What moves substances in and out of a cell?
What are the four ways substances can move across a cell membrane?
- Simple Diffusion. requires no energy.
- Passive diffusion. requires no energy.
- Facilitated diffusion. Movement of specific molecules across cell membranes through protein channels.
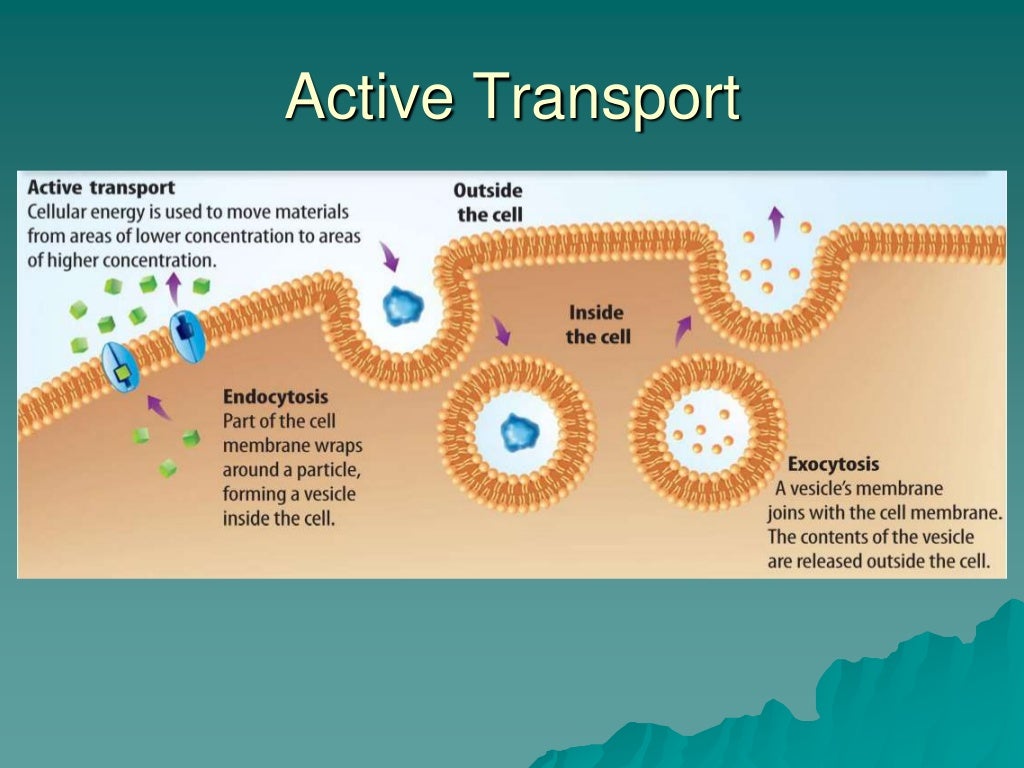
- Active transport.
- Bulk transport.
- Exocytosis.
- Endocytosis.
- Phagocytosis.
How substances are transported into and out of the cell?
Passive transport.
- a) Passive diffusion: Here the solute molecules move from a region of higher concentration to the region of lower concentration.
- b) Facilitated diffusion ( passive-mediated transport) This route is used by those materials that cannot diffuse across the cell membrane without some aid.
- c) Osmosis. ...
Are substances transfered in or out of the cells?
The movement of substances in and out of the cell by diffusion is known as passive transport. However, sometimes substances will not diffuse across the membrane and need to be chemically assisted. This is known as active transport.
What substances move into and out of cells by diffusion?
begins the process of decay as substances leave the vacuole by diffusion.
- it loses its green color.
- is full of water molecules.
- begins the process of decay as substances leave the vacuole by diffusion.

How substances are transported across a cell membrane?
The cell membrane is selectively permeable . It lets some substances pass through rapidly and some substances pass through more slowly, but prevents other substances passing through it at all. Some small molecules such as water, oxygen and carbon dioxide can pass directly through the phospholipids in the cell membrane.
How are substances transported within the cell?
Water, carbon dioxide, and oxygen are among the few simple molecules that can cross the cell membrane by diffusion (or a type of diffusion known as osmosis ). Diffusion is one principle method of movement of substances within cells, as well as the method for essential small molecules to cross the cell membrane.
What are the three methods of transport in cells?
Types of TransportSimple diffusion – movement of small or lipophilic molecules (e.g. O2, CO2, etc.)Osmosis – movement of water molecules (dependent on solute concentrations)Facilitated diffusion – movement of large or charged molecules via membrane proteins (e.g. ions, sucrose, etc.)
How do cells perform transport?
0:482:32Active Transport | Cells | Biology | FuseSchool - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWork active transport is carried out by protein carriers within the cell membrane. And they have aMoreWork active transport is carried out by protein carriers within the cell membrane. And they have a specific binding site for the exact molecules they are transporting.
How do substances move in and out of cells?
Substances move in and out of cells by diffusion down a concentration gradient, through a partially permeable membrane. The efficiency of movement of substances in and out of a cell is determined by its volume to surface area ratio.
How do substances move in and out of cells by active transport?
During active transport, substances move against the concentration gradient, from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. This process is “active” because it requires the use of energy (usually in the form of ATP). It is the opposite of passive transport.
What are the types of transport in a cell?
There are two major types of cell transport: passive transport and active transport. Passive transport requires no energy. It occurs when substances move from areas of higher to lower concentration.
What are the four types of cell transport?
