
Chemical feed pumps work by injecting the selected chemical under pressure into the water stream. The pump draws the liquid solution via the pick-up tube (dotted line in the diagram) and injects it under pressure into the water line on its way to the well's pressure tank. Click to see full answer. Considering this, what is a chemical feed pump?
What is a chemical feed pump?
A chemical feed pump, also known as a chemical dosing pump, is a compact positive displacement pump that injects a precise amount of chemical or other substance into water, gas, or steam. It is typically part of a chemical feed system that comprises a pump or multiple pumps, storage tank, pipes, and control panel.
How does a chemical feed system work?
Thus, chemical feed precisely matches system demand, virtually eliminating the possibility of underfeed or overfeed. Feed verification is another important facet of some computerized feed systems. The actual output of the pump is continuously measured and compared to a computer-calculated setpoint.
What is manual adjustment of a chemical feed pump?
Manual adjustment of a chemical feed pump, based on a boiler water phosphate residual test, is a simple form of feedback control. The accuracy of this method is limited only by the frequency of testing, the time required to affect a change, and the reliability of the monitoring technique.
What is the difference between peristaltic and chemical feed pumps?
Peristaltic and diaphragm are two types of metering pumps. A chemical feed pump, also known as a chemical dosing pump, is a compact positive displacement pump that injects a precise amount of chemical or other substance into water, gas, or steam.
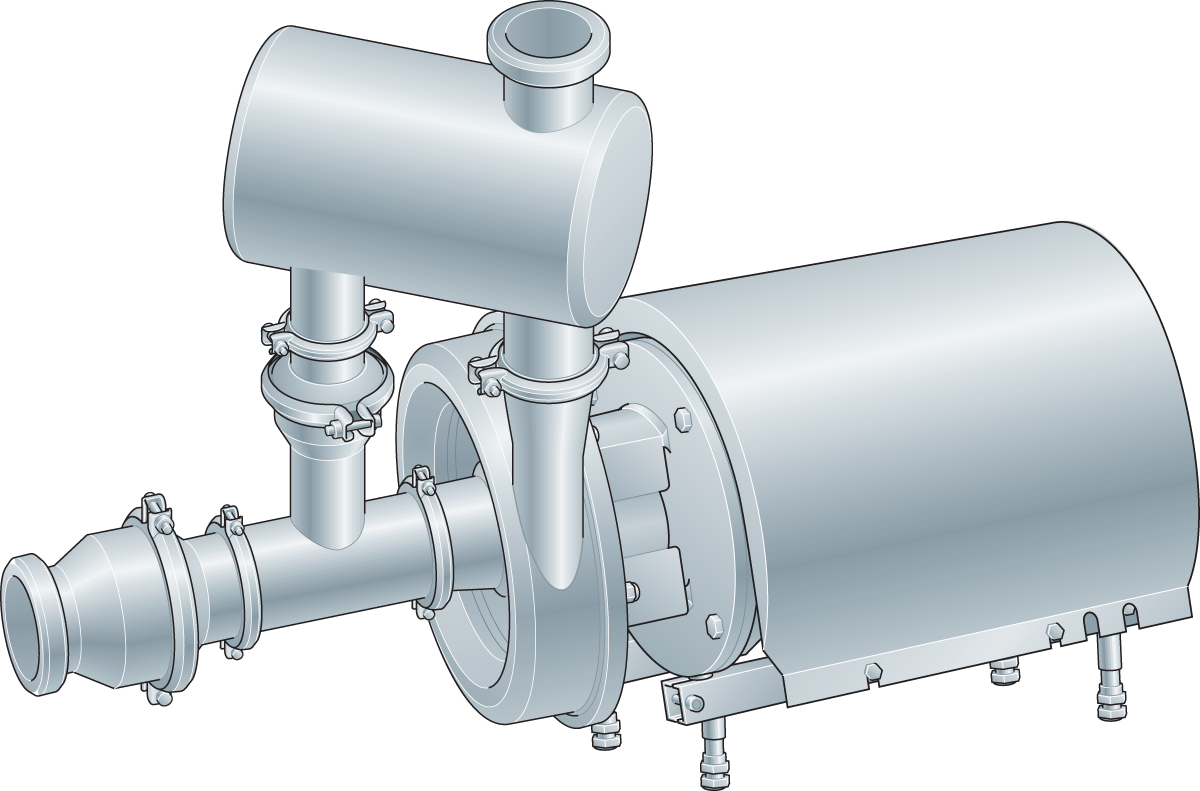
How does a chemical pump work?
