Once Watson and Crick applied the Chargaff rule to their research, they determined that the base pairs were held together by hydrogen bonds. Watson and Crick made their discovery that the DNA was a double helix, and they constructed their model on February 28, 1953.
What is the double helix of DNA?
Double Helix. Double helix is the description of the structure of a DNA molecule. A DNA molecule consists of two strands that wind around each other like a twisted ladder. Each strand has a backbone made of alternating groups of sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate groups. Attached to each sugar is one of four bases: adenine (A), cytosine (C ...
What did Watson and Crick accomplish?
Watson and Francis H.C. Crick announce that they have determined the double-helix structure of DNA, the molecule containing human genes. Though DNA–short for deoxyribonucleic acid–was discovered in 1869, its crucial role in determining genetic inheritance wasn't demonstrated until 1943.
Who discovered double helix DNA?
The discovery in 1953 of the double helix, the twisted-ladder structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), by James Watson and Francis Crick marked a milestone in the history of science and gave rise to modern molecular biology, which is largely concerned with understanding how genes control the chemical processes within cells.
Who did Watson and Crick steal?
They stole Franklin and Wilkins' data, and made inferences on the data that neither Franklin nor Wilkins had made. Ultimately Watson and Crick do deserve the majority of the credit for the finding, in my opinion, but it is a shame that Franklin and Wilkins team isn't more widely acknowledged for their contribution.

How did Watson and Crick contribute to the discovery of the structure of DNA?
Watson and Crick developed their ideas about genetic replication in a second article in Nature, published on May 30, 1953. The two had shown that in DNA, form is function: the double-stranded molecule could both produce exact copies of itself and carry genetic instructions.
How did James Watson discover DNA?
After working at the University of Copenhagen, where he first determined to investigate DNA, he did research at the Cavendish Laboratory (1951–53). There Watson learned X-ray diffraction techniques and worked with Crick on the problem of DNA structure.
What do you understand by Watson and Crick model of DNA?
In Watson and Crick's model, the two strands of the DNA double helix are held together by hydrogen bonds between nitrogenous bases on opposite strands. Each pair of bases lies flat, forming a "rung" on the ladder of the DNA molecule. Base pairs aren't made up of just any combination of bases.
What facts about DNA does the Watson-Crick model explain?
In “A Structure of Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid,” Watson and Crick described DNA as a double helix that contained two long, helical strands wound together. In their model, each DNA strand contained individual units called bases, and the bases along one DNA strand matched the bases along the other DNA strand.
What did James Watson do for DNA?
James Watson was a pioneer molecular biologist who is credited, along with Francis Crick and Maurice Wilkins, with discovering the double helix structure of the DNA molecule. The trio won the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 1962 for their work.
Who actually discovered DNA?
Many people believe that American biologist James Watson and English physicist Francis Crick discovered DNA in the 1950s. In reality, this is not the case. Rather, DNA was first identified in the late 1860s by Swiss chemist Friedrich Miescher.
Why did Watson study DNA?
D. in 1950, Watson spent time in Europe, first in Copenhagen and then at the Cavendish Laboratory of the University of Cambridge. By now, Watson knew that DNA was the key to understanding life and he was determined to solve its structure.
When did Watson and Crick discover DNA?
On February 28, 1953, Cambridge University scientists James D. Watson and Francis H.C. Crick announce that they have determined the double-helix structure of DNA, the molecule containing human genes.
What is the DNA helix?
According to the Watson and Crick model, the DNA is a double-stranded helix, which consists of two polynucleotide chains. The two polynucleotide chain are spirally or helically twisted, which gives it a twisted ladder-like look.
What is the Watson and Crick model of DNA?
Watson and Crick model of DNA provides one of the best ways to demonstrate the structure of double-helix DNA. A DNA is a polymer composed by the combination of several monomer units ( deoxyribonucleotides) linked by the phosphodiester bond. In the discovery of DNA, many scientists have contextualized the structure of DNA, ...
What are the three components of DNA?
Polynucleotide strands of DNA consist of three major components, namely nitrogenous bases, deoxyribose sugar and a phosphate group.
How do the nucleotide bases in DNA join?
