Why did the voters of 1860 decide the issue of slavery?
For the voters of 1860 this was not merely an issue of human rights. The economic system based on slave grown cotton not only controlled the south but the entire United States, and reached across the ocean as well.
What was at stake in the election of 1860?
In 1860 Americans understood what was at stake, though they scarcely knew how to respond. Defeated Democratic candidate Stephen Douglas labored to craft a compromise to bring the seceding states back into the union. Meanwhile, President-elect Lincoln refused to budge on his party's opposition to slavery in the territories.
What was the Democratic Party like in 1860?
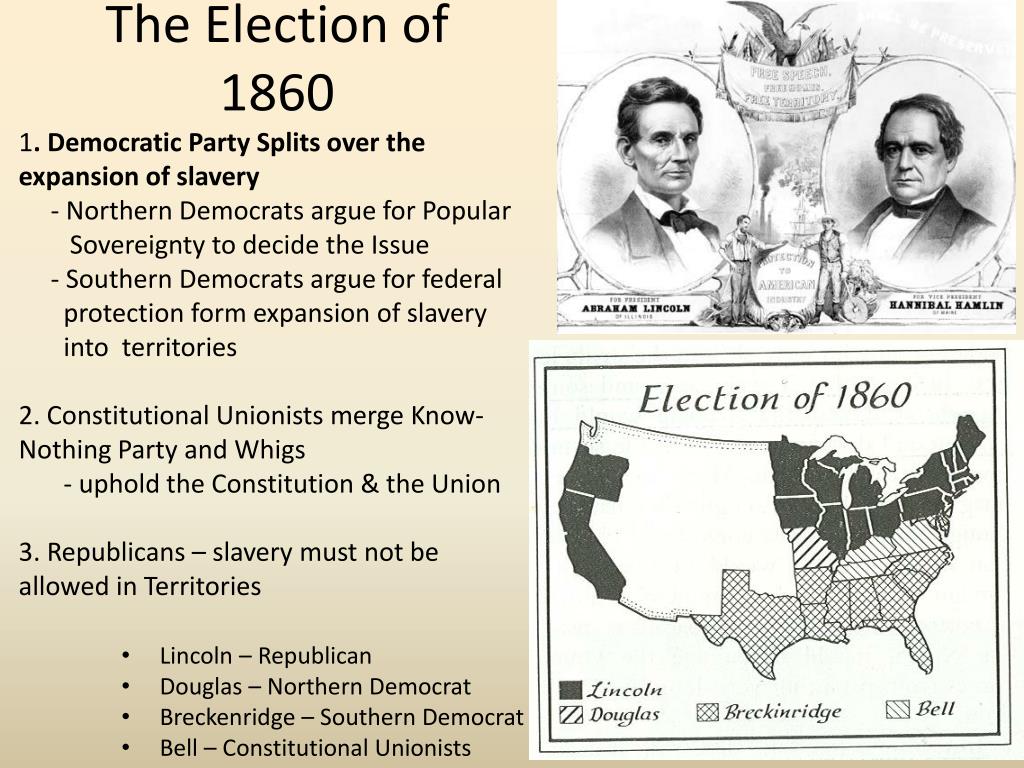
The Democratic Party was in shambles in 1860. They should have been the party of unity, but instead were divided on the issue of slavery. Southern Democrats thought slavery should be expanded but Northern Democrats opposed the idea. States’ rights were also hotly debated.
Why did South Carolina secede from the Union in 1860?
South Carolina was the first state to secede in December 1860, just one month after the election. The South Carolina Declaration of Secession directly addressed the issues, most notably slavery, state’s rights to maintain slavery and the demand to uphold the Fugitive Slave Act.

What were the consequences of the election of 1860?
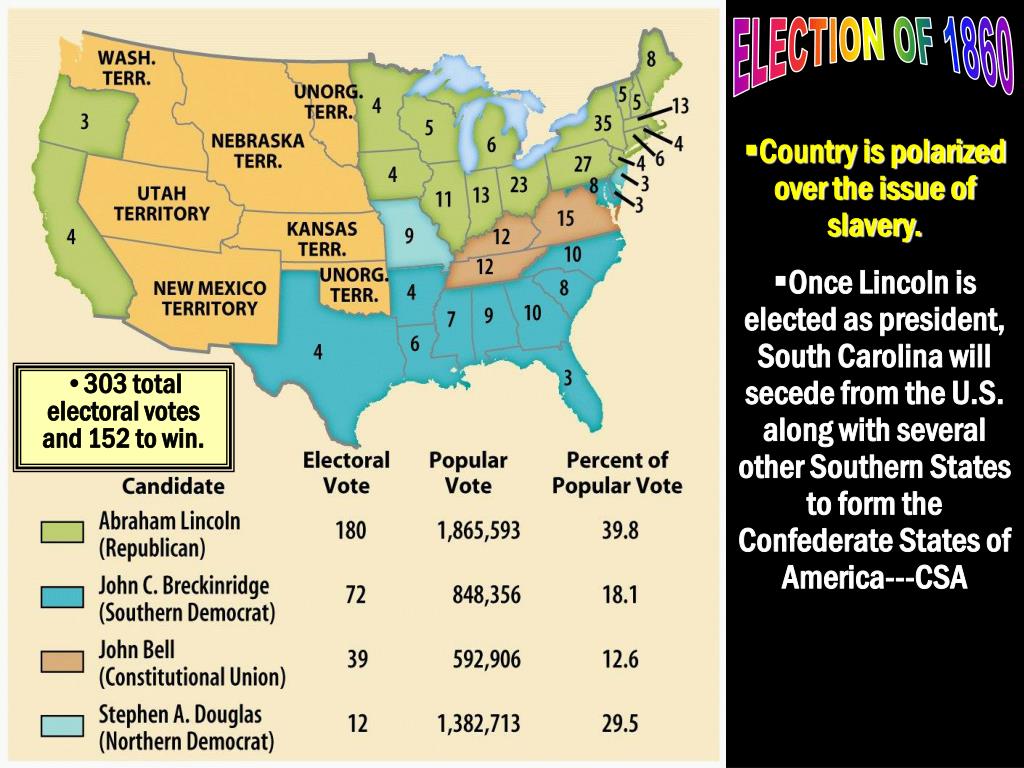
The 1860 presidential election turned on a number of issues including secession; the relationship between the federal government, states, and territories; and slavery and abolition.
