
What can cause a change in allele frequency?
Random events that alter allele frequencies will have a much larger effect when the gene pool is small. Genetic drift and natural selection usually occur simultaneously in populations, but the cause of the frequency change is often impossible to determine. Natural selection also affects allele frequency.
When allele frequencies are not changing it is called?
Genetic Equilibrium is the condition of an allele in a gene pool where the frequency does not change from generation to generation Five Disruptions: 1) nonrandom mating, 2)small population size, 3)immigration or emigration, 4) mutations, and 5) natural select
What is it when allele frequencies do not change?
Random mating alone does not change allele frequencies, and the Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium assumes an infinite population size and a selectively neutral locus. In natural populations natural selection (adaptation mechanism), gene flow, and mutation combine to change allele frequencies across generations.
How can Nonrandom mating change allele frequencies?
Non-random mating. In non-random mating, organisms may prefer to mate with others of the same genotype or of different genotypes. Non-random mating won't make allele frequencies in the population change by itself, though it can alter genotype frequencies.
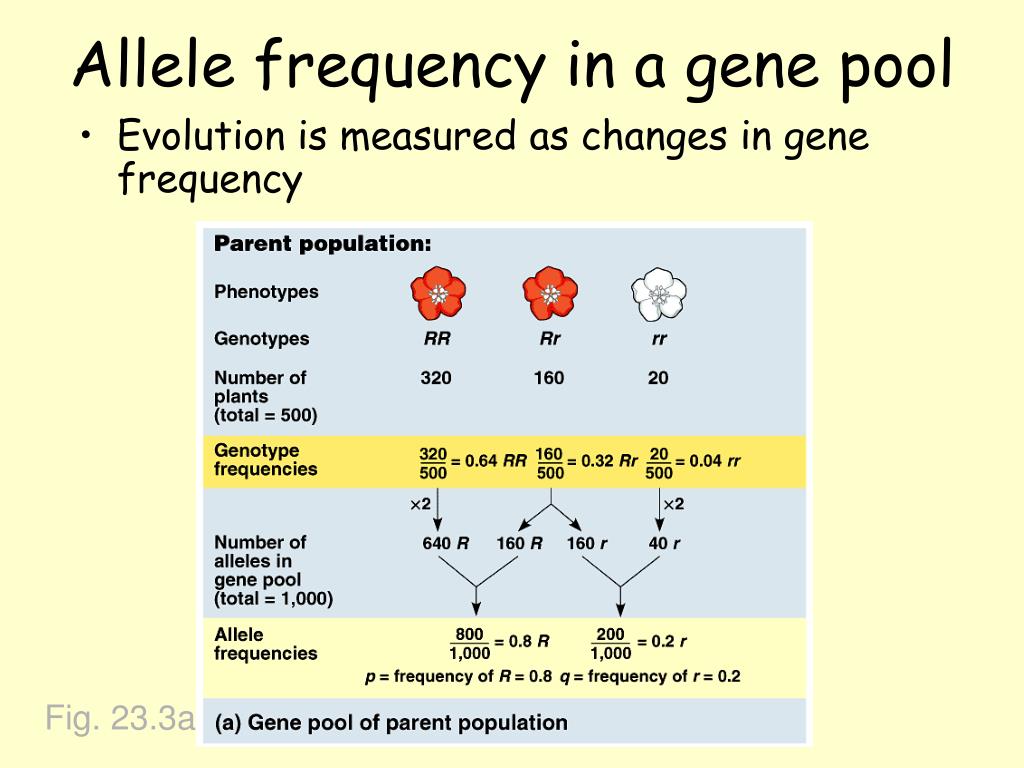
What are the 4 main ways allele frequencies can change in a population?
There are five key mechanisms that cause a population, a group of interacting organisms of a single species, to exhibit a change in allele frequency from one generation to the next. These are evolution by: mutation, genetic drift, gene flow, non-random mating, and natural selection.