The nucleotide bases in the polynucleotide strands of DNA will join with each other through a strong hydrogen bond.
What is the base composition of DNA?
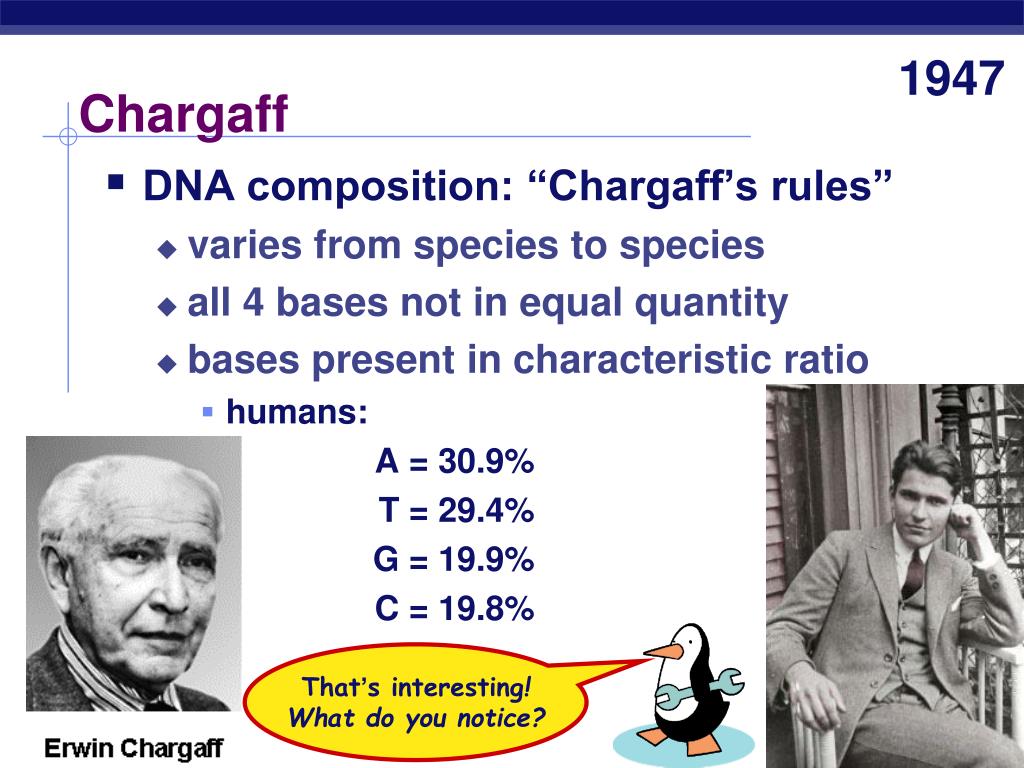
The nucleotide base composition of DNA follows the Chargaff’s rule where the sum of purines is equal to the number of pyrimidines. The base composition of A + G = T + C obeys the Chargaff’s rule, but the base composition of A + T is not equal to the G + C.
What is the diameter of a DNA helix?
The diameter of ds-stranded DNA helix is 20Å.
How many base pairs does DNA have?
The length of DNA helix is 34Å after a full turn and it possesses 10 base pairs per turn. The DNA is twisted in “Right-handed direction” or we can say in a “ Clockwise direction ”. Turning of DNA causes a formation of wide indentations, i.e. “ Major groove ”.
What is the double helix of DNA?
Watson, Crick and the DNA Double Helix. Several researchers, over many years, had discovered that in the nucleus of our cells there was a substance called DNA which contained all our genetic information and it was made of four compounds: Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine and Guanine. But this molecule was so simple that many scientists were sceptical ...
What are the compounds in DNA?
Several researchers, over many years, had discovered that in the nucleus of our cells there was a substance called DNA which contained all our genetic information and it was made of four compounds: Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine and Guanine.
Who discovered the structure of DNA?
James Watson and Francis Crick thought that maybe the answer was in the structure of DNA, and in 1953 they eventually solved this four-pieced puzzle that was driving all the scientific community crazy. Ten years after they received the Nobel Prize for this discovery, and the DNA revolution spread across any biology laboratory in the world.