A dosing pump draws a measured amount of liquid into its chamber and injects the chemical into a tank or pipe that contains the fluid that is being dosed. It's powered by an electric motor or an air actuator and has a controller that turns the pump on and off and manages the flow rate.
What is a chemical feed pump?
A chemical feed pump, also known as a dosing pump, is a compact positive displacement pump that injects a precise amount of chemical or other substance into water, gas or steam. It is typically part of a chemical feed system that comprises a pump or multiple pumps, storage tank, pipes and control panel.
How do Aquarium dosing pumps work?
Aquarium Dosing Pumps are small fluid pumps that accurately add measured amounts of liquid supplements, foods, and trace elements to an aquarium. Controlled via timers or integrated electronics to ensure they dose the correct amount of fluid at the time specified by the user.
Which pumps are commonly used for chemical dosing?
Gear pumps, piston pumps, peristaltic pumps, and diaphragm type pumps are all available pumps to consider when injecting chemicals.
How do you size a chemical feed pump?
When sizing the pump, the pump should be set 50-70% of its maximum output to maximize efficiency and not overrun pump. The 3 gpd pump would be set to inject 1-1.5 gpd; the 10 gpd would be set to inject at 3-5 gpd. In the example above, our “required feed rate” is 0.41 gpd.
How do chlorine dosing pumps work?
The major part of these pumps is a valve that will suck the chemical liquid from the chemical tank to the pump. The pumps are built with a switch that gives an alarm when the chemical liquid has decreased. With the use of a piston or plunger, the dosing pump forces the fluid from the inlet to the outlet of the pump.
Where should a dosing pump be placed?
Ideally the dosing pump should be mounted above the sump and dosing reservoir in an area that is not prone to splashing or spills. The dosing pump can be mounted vertically or horizontally. When affixing the tubing, take care that the tubing is inserted all the way over the connector until it can go no further.
How do you set up a automatic dosing pump?
0:3310:12Jebao DP-4 Dosing Pump Setup | Beginner Guide To ... - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipYou can set it March. And then you can pick your day once you do that you go ahead and slip theMoreYou can set it March. And then you can pick your day once you do that you go ahead and slip the middle button and then the time here now this is in the 24 hour military. Time style so if.
What is chemical dosing system?
A chemical dosing system is a facility for automated injection of reagents into a wastewater network for the control of septicity and odour emissions. These systems are typically used at pump stations, sewer manholes, and rising mains. However, they can be installed any place where odour containment is required.
Which type of pump is used when chemicals are to be dosed in water treatment plant?
positive displacement pumpA dosing pump is a positive displacement pump designed to transport very precise flow rates of a chemical or other substance into a fluid stream.
Which type of pump is used when chemicals are to be dosed in water treatment plant Mcq?
Positive Displacement Pump10. Which type of pump is used when chemicals are to be dosed in water treatment plant? Explanation: Positive Displacement Pump is used to pump liquids with high viscosity. These are also known as a reciprocating pump.
What is a chemical feed tank?
Chemical Feed Tanks Features Chemical Feed Tanks | For water treatment in closed circulating water systems and boilers Carbon Steel Construction Great for use with chilled water treatment such as cooling systems and hot water treatment in heating systems Helps prolