What process is used to link amino acids together?
Hydrolysis is the process used to link amino acids together. The bond found between amino acids is a peptide bond. A disaccharide is two monosaccharides linked together. A polysaccharide is multiple monosaccharides linked together. An example of a disaccharide is sucrose and an example of a polysaccharide is starch. Thanks (17) Useless
What are the bonds that hold two amino acids together?
Types of Chemical Bonds in Proteins
- Peptide Bonds. The primary structure of a protein consists of amino acids chained to each other. ...
- Hydrogen Bonds. The secondary structure describes the three-dimensional folding or coiling of a chain of amino acids (e.g., beta-pleated sheet, alpha helix).
- Hydrogen Bonds, Ionic Bonds, Disulfide Bridges. ...
- Hydrophobic and Hydrophilic Interactions. ...
What can amino acids can be joined together to make?
Amino acids are made into proteins by being joined together in a chain by peptide bonds. Each different protein has a unique sequence of amino acid residues: this is its primary structure. Just as the letters of the alphabet can be combined to form an almost endless variety of words, amino acids can be linked in varying sequences to form a huge ...
What is the type of bond joining amino acids together?
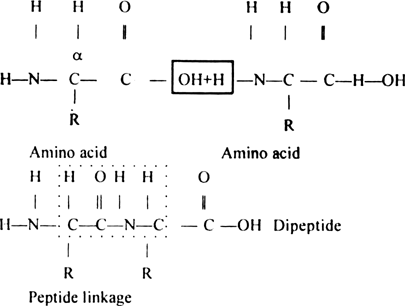
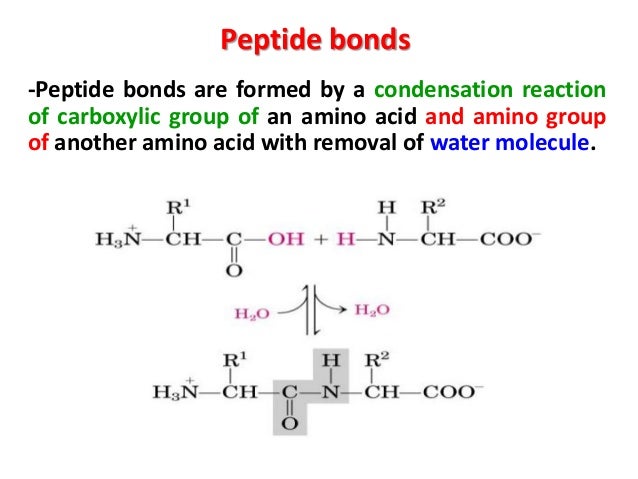
The bond that holds together the two amino acids is a peptide bond, or a covalent chemical bond between two compounds (in this case, two amino acids). It occurs when the carboxylic group of one molecule reacts with the amino group of the other molecule, linking the two molecules and releasing a water molecule.
How do amino acids join together?
To form polypeptides and proteins, amino acids are joined together by peptide bonds, in which the amino or NH2 of one amino acid bonds to the carboxyl (acid) or COOH group of another amino acid.
How do amino acids bonds?
A covalent bond, known as a peptide bond, connects each amino acid to another amino acid. The carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of the incoming amino acid interact and release a molecule of water as two amino acids are covalently bound by a peptide bond.
What bond holds amino acids together?
peptide bondThe resulting group of atoms, which hold the amino acids together, is called a peptide bond. Any of the 20 different amino acids can occur in any position along a polypeptide chain.
How do amino acids form proteins?
A protein molecule is made from a long chain of these amino acids, each linked to its neighbor through a covalent peptide bond (Figure 3-1). Proteins are therefore also known as polypeptides. Each type of protein has a unique sequence of amino acids, exactly the same from one molecule to the next.
What type of bonds are formed between amino acids during translation?
Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins During translation, peptide bonds are formed from the amino (N) to the carboxyl (C) terminus by removal of water (also referred to as dehydration or condensation) and catalyzed by RNA (referred to as a ribozyme) that forms part of the ribosome.
What causes an amino acid chain to fold?
Protein folding is the physical process by which a linear polypeptide folds into its characteristic and functional three-dimensional structure. Folding of a polypeptide chain is strongly influenced by the solubility of the AA R-groups in water.
How are ionic bonds formed in proteins?
A. Ionic bonds are formed as amino acids bearing opposite electrical charges are juxtaposed in the hydrophobic core of proteins. Ionic bonding in the interior is rare because most charged amino acids lie on the protein surface.
How are peptide bonds formed?
Peptide bonds are formed when the amine group of one amino acid binds with the carbonyl carbon of another amino acid.
