Palms because of the 29 Washingtonia filifera palm trees surrounding the Oasis.
How deep are Joshua tree roots?
Joshua tree has complex root system that consists of deep and shallow root. Deep root can reach depth of 10 to 30 feet and collect hardly accessible water. It also produces large bulbs that can reach 4 feet in width and 40 pounds of weight. Shallow root grows few feet below the ground and absorbs water after rainfall.
Who lived in Joshua tree?
Humans have occupied the area we now know as Joshua Tree National Park for at least 5,000 years. The first group known to inhabit the area was the Pinto Culture, followed by American Indians including the Serrano, the Chemehuevi, and the Cahuilla.
What kind of tree is a Joshua tree?
You often hear that Joshua trees aren't actually trees, but they're as much a tree as a palm tree is. In the Yucca genus, they're a type of grass-like flowering plant called a monocot. Joshua trees comprise two distinct species: the western Joshua tree (Yucca brevifolia) and the eastern Joshua tree (Y. jaegeriana).
Where is the 1000 year old Joshua tree?
Tehachapi, CA (93561)
Is it illegal to have a Joshua tree?
Federal laws prohibit taking or damaging National Park wildlife and plants. Joshua trees also are a protected species under state law.
Can a Joshua tree survive in the desert?
Rigid leaves covered by a waxy surface help the Joshua tree survive in the desert by being able to resist wilting and water loss. Its widespread roots are about 3 feet deep.
How long has Joshua Tree been inhabited?
While the Joshua Tree area has been inhabited by humans for at least 5,000 years, by the late 1920s the development of new roads into the desert had brought an influx of land developers and cactus poachers.
How many archaeological sites are there in Joshua Tree?
Joshua Tree has one paleontological area and potentially eight more. The park protects over 700 archeological sites, 88 historic structures, 19 cultural landscapes, and houses 230,300 items in its museum collection.
Is the Joshua Tree endangered?
The federal register lists one park reptile, the desert tortoise, as threatened and one park plant species, the triple-ribbed milk vetch, as endangered, and one plant species, Parish′s daisy as threatened. In addition there are 49 plant species of special concern being protected within the park. Joshua Tree has one paleontological area ...
Who discovered the Joshua Tree?
In 1772, a group of Spaniards led by Pedro Fages made the first European sightings of Joshua trees while pursuing native converts to Christianity who had run away from a mission in San Diego. By 1823, the year Mexico achieved independence from Spain, a Mexican expedition from Los Angeles, in what was then Alta California, is thought to have explored as far east as the Eagle Mountains in what later became the park. Three years later, Jedediah Smith led a group of American fur trappers and explorers along the nearby Mojave Trail, and others soon followed. Two decades after that, the United States defeated Mexico in the Mexican–American War (1846–48) and took over about half of Mexico's original territory, including California and the future parkland.
How many acres are there in Joshua Tree National Park?
Roosevelt used the power of the 1906 Antiquities Act to establish Joshua Tree National Monument, protecting about 825,000 acres (1,289.1 sq mi; 3,338.7 km 2 ). In 1950, the size of the park was reduced by about 290,000 acres (453.1 sq mi; 1,173.6 km 2) to open the land to more mining. The monument was redesignated as a national park on October 31, 1994, by the Desert Protection Act, which also added 234,000 acres (365.6 sq mi; 947.0 km 2 ). In 2019, the park expanded by 4,518 acres (7.1 sq mi; 18.3 km 2) under a bill included in the John D. Dingell, Jr. Conservation, Management, and Recreation Act.
What is the Joshua Tree?
It is named after the Joshua trees ( Yucca brevifolia) native to the Mojave Desert. Originally declared a national monument in 1936, Joshua Tree was redesignated as a national park in 1994 when the U.S. Congress passed the California Desert Protection Act.
What type of vegetation is in Joshua Tree National Park?
According to the A. W. Kuchler U.S. Potential natural vegetation types, Joshua Tree National Park has two categories, a creosote bush potential vegetation type with a desert shrubland potential vegetation form in most of the area, and a juniper / pinyon pine potential vegetation type with a Great Basin montane forest /southwest forest potential vegetation form on the higher elevations of the western side of the park.
What is the Mojave Desert?
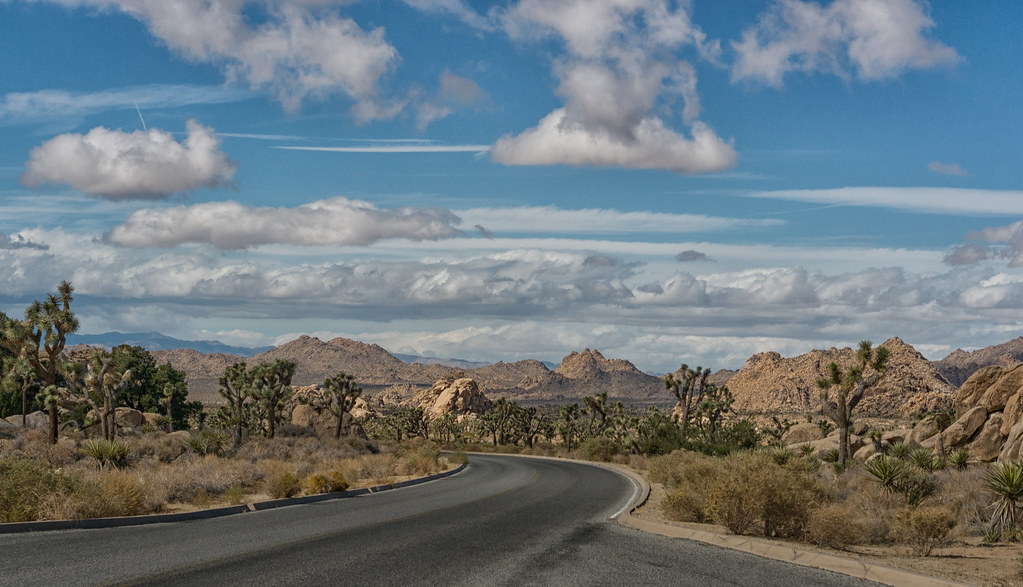
The higher and cooler Mojave Desert is the special habitat of Yucca brevifolia, the Joshua tree for which the park is named. It occurs in patterns from dense forests to distantly spaced specimens. In addition to Joshua tree forests, the western part of the park includes some of the most interesting geologic displays found in California's deserts. The dominant geologic features of this landscape are hills of bare rock, usually broken up into loose boulders. These hills are popular among rock climbing and scrambling enthusiasts. The flatland between these hills is sparsely forested with Joshua trees. Together with the boulder piles and Skull Rock, the trees make the landscape otherworldly. Temperatures are most comfortable in the spring and fall, with an average high/low of 85 and 50 °F (29 and 10 °C), respectively. Winter brings cooler days, around 60 °F (16 °C), and freezing nights. Snows occur occasionally at higher elevations. Summers are hot, over 100 °F (38 °C) during the day and not cooling much below 75 °F (24 °C) until the early hours of the morning.
When did the Pinto tribe live in Joshua Tree?
The earliest known residents of the land in and around what later became Joshua Tree National Park were the people of the Pinto Culture, who lived and hunted here between 8000 and 4000 BCE. Their stone tools and spear points, discovered in the Pinto Basin in the 1930s, suggest that they hunted game and gathered seasonal plants, ...
Why are the trails closed in California?
They blame the increase in vandalism on the increased use of social media.
How long has the Joshua Tree been around?
Human history in the Joshua Tree region stretches back well over 5,000 years. In the people section, find out about the different cultures that have called this area home, as well as a few prominent individuals in our history.
How many objects are there in Joshua Tree National Park?
Joshua Tree National Park houses more than 241,000 objects in its museum collections. The park also protects more than 838 documented archeological sites, 160 historic structures, and 5 cultural landscapes.
What are the origins of Joshua Tree National Park’s rock formation?
Massive rock piles cover the park’s landscape. They are arranged in such a way that it seems more like intentional art than natural erosion. These unusual rock formations were created by billions of years of heating and cooling in the earth’s crust, earthquakes, and wind and water erosion. This short-animated video illustrates the complex geologic processes that created the park’s iconic boulders.
What do Joshua trees do?
Joshua trees are an essential part of the Mojave Desert ecosystems, providing food and habitat for many other living things. Dozens of birds’ species nest in the Joshua tree, and the desert night lizard lives in the trees’ fallen branches. Numerous animals feed on Joshua tree flowers, fruit, and seeds.