Can you add videos to your watch history?
Videos you watch may be added to the TV's watch history and influence TV recommendations. To avoid this, cancel and sign in to YouTube on your computer.
What did Franklin prove about the backbones of sugar phosphate?
Her evidence demonstrated that the two sugar-phosphate backbones lay on the outside of the molecule, confirmed Watson and Crick's conjecture that the backbones formed a double helix, and revealed to Crick that they were antiparallel. Franklin's superb experimental work thus proved crucial in Watson and Crick's discovery.
What evidence did Watson and Crick use?
A more enduring controversy has been generated by Watson and Crick's use of Rosalind Franklin's crystallographic evidence of the structure of DNA , which was shown to them, without her knowledge, by her estranged colleague, Maurice Wilkins, and by Max Perutz. Her evidence demonstrated that the two sugar-phosphate backbones lay on the outside of the molecule, confirmed Watson and Crick's conjecture that the backbones formed a double helix, and revealed to Crick that they were antiparallel. Franklin's superb experimental work thus proved crucial in Watson and Crick's discovery. Yet, they gave her scant acknowledgment. Even so, Franklin bore no resentment towards them. She had presented her findings at a public seminar to which she had invited the two. She soon left DNA research to study tobacco mosaic virus. She became friends with both Watson and Crick, and spent her last period of remission from ovarian cancer in Crick's house (Franklin died in 1958). Crick believed that he and Watson used her evidence appropriately, while admitting that their patronizing attitude towards her, so apparent in The Double Helix, reflected contemporary conventions of gender in science.
What are the four types of bases in DNA?
The biochemist Erwin Chargaff had found that while the amount of DNA and of its four types of bases--the purine bases adenine (A) and guanine (G), and the pyrimidine bases cytosine (C) and thymine (T)--varied widely from species to species, A and T always appeared in ratios of one-to-one, as did G and C. Maurice Wilkins and Rosalind Franklin had obtained high-resolution X-ray images of DNA fibers that suggested a helical, corkscrew-like shape. Linus Pauling, then the world's leading physical chemist, had recently discovered the single-stranded alpha helix, the structure found in many proteins, prompting biologists to think of helical forms. Moreover, he had pioneered the method of model building in chemistry by which Watson and Crick were to uncover the structure of DNA. Indeed, Crick and Watson feared that they would be upstaged by Pauling, who proposed his own model of DNA in February 1953, although his three-stranded helical structure quickly proved erroneous.
What did Crick and Watson discover?
They seized on this problem during their very first encounter, in the summer of 1951, and pursued it with single-minded focus over the course of the next eighteen months. This meant taking on the arduous intellectual task of immersing themselves in all the fields of science involved: genetics, biochemistry, chemistry, physical chemistry, and X-ray crystallography. Drawing on the experimental results of others (they conducted no DNA experiments of their own), taking advantage of their complementary scientific backgrounds in physics and X-ray crystallography (Crick) and viral and bacterial genetics (Watson), and relying on their brilliant intuition, persistence, and luck, the two showed that DNA had a structure sufficiently complex and yet elegantly simple enough to be the master molecule of life.
What is the double helix?
The discovery in 1953 of the double helix, the twisted-ladder structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), by James Watson and Francis Crick marked a milestone in the history of science and gave rise to modern molecular biology, which is largely concerned with understanding how genes control the chemical processes within cells. In short order, their discovery yielded ground-breaking insights into the genetic code and protein synthesis. During the 1970s and 1980s, it helped to produce new and powerful scientific techniques, specifically recombinant DNA research, genetic engineering, rapid gene sequencing, and monoclonal antibodies, techniques on which today's multi-billion dollar biotechnology industry is founded. Major current advances in science, namely genetic fingerprinting and modern forensics, the mapping of the human genome, and the promise, yet unfulfilled, of gene therapy, all have their origins in Watson and Crick's inspired work. The double helix has not only reshaped biology, it has become a cultural icon, represented in sculpture, visual art, jewelry, and toys.
What is the smallest unit of genetic information?
