
The Dutch colony of New Netherland became the English colonies of New York and New Jersey through military conquest and through treaties. New Netherland was created as a Dutch colony in the 1610s. At this point, there was very little British presence in what is now the United States.
How long was New Netherland a Dutch colony?
New Netherland was a Dutch colony from 1614 to 1664, about 50 years. In 1664, the English took the colony from the Dutch by force—even though the two countries were not at war and few if any shots were fired. Even after New Netherland became an English possession, Dutch settlers remained,...
How did life change in New Netherland after 1664?
New Netherland was a Dutch colony from 1614 to 1664, about 50 years. In 1664, the English took the colony from the Dutch by force—even though the two countries were not at war and few if any shots were fired. Even after New Netherland became an English possession, Dutch settlers remained, and life in the colony did not much change.
When did New York pass from Dutch to English control?
In 1664, New Amsterdam passed to English control, and English and Dutch settlers lived together peacefully. How was the colony of New York gained from the Dutch by the English?
What happened to New Netherland after the British took over?
As a consequence of these wars, New Netherland came under British control in 1664. Despite this transfer of power, Dutch influence remained strong in the former New Netherland, throughout the seventeenth century and beyond; many parts of the colony remained culturally Dutch up to and beyond the American Revolution.
See more

How did New Netherlands became a British colony?
In 1664, the English took the colony from the Dutch by force—even though the two countries were not at war and few if any shots were fired. Even after New Netherland became an English possession, Dutch settlers remained, and life in the colony did not much change.
When did New Netherlands became a British colony?
1664As a consequence of these wars, New Netherland came under British control in 1664. Despite this transfer of power, Dutch influence remained strong in the former New Netherland, throughout the seventeenth century and beyond; many parts of the colony remained culturally Dutch up to and beyond the American Revolution.
Why did the English take over New Netherland?
Some English from New England had infiltrated onto Long Island. Charles II decided to seize New Netherland, take over the valuable fur trade and give the colony to his younger brother James, Duke of York and Albany (the future James II).
How did Dutch New Netherland became English New York?
In 1664, the English sent a fleet to seize New Netherlands, which surrendered without a fight. The English renamed the colony New York, after James, the Duke of York, who had received a charter to the territory from his brother King Charles II.
What was one reason New Netherland fell to the English with little difficulty?
What was one reason New Netherland fell to the English with little difficulty? Much of the population of Manhattan was not even Dutch and was contemptuous of the colonial government.
How did the English conquer New Netherland quizlet?
Why did the Dutch surrender New Netherland to the English? The English king, Charles II, believed that New Netherland belong to England. Based upon this, he gave the land to his brother, James, Duke of York. James sent ships to New Amsterdam and demanded that the Dutch surrender.
What did the English call New Netherland?
Following its capture, New Amsterdam's name was changed to New York, in honor of the Duke of York, who organized the mission. The colony of New Netherland was established by the Dutch West India Company in 1624 and grew to encompass all of present-day New York City and parts of Long Island, Connecticut and New Jersey.
Why did the English want control of the Dutch colony?
Why did the English want control of the Dutch colony? The English wanted to expand in the direction of the Dutch colony.
When did New Amsterdam become British?
1664In 1664, New Amsterdam passed to English control, and English and Dutch settlers lived together peacefully. In 1673, there was a short interruption of English rule when the Netherlands temporary regained the settlement.
How did New Amsterdam become British?
The Dutch city of New Amsterdam became the English city of New York in 1664 when Dutch Director General Peter Stuyvesant handed it over to British troops under the command of Colonel Richard Nicholls.
Who colonized New Netherlands?
New Amsterdam became the seat of New Netherland government. In the fifty-five years that followed, the Dutch colony drew immigrants from all over Europe as it developed socially, and politically, and economically, offering a strategic point for trade.
What was the New Netherland?
It became an entrepôt for Chesapeake tobacco and a hub of trade between New England and the Caribbean. New Netherland developed into a culturally diverse and politically robust settlement. This diversity was fostered by Dutch respect for freedom of conscience.
What did the Dutch claim to the Netherlands?
Upon his return to the Netherlands, Hudson described what he had found: a magnificent harbor, wide navigable rivers, and a land rich in natural resources.
What was the Dutch claim to the Delaware Bay?
The Dutch claim to this territory derived from their sponsorship of Henry Hudson’s voyages of exploration. In 1609, Hudson and his crew sailed the ship de Halve Maen (the Half Moon) from the Delaware Bay up to the river now named for Hudson.
What was the first Dutch colony in North America?
New Netherland was the first Dutch colony in North America. It extended from Albany, New York, in the north to Delaware in the south and encompassed parts of what are now the states of New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Maryland, Connecticut, and Delaware. The Dutch claim to this territory derived from their sponsorship ...
What was the Dutch colony's primary source of wealth?
Initially, beaver pelts purchased from local Indians were the colony’s primary source of wealth. In Europe, these pelts were used to produce fashionable men’s hats. Over time, the Dutch colony’s economy broadened and diversified.
What rights did Dutch women have?
Furthermore, under Dutch rule, women enjoyed legal, civil, and economic rights denied their British counterparts in New England and Virginia. Towns within New Netherland were granted the protections and privileges of self-government.