How does hydrogen bonds stabilize protein structure?
Hydrogen bonds form between the oxygen of each C=O. bond in the strand and the hydrogen of each N-H group four amino acids below it in the helix. The hydrogen bonds make this structure especially stable. The side-chain substituents of the amino acids fit in beside the N-H groups.
How are amino acids joined together?
The resulting amino acids are joined together through dehydration synthesis, a process in which a peptide bond is formed between the amino acids. A polypeptide chain is formed when a number of amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds.
What are amino acids made of?
From a structural perspective, amino acids are typically composed of a carbon atom, a hydrogen atom, a carboxyl group along with an amino group and a variable group.
How many amino acids are there in the human body?
While amino acids are necessary for life, not all of them can be produced naturally in the body. Of the 20 amino acids, 11 can be produced naturally. These nonessential amino acids are alanine, arginine, asparagine, aspartate, cysteine, glutamate, glutamine, glycine, proline, serine, and tyrosine. With the exception of tyrosine, nonessential amino ...
What are nonessential amino acids?
With the exception of tyrosine, nonessential amino acids are synthesized from products or intermediates of crucial metabolic pathways. For example, alanine and aspartate are derived from substances produced during cellular respiration. Alanine is synthesized from pyruvate, a product of glycolysis.
What are the structural properties of amino acids?
Generally, amino acids have the following structural properties: All amino acids have the alpha carbon bonded to a hydrogen atom, carboxyl group, and amino group. The "R" group varies among amino acids and determines the differences between these protein monomers.
How many amino acids are in proteins?
Although there are hundreds of amino acids found in nature, proteins are constructed from a set of 20 amino acids.
Why are amino acids important to life?
Amino acids are essential to life because the proteins they form are involved in virtually all cell functions. Some proteins function as enzymes, some as antibodies, while others provide structural support.
How do amino acids bond?
Inside your cells, the individual amino acids can bond together by forming a peptide bond, which is simply a chemical bond that joins amino acids together. More specifically, peptide bonds join the carboxyl group of one amino acid with the amino group of another. For example, the amino acid called glycine can bond with the amino acid called alanine ...
Where do amino acids come from?
We mentioned that some of the amino acids are made by your body, while others come from your diet. Now, we don't really think in terms of eating different amino acids. What we eat is protein, which is found in foods like meat, fish, eggs and some plant foods, such as beans and nuts.
What are the building blocks of proteins?
The basic building blocks of proteins are amino acids. The 20 different amino acids needed by your body all have the same basic structure, which is a central carbon atom attached to a hydrogen atom, a carboxyl group, an amino group, and a variable R group or side chain that gives the amino acid its uniqueness.
How many amino acids are needed for protein?
Regardless of whether a protein is found in the food on your dinner plate or within your body, it is made up of a chain of amino acids. There are 20 different amino acids needed by your body; some of them are made in your body while others must come from your diet.
What are the elements that make up amino acids?
All of the amino acids have the same basic structure. We see a central carbon atom, which is represented by the letter C, bonded to four different components. We see a hydrogen atom, which is represented by this letter H. We also have a carboxyl group, which is the COOH seen here; and an amino group, which is this NH2 on the other side.
How is a protein made?
So, a protein is built through dehydration synthesis. Of course, simply joining two amino acids together is still a long way off from having a protein.
What are the most common atoms in amino acids?
So we have a bunch of C's, some O's, H's and N's in the basic structure of an amino acid, which means the most common atoms in amino acids are carbon, oxygen, hydrogen and nitrogen, but you probably also noticed the R Group.
What are the reactions that occur when amino acids combine?
The amine group of one amino acid and the carboxylic acid of another amino acid can react to form amide bonds and one water molecule, which is considered a condensation reaction . Polymerization of amino acids results in peptides and proteins depending on the number of amino acids involved.
How are proteins determined?
The primary structure of a protein is determined by a specific sequence of amino acids that makes up the polypeptide chain with each amino acid being held together by peptide bonds. The ends of the polypeptide chain are called the carboxy (C) terminus and the amino (N) terminus as determined by the amino acid at each end of the polypeptide chain. A specific sequence of nucleotides for DNA is transcribed into mRNA and is then translated into a protein. Three nucleotides encode for a single amino acid, otherwise called the triplet codon with some amino acids being encoded by several triplet codons.
What is the tertiary structure of a protein?
The tertiary structure indicates the 3D structure of the monomeric and multimeric protein molecules. Alpha-helixes and beta-pleated-sheets can be arranged into a globular structure. Such folding is dependent upon non-specific hydrophobic interactions.
Do you have to be a Study.com member to unlock this lesson?
To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member.
