
See 7 key topics from this page
What is the energy that cells use to make food?
Cells constantly generate high-energy molecules called ATP from the sugar glucose. ATP is the cellular "food" consumed by the workers—enzymes—within cells. The enzymes use this energy to build biomass or do other cellular work. The more ATP available, the better the microbial workhorses perform in fermentations; at least in principle—many other aspects play a part as well.
Do cells use both pathways?
Furthermore, the investigators showed that cells performing their best actually used both pathways, not only the high yielding one, and that more proteins available meant more efficiency in a given pathway.
What is the cell's energy?
Cellular energy (respiration) Our bodies primarily use sugars broken down from carbohydrates for energy, but if sugar levels drop in the bloodstream, cells use fats and, if needed, proteins. The biochemical pathways responsible for energy are ultimately responsible for the formation of a chemical called adenosine triphosphate (ATP), ...
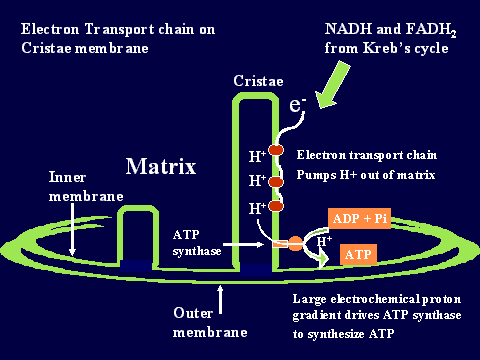
What is the process of producing ATP?
The process of producing these energy-storing molecules is called cellular respiration. The three phases of cellular respiration are: Glycolysis – producing 2 ATP and 2 NADH. The critic acid (TCA) cycle or Kreb’s cycle – producing 2 ATP + 4NADH.
How are fatty acids changed?
As mentioned above, fatty acids are changed via a series of reactions called beta-oxidation into ketones, then acetyl CoA molecules, which enter the Krebs cycle to produce energy molecules. The three main ketones are; Acetone, B-hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate.
How are ketones produced?
Ketones are produced when the body burns fats or proteins to produce energy molecules. They are also produced when there is not enough insulin to help your body use sugar for energy, such as during an uncontrolled type 1-diabetic crisis. As mentioned above, fatty acids are changed via a series of reactions called beta-oxidation into ketones, then acetyl CoA molecules, which enter the Krebs cycle to produce energy molecules. The three main ketones are; Acetone, B-hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate.
What is the process of converting glucose into pyruvic acid?
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway which converts glucose, galactose (from milk), fructose (from fruit) and glycerol (from triglyceride fats) into pyruvic acid. The pyruvic acid generated enters the next stage of cellular respiration known as the Critic acid (otherwise known as the TCA or Krebs cycle). Glycolysis is an oxygen-independent metabolic pathway, meaning it does not use molecular oxygen for any of its reactions. When molecular oxygen is present under normal breathing conditions (aerobic respiration), pyruvic acid enters the Krebs’s Cycle. If no oxygen is available (sprint training or hypoxia due to respiratory illnesses), the process is said to be anaerobic, in which case pyruvic acid is fermented into lactate (lactic acid). Lactic acid can be used as an energy source by heart, but it is generally converted back to pyruvic acid when oxygen becomes available again.
How do fats get stored in the body?
Fats (lipids) are stored in adipose tissue, usually as triglycerides. They are composed of glycerol and fatty acids which can be broken down in a process known as lipogenesis. Eating excess calories leads to more fats being made and stored between muscles and under the skin. Conversely, when we eat less, levels of both blood glucose and insulin fall, and production of a hormone called glucagon increases. This stimulates the release of triglycerides from the adipose stores and its breakdown into glycerol and free fatty acids (FFA). Glycerol then enters glycolysis to produce pyruvic acid which, if oxygen is present, then enters the Krebs cycle. Fatty acids are changed, via a series of reactions called beta-oxidation, into ketones. The enzyme carnitine is important in this process, as it is also increased by glucagon and enhances the utilisation of FFA by increasing their transport into the mitochondria of cells where the conversion to ketones then acetyl CoA occurs. Cells can happily utilise sugar or fatty acid throughout the day depending on the timing of meals and the amount of sugar in the bloodstream.
What happens to glycolysis when blood sugar drops?
Likewise, when blood sugars drop, they switch to fatty acid metabolism, which by-passes glycolysis. In normal conditions, the cell metabolism consumes energy, of which 70% is supplied by OXPHOS.
Which step of glycolysis is phosphorylated?
Glucose is phosphorylated in step 1 of glycolysis to :
How many binding sites does ATP have?
has 2 binding sites (high and low affinity) for ATP
What is the transfer potential of phosphorylation group?
By dehydration, the phosphorylation group transfer potential increases to G=-61.9 kJ/mol (phosphoenolpyruvate)
What is the function of polysaccharides?
a polysaccharide whose function is to store carbohydrates in bodily tissues;
Does glycolysis increase ATP?
glucokinase-driven glycolysis leads to an increased ratio of ATP to ADP (ATP goes up while ADP stays same);