Why are Joshua trees called Joshua trees?
One tells of the name being given by Mormon settlers as they crossed the Mojave Desert in the mid 1800s. The shape of the tree reminded the settlers of the story where Joshua reaches up his hands to the sky in prayer.
What are Joshua Trees?
Yucca brevifolia, otherwise known as the Joshua Tree, is a species belonging to the Yucca genus. Joshua Trees are actually the world’s largest Yucca in the world. They are sometimes called Yucca Palms, Tree Yuccas, and Palm Tree Yuccas. It also bears the Spanish name izote de desierto, which means “desert dagger.”
Where do Joshua Trees grow?
Where do Joshua trees take up residence? These unique trees have a fairly limited range. Their range is within the Mojave Desert of California, Nevada , Utah, and Arizona. They only grow between elevations of 2,000 and 6,000 feet.
Why are Joshua trees unusual?
Joshua Trees are an incredibly unusual looking tree, in part because they’re not actually a tree at all! Joshua Trees are an incredibly unusual looking tree, in part because they’re not actually a tree at all! They’re a plant belonging to the Yucca genus that happens to resemble the size and growth pattern of a tree.
How many Joshua trees are there in the world?
There doesn’t seem to be a clear estimate on how many Joshua Trees exist in the world, but given their limited range, protecting each Joshua Tree is critical.
What is the shape of the Yucca Palm?
By the 1870s, some Mormons were referring to the Yucca Palm as “The Joshua.”. But the exact origin is a mystery.
How long does it take for a Joshua tree to grow?
Joshua Trees are slow growing trees, adding only 2 to 3 inches each year. It will take 50 to 60 years for a Joshua Tree to reach full height. They will live on average around 500 years.
Who gave Joshua the tree?
The Joshua (Yucca brevifolia) was given by Mormons people after comparing the tree limbs with biblical figure Joshua in the position of praying.
Where are Joshua trees found in the Bible?
There is no reference to the Joshua trees in the Bible. Joshua trees, Yucca brevifolia, are a big, tree-like yucca. Yuccas are native only to North America, Central America and the Caribbean. Yuccas are related to Agave which also are only in the Americas. In Spanish Joshua tree are called izote de desierto (desert dagger). Yucca brevifolia is endemic (only is native to) western Arizona, southeastern California, southern Nevada, and southwestern Utah. It lives at between 1,300 and 5,900 ft. It is a remnant of a larger Pleistocene range.
Where did the tree with raised arms come from?
It did not exist in the Near East so, it cannot be in the bible. That name is said to come from Mormon settlers. If one looks at the map, one can see these people named large numbers of places from bible references. To the Mormons the tree with raised arms reminded them of Joshua guiding the conquest of Canaan. Mormon settlers and leadership hoped to settle a large area of the west, including Southern California, for a theocratic state. The Joshua tress were on the path to this conquest.

Overview
History
Geography
Geology
Recreation
Joshua Tree National Park is an American national park in southeastern California, east of San Bernardino and Los Angeles and north of Palm Springs. It is named after the Joshua trees (Yucca brevifolia) native to the Mojave Desert. Originally declared a national monument in 1936, Joshua Tree was redesignated as a national park in 1994 when the U.S. Congress passed the California Desert …
Wildlife
The earliest known residents of the land in and around what later became Joshua Tree National Park were the people of the Pinto Culture, who lived and hunted here between 8000 and 4000 BCE. Their stone tools and spear points, discovered in the Pinto Basin in the 1930s, suggest that they hunted game and gathered seasonal plants, but little else is known about them. Later residents i…
Wilderness
According to the A. W. Kuchler U.S. Potential natural vegetation types, Joshua Tree National Park has two categories, a creosote bush potential vegetation type with a desert shrubland potential vegetation form in most of the area, and a juniper/pinyon pine potential vegetation type with a Great Basin montane forest/southwest forest potential vegetation form on the higher elevations of the we…
Vandalism
The park's oldest rocks, Pinto Gneiss among them, are 1.7 billion years old. They are exposed in places on the park's surface in the Cottonwood, Pinto, and Eagle Mountains. Much later, from 250 to 75 million years ago, tectonic plate movements forced volcanic material toward the surface at this location and formed granites, including monzogranite common to the Wonderland of Rocks, …