How many wars did the Dutch and English fight?
Dutch success produced many rivals, the English chief among them. Between 1652 and 1674, the two nations fought three wars. As a consequence of these wars, New Netherland came under British control in 1664.
Origin
Map based on Adriaen Block 's 1614 expedition to New Netherland, featuring the first use of the name. It was created by Dutch cartographers in the Golden Age of Dutch exploration (ca. 1590s–1720s) and Netherlandish cartography (ca. 1570s–1670s).
Development
The storehouse of the Dutch West India Company in Amsterdam, built in 1642, became the headquarters of the board in 1647 because of financial difficulties after the loss of Dutch Brazil.
Expansion and incursion
Apart from the second Fort Nassau, and the small community that supported it, settlement along the Zuyd Rivier was limited. An attempt by patroons of Zwaanendael, Samuel Blommaert and Samuel Godijn was destroyed by the local population soon after its founding in 1631 during the absence of their agent, David Pietersen de Vries .
Capitulation, restitution, and concession
In March 1664, Charles II of England, Scotland, and Ireland resolved to annex New Netherland and "bring all his Kingdoms under one form of government, both in church and state, and to install the Anglican government as in old England".
Legacy
New Netherland grew into the largest metropolis in the United States, and it left an enduring legacy on American cultural and political life, "a secular broadmindedness and mercantile pragmatism" greatly influenced by the social and political climate in the Dutch Republic at the time, as well as by the character of those who immigrated to it.
See also
First Shearith Israel Graveyard, the only remaining 17th century structure in Manhattan.
Who took the colony from the Dutch?
King Charles II gave it to the Duke of York who took the colony from the Dutch by force.
What would shape and dominate all the colonies?
English laws, ideas, habits, and language would shape and dominate all the colonies.
Which colony had the greatest influence on the development of the mainland colonies of the West Indies?
English settlements in the West Indies had the greatest influence upon the development of the mainland colonies of
What chapter is the Colonial Experiment?
Start studying Chapter 4 (The Colonial Experiment). Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
When did the Chesapeake planters rely on slave labor?
After 1680, Chesapeake planters began to rely more heavily on African slave labor than on indentured white servants for all of the following reasons EXCEPT
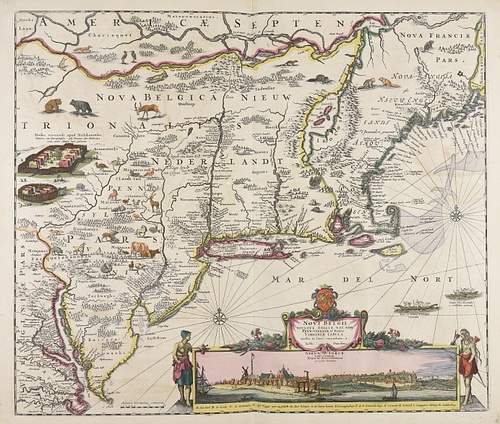
Overview
Development
The immediate and intense competition among Dutch trading companies in the newly charted areas led to disputes in Amsterdam and calls for regulation. The States General was the governing body of the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands, and it proclaimed on 17 March 1614, that it would grant an exclusive patent for trade between the 40th and 45th parallels. This monopoly …
Origin
During the 17th century, Europe was undergoing expansive social, cultural, and economic growth known as the Dutch Golden Age in the Netherlands. Nations vied for domination of lucrative trade routes around the globe, particularly those to Asia. Simultaneously, philosophical and theological conflicts were manifested in military battles throughout the European continent. The Republi…
Society
New Netherlanders were not necessarily Dutch, and New Netherland was never a homogeneous society. Governor Peter Minuit was a Walloon born in Germany who spoke English and worked for a Dutch company. The term New Netherland Dutch generally includes all the Europeans who came to live there, but may also refer to Africans, Indo-Caribbeans, South Americans, and even the Indians who were integral to the society. Dutch was the official language and likely the lingua franca of t…
Expansion and incursion
Apart from the second Fort Nassau, and the small community that supported it, settlement along the Zuyd Rivier was limited. An attempt by patroons of Zwaanendael, Samuel Blommaert and Samuel Godijn was destroyed by the local population soon after its founding in 1631 during the absence of their agent, David Pietersen de Vries.
Capitulation, restitution, and concession
In March 1664, Charles II of England, Scotland, and Ireland resolved to annex New Netherland and "bring all his Kingdoms under one form of government, both in church and state, and to install the Anglican government as in old England". The directors of the Dutch West India Company concluded that the religious freedom that they offered in New Netherland would dissuade English …
Legacy
New Netherland grew into the largest metropolis in the United States, and it left an enduring legacy on American cultural and political life, "a secular broadmindedness and mercantile pragmatism" greatly influenced by the social and political climate in the Dutch Republic at the time, as well as by the character of those who immigrated to it. It was during the early British colonial period tha…
Further reading
• Archdeacon, Thomas J. New York City 1664–1710. Conquest and Change (1976).
• Bachman, V.C. Peltries or Plantations. The Economic Policies of the Dutch West India Company in New Netherland 1633–1639 (1969).
• Balmer, Randall H. "The Social Roots of Dutch Pietism in the Middle Colonies," Church History Volume: 53. Issue: 2. 1984. pp 187+ online edition