Researchers working on DNA in the early 1950s used the term "gene" to mean the smallest unit of genetic information, but they did not know what a gene actually looked like structurally and chemically, or how it was copied, with very few errors, generation after generation. In 1944, Oswald Avery had shown that DNA was the "transforming principle," the carrier of hereditary information, in pneumococcal bacteria. Nevertheless, many scientists continued to believe that DNA had a structure too uniform and simple to store genetic information for making complex living organisms. The genetic material, they reasoned, must consist of proteins, much more diverse and intricate molecules known to perform a multitude of biological functions in the cell.
What is the function of DNA?
The two had shown that in DNA, form is function: the double-stranded molecule could both produce exact copies of itself and carry genetic instructions. During the following years, Crick elaborated on the implications of the double-helical model, advancing the hypothesis, revolutionary then but widely-accepted since, that the sequence of the bases in DNA forms a code by which genetic information can be stored and transmitted.
Author
In 1866, Gregor Mendel, the father of modern genetics, discovered that traits were inherited and passed on to generations through genes. However, Mendel did not know what the genes were composed of or what allowed the traits to be passed on.
David Crockett and the Alamo: The Thrilling Battle for Independence
David Crockett was a man with a plethora of unique skills and talents. He was
Table of Contents
James Watson and Francis Crick were scientists during the middle part of the twentieth century. The work of Watson and Crick extends back several decades prior to their actual scientific discoveries as they utilized information and research of several other scientists to ultimately complete their own experiments.
Watson and Crick Experiment
Science is often collaborative, whether intentional or not. This collaborative nature is demonstrated through Watson and Crick's experiments, which were based on the ideas and research of several other scientists including:
How many strands are in a DNA molecule?
D. each DNA molecule is composed of two strands that are twisted into a double helix.
What is DNA function?
C. DNA functions as the genetic material.
Which direction is the new strand synthesized?
C. Synthesis of both new strands is in the 5' to 3' direction.
When does the nucleus of a mouse cell repair itself?
B. the nucleus of a mouse cell repairs itself when damaged by bacterial infection.
What did Franklin do before leaving the lab?
While Watson and Crick were working feverishly in Cambridge, fearful that Pauling might scoop them, Franklin was finishing up her work on DNA before leaving the lab. The progress she made on her own, increasingly isolated and without the benefit of anyone to exchange ideas with, was simply remarkable.
What did Watson and Crick need?
What Watson and Crick needed was far more than the idea of a helix – they needed precise observations from X-ray crystallography. Those numbers were unwittingly provided by Franklin herself, included in a brief informal report that was given to Max Perutz of Cambridge University.
What did Franklin discover about DNA?
Franklin’s laboratory notebooks reveal that she initially found it difficult to interpret the outcome of the complex mathematics – like Crick, she was working with nothing more than a slide rule and a pencil – but by 24 February, she had realised that DNA had a double helix structure and that the way the component nucleotides or bases on each strand were connected meant that the two strands were complementary, enabling the molecule to replicate.
How did Watson prove her point?
To prove her point, she would have to convert this insight into a precise, mathematically and chemically rigorous model. She did not get the chance to do this, because Watson and Crick had already crossed the finishing line – the Cambridge duo had rapidly interpreted the double helix structure in terms of precise spatial relationships and chemical bonds, through the construction of a physical model.
What is the significance of photo 51?
According to Watson, photo 51 provided the vital clue to the double helix. But despite the excitement that Watson felt, all the main issues, such as the number of strands and above all the precise chemical organisation of the molecule, remained a mystery. A glance at photo 51 could not shed any light on those details.
When did Watson and Crick crack DNA?
Watson and Crick’s first foray into trying to crack the structure of DNA took place in 1952. It was a disaster. Their three-stranded, inside-out model was hopelessly wrong and was dismissed at a glance by Franklin.
Did Watson and Crick steal Rosalind Franklin's data?
Sexism in science: did Watson and Crick really steal Rosalind Franklin’s data? The race to uncover the structure of DNA reveals fascinating insights into how Franklin’s data was key to the double helix model, but the ‘stealing’ myth stems from Watson’s memoir and attitude rather than facts. Rosalind Franklin in 1950.