Why was the election of 1860 a problem?
While the platforms of the various parties competing for the presidency in 1860 discussed issues such as a national tariff, the Homestead Act, and a transcontinental railroad, the main issue dominating the campaign was slavery. The Democratic Party split over the issue of slavery.
What were some effects of the 1860 election quizlet?
Lincoln, the Republican candidate, won because the Democratic party was split over slavery. As a result, the South no longer felt like it has a voice in politics and a number of states seceded from the Union.
How did Abraham Lincoln's election cause the Civil War?
A former Whig, Lincoln ran on a political platform opposed to the expansion of slavery in the territories. His election served as the immediate impetus for the outbreak of the Civil War. After being sworn in as president, Lincoln refused to accept any resolution that would result in Southern secession from the Union.
How did the election of 1860 increase sectional tensions?
Terms in this set (27) how did the election of 1860 increase sectional tension? Because the newly-elected Lincoln would not agree to any extension of slavery. So the final attempt at compromise failed.
How did the Election of 1860 lead to the American Civil War quizlet?
They thought Lincoln would abolish slavery, and Lincoln did not win a single southern state in the election, the south knew they had lost the balance of power. Reasons why Southerners were upset about Lincoln's election in 1860. April 12th, 1861- Confederate soldiers firing on this fort initiated the Civil War.
What was the significance of the Election of 1860 Apush quizlet?
It called for a constitutional amendment recognizing slavery in all territory south of the 36-30 line and an ironclad amendment guaranteeing slavery in slave states.
How did the Election of 1860 lead to secession quizlet?
Terms in this set (19) election where slavery was the central issue, Abraham Lincoln (Republican) won over John Breckinridge (Democrat), and John Bell (Constitutional Union Party). Lincoln won 40% of popular vote, but won a large majority of electoral votes. Lincoln's victory leads the south to secede.
Coming of War, Coming of Freedom
The fight for the nation gained momentum as proslavery advocates and abolitionists competed in the press, the ballot box, and the marketplac…
A Divided Nation Fights for Freedom
The election of 1860 was a turning point for the nation. The outcome would determine how the country would move forward regarding slavery. One month after the election of President Lincoln, states began to secede from the Union citing several reasons.
A Divided Nation Fights for Freedom
The nation fragmented in 1860 when four candidates ran for president, each with a different stance on the future of slavery.
Election of 1860: Slavery & Southern Secession
The nation fragmented in 1860 when four candidates ran for president, each with a different stance on the future of slavery.
What was the significance of the election of 1860?
For a nation standing at the brink of civil war, a nation where four million lived in bondage, a nation whose entire economic system lay threatened by its outcome, the election of 1860 poised the United States at the edge of an uncertain precipice from which the great American experiment would either soar or plunge to its untimely demise.
What was the election of 1860?
Election of 1860. Tensions often run high as Americans prepare to cast their vote for president of the United States. But perhaps no election carried more weight for the United States than the election of 1860. For a nation standing at the brink of civil war, a nation where four million lived in bondage, a nation whose entire economic system lay ...
What was the economic system of 1860?
The economic system based on slave grown cotton not only controlled the south but the entire United States, and reached across the ocean as well. For four million enslaved Americans who could not share their voice by the vote, the outcome of this issue and ...
What were the issues of the 1860s?
The construction of a transcontinental railroad. Extravagance in the government. The rights of immigrants. The principal issue was the clash of slavery and its expansion. For the voters of 1860 this was not merely an issue of human rights.
What party did Abraham Lincoln represent?
Abraham Lincoln of Illinois represented the Republican Party. He wanted to stop the spread of slavery in new territories and states.
How many people were eligible to vote in 1860?
Around 6.9 million, or just fewer than 45% of the age eligible population, had the option to represent the nation at the polls. On November 6, 1860, 81% of eligible voters, compared with 57.5% in 2012, cast their ballot for President of the United States of America. There was not yet a national standard for voting qualifications ...