Do gene frequencies change over time?
Gene frequencies tend to remain constant from generation to generation when disturbing factors are not present. Factors that disturb the natural equilibrium of gene frequencies include mutation, migration (or gene flow), random genetic drift, and natural selection.
Do allele frequencies decrease over time?
Sometimes, there can be random fluctuations in the numbers of alleles in a population. These changes in relative allele frequency, called genetic drift, can either increase or decrease by chance over time.
What factors can change allele frequencies?
Allele frequencies of a population can be changed by natural selection, gene flow, genetic drift, mutation and genetic recombination. They are referred to as forces of evolution.
What are the factors that affect allele frequency and how they are affected?
Answer : Five factors are known to affect allele frequency in populations i.e., Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. These are gene migration or gene flow, genetic drift, mutation, genetic recombination and natural selection. Gene migration or gene flow – it is movement of alleles into a gene pool or out of a gene pool.
Does allele frequency change among generations?
allele frequencies in a population will not change from generation to generation.
Why do allele frequencies change in genetic drift?
Genetic drift is change in allele frequencies in a population from generation to generation that occurs due to chance events. To be more exact, genetic drift is change due to "sampling error" in selecting the alleles for the next generation from the gene pool of the current generation.
How does population size affect allele frequency?
So, while allele frequencies are almost certain to change in each generation, the amount of change due to sampling error decreases as the population size increases. Perhaps the most important point is that the direction of the change is unpredictable; allele frequencies will randomly increase and decrease over time.
How are allele frequencies changed within a population due to natural selection?
Natural selection can cause microevolution When a phenotype produced by certain alleles helps organisms survive and reproduce better than their peers, natural selection can increase the frequency of the helpful alleles from one generation to the next – that is, it can cause microevolution.
What are the five factors that affect gene frequency?
They are: mutation, non-random mating, gene flow, finite population size (genetic drift), and natural selection.
What are the five factors that can alter the allele frequencies of a population?
These are:Mutations.Recombination of genes.Gene migration or gene flow.Genetic drift.Natural selection.
What are the five factors that affect gene frequency?
They are: mutation, non-random mating, gene flow, finite population size (genetic drift), and natural selection.
Which factors may alter the gene frequency of a population?
Four major forces are usually listed for changing gene frequencies in populations, namely migration, mutation, selection and random genetic drift. These forces constitute the mechanisms underlying the evolutionary process.
In which condition the gene frequency of a population will remain constant?
So, the correct answer is 'Random mating'
How does mutation affect gene frequency?
How Do Mutations Impact Allele Frequencies? Mutations add new alleles into a gene pool. This causes a change in the frequency of certain allele combinations in the population, which will cause the population to evolve over time. They are a major evolutionary force that creates new gene variations.
Allele Frequency Definition
Allele Frequency Overview
How to Calculate Allele Frequency
- To find the number of alleles in a given population, you must look at all the phenotypes present. The phenotypes that represent the allele are often masked by dominant and recessive alleles working in conjunction. To analyze the allele frequency in a population, scientists use the Hardy-Weinberg (HW) equation.The Hardy-Weinberg equation is written as follows: 1 = p2 + 2pq + q2 …
Allele Frequency Example
- In a simplified scenario, p and q are the only alleles in the population, and the population is not developing any mutations.If this is the case, the sum of the allele frequencies of p and q must equal 1 because with only two alleles the combined frequency must equal 100%.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Trying to Find p First
One mistake that students commonly make is trying to calculate p by observing the population, then taking the square root. This does not work in typical recessive/dominant allele relationships, simply because a dominant allele can hide a recessive allele. For instance, if we were to calculat… - Relating Allele Frequency to Fitness
A common misconception of allele frequency is that it is directly related to the evolutionary fitness of a particular allele. Just because an allele is frequent or infrequent has no bearing on the fitness of that allele.For example, many recessive traits that are deleterious “hide” in a populatio…