There are four major types of passive transport are (1) simple diffusion, (2) facilitated diffusion, (3) filtration, and (4) osmosis.
What are the different types of cell transport explain?
They are passive, active, and facilitated transport. Passive transport does not require energy. During passive transport, molecules move from higher concentration to lower concentration. But, active transport requires energy.
How do substances move in active transport?
During active transport, substances move against the concentration gradient, from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. This process is “active” because it requires the use of energy (usually in the form of ATP). It is the opposite of passive transport.Active transport review (article) - Khan Academyhttps://www.khanacademy.org › hs-energy-and-transporthttps://www.khanacademy.org › hs-energy-and-transport
What are 4 methods of transport across the membrane?
Particles move across membranes by simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis and active transport.1.4 Membrane Transport - BioNinjahttp://ib.bioninja.com.au › topic-1-cell-biology › 14-mem...http://ib.bioninja.com.au › topic-1-cell-biology › 14-mem...
What are 3 types of active transport?
Active TransportDiffusion.Facilitated diffusion.Active transport.Passive transport.Definition And Types Of Active Transport - BYJU'Shttps://byjus.com › biology › active-transporthttps://byjus.com › biology › active-transport
How do membrane proteins serve as pumps?
Those membrane proteins serving as pumps accomplish this by coupling the energy required for transport to the energy produced by cell metabolism or by the diffusion of other solutes.
What is the role of lipids in the cell membrane?
Lipid-soluble molecules and some small molecules can permeate the membrane , but the lipid bilayer effectively repels the many large , water-soluble molecules and electrically charged ions that the cell must import or export in order to live. Transport of these vital substances is carried out by certain classes of intrinsic proteins ...
What are the holes in the cell membrane called?
In these cases special holes in the membrane, called channels , allow specific ions and small molecules to diffuse directly through the bilayer. Load Next Page.
What is the principle of diffusion?
According to this principle, a dissolved substance diffuses down a concentration gradient; that is, given no energy from an outside source, it moves from a place where its concentration is high to a place where its concentration is low.
Can sugar molecules pass through the membrane?
Large sugar molecules in the solution cannot pass through the membrane into the water (top). In contrast, small water molecules easily diffuse through the membrane (bottom). The ability of water to readily cross membranes is vital for establishing equilibrium. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. For all cell membranes that have been studied in ...
What is the primary active transport of ATP?
Transport that directly uses ATP for energy is considered primary active transport. In this case, that’s moving sodium from a concentration of 10mM to one of 145 mM.
What are the molecules that the body uses to sustain itself?
Your body uses all kinds of molecules, like water molecules, gas molecules, ions, vitamins and a lot more to sustain itself. Passive transport AND active transport will both help in the transport of different substances... Comment on JoyceIsBreathing ジョイス's post “Your body uses all kinds of molecules, like water ...”.
What is facilitated diffusion?
Facilitated diffusion is diffusion that is helped along (facilitated by) a membrane transport channel. These channels are glycoproteins (proteins with carbohydrates attached) that allow molecules to pass through the membrane.
Why is simple diffusion disrupted?
Simple diffusion can be disrupted if the diffusion distance is increased. If the alveoli in our lungs fill with fluid (pulmonary edema), the distance the gases must travel increases, and their transport decreases.
Why is transport regulated?
Transport across a cell membrane is a tightly regulated process, because cell function is highly dependent on maintain strict concentrations of various molecules. When a molecule moves down its concentration gradient is it participating in passive transport; moving up the concentration gradient requires energy making it active transport.
What is the process of moving molecules against their gradient called?
Active Transport. Sometimes the body needs to move molecules against their gradient. This is known as moving “uphill ”, and requires energy from the cell - imagine how much easier it is to shake the trail mix together than it would be to then separate all the pieces again.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
It provides structure for the cell, protects cytosolic contents from the environment, and allows cells to act as specialized units. A membrane is the cell’s interface with the rest of the world - it’s gatekeeper, if you will. This phospholipid bilayer determines what molecules can move ...
Abstract
All cells can take in certain substances and rid themselves of others. Certain cells are capable of taking up a substance at one of their surfaces, transferring it through their cytoplasm, and releasing it from another surface. This entire process is called transcellular transport.
Keywords
These keywords were added by machine and not by the authors. This process is experimental and the keywords may be updated as the learning algorithm improves.
Why do multicellular organisms need transport systems?
They need transport systems to be able to get all of the substances that cells need to the correct place.
How do multicellular organisms take in food?
Multicellular organisms take in food by eating. This is broken down in the digestive system. The dissolved food molecules are transferred into the bloodstream at the small intestine by diffusion and other transport processes. Once the dissolved food molecules are in the bloodstream, they can be transported to all the cells in the body.
What is the system that transports oxygen from the lungs to the bloodstream?
The gaseous exchange system. When we breathe in air, it goes into lungs and oxygen diffuses from the lungs into our bloodstream. The oxygen is then carried around the body by red blood cells in the bloodstream to the cells that need it for respiration.
Which organ processes waste products?
The excretory system. The liver is an organ that processes the body's waste products, for example, urea, which is made when excess amino acids are broken down. Too much urea is toxic so the body must get rid of it. The urea is transported from the liver to the kidneys using the circulatory system.
Where does carbon dioxide go in the body?
At the respiring cells, waste carbon dioxide diffuses into the bloodstream to be taken back to the lungs to be exhaled. Like with the digestive system, the success of the gaseous exchange system relies on the circulatory system.