Why are the opinions of the general population in South Carolina not represented?
The opinions of the general population in South Carolina were not represented as they did not yet have a popular vote. Slave states counted 3/5 of their enslaved population when determining the number of electoral votes. This meant more votes for the state even though the opinions of these people were not represented.
Which state was the only northern state where Abraham Lincoln lost the popular vote?
Princeton students engaged in heated debates over slavery during the contentious 1860 election, in which New Jersey was the only northern state where Abraham Lincoln lost the popular vote.
Who was the abolitionist who fought for the freedom of slaves?
Beecher, a Congregationalist clergyman and brother of famous anti-slavery author Harriet Beecher Stowe, became an ardent abolitionist when the Fugitive Slave Act of 1850 required all citizens in slaveholding and free states alike to return escaped slaves to their masters. After campaigning for John C. Frémont, the Republican Party’s 1856 presidential nominee, Beecher continued to make a name for himself with frequent speeches. He even organized auctions to buy the freedom of enslaved people, and by 1863 Beecher was touring Europe at Lincoln’s behest to advocate the Union’s case for abolition. [6]
What was John Brown's role in the Fugitive Slave Act?
In October 1859 he attempted to organize an armed slave revolt by seizing a federal arsenal in Harpers Ferry, Virginia. Though daring and provocative, the attack failed, and Brown was arrested and found guilty of treason. [7] To many in the North, Brown was a hero. Henry David Thoreau quickly penned his famous essay, “A Plea for Captain John Brown,” and delivered it in front of crowds throughout New England. Nonetheless, Brown was executed on the morning of December 2, 1859. [8]
Who were the antislavery figures at Princeton?
To the students who marched through Princeton as evening fell a few hours later, antislavery figures like Brown, Beecher, Garrison, and Seward were not heroes but enemies. And as the students attempted to stake out the campus’s southern allegiance, the stir of their shouts, speeches, and ritual executions rippled through newspapers from Philadelphia to Boston to far-off Sacramento.
What happened to Lincoln in New Jersey?
On Election Day less than a year later, Abraham Lincoln lost the popular vote in New Jersey , the only free state to vote against him (though he won the support of a majority of New Jersey delegates in the electoral college). [9] After Lincoln won the presidency, he refrained from appearing in Princeton while making a celebratory tour of New Jersey. [10] As the state was conflicted during the election—with the popular vote going one way and the electoral vote the other—Princeton’s allegiances were equally divided. Four Princetonians signed the Ordinance of Secession in South Carolina on December 20th, 1860. And in the coming years, more than 300 others would fight for the Confederacy during the Civil War. [11] Though Princeton lay north of the Mason-Dixon line that divided Union and Confederacy, students' attachment to the South remained strong.
What was the Democratic Party's compromise on slavery?
The Democratic Party tried to diffuse “ Southern rights ” and the slavery issue with a compromise called “ popular sovereignty. ” Identified in 1848 with the candidacy of Lewis Cass of Michigan, popular sovereignty left it to a territory ’ s settlers whether or not to allow slavery within its borders.
Why did Southerners assume that popular sovereignty was the first step toward a new institution such as slavery?
For this reason Southerners tended to assume that this was what was meant by popular sovereignty. If the decision was made at the initial organizational stage, as many Northerners assumed it would be, there could be at most a few slaves and slave owners in a given territory since under Mexican law slavery had been abolished. When the Democratic convention met and nominated Cass, delegates from two state delegations walked out in protest: Alabama because slavery ’ s future was not guaranteed in the platform, and New York because its favorite son, the former president Martin Van Buren, was passed over for the nomination.
Why did the Democratic convention walk out?
When the Democratic convention met and nominated Cass, delegates from two state delegations walked out in protest: Alabama because slavery ’ s future was not guaranteed in the platform, and New York because its favorite son, the former president Martin Van Buren, was passed over for the nomination. Another Whig War Hero.
What did Van Buren say about slavery?
Van Buren, however, had decided the time had come to take a stand against what free soilers called the Slave Power. “ The minds of nearly all mankind, ” declared Van Buren, “ have been penetrated by a conviction of the evils of slavery. ” . Southern Choice. The campaign itself was divided.
What did Calhoun say about secession?
Calhoun articulated in 1848 what secessionists would repeat in 1860: that the Constitution itself protects the right of property and that no law passed by Congress can ever tell a man where he can or cannot take his property. Democrats and “Popular Sovereignty.”.
How many slave states did Taylor have?
Another Victory for Taylor. When the votes were counted, Taylor carried eight of the fifteen slave states and seven of the fifteen free states. The Free Soil Party polled 290,000 votes (about 10 percent of the total, 14 percent in the North), enough to throw New York State and the election to Taylor.
Which party supported the Wilmot Proviso?
In the North both the Whig and Democratic parties claimed to support the Wilmot Proviso; in the South, Democrats pointed to the thousands of square miles of new slave territory their party had delivered. The Whig war hero Taylor proved to be by far the strongest candidate in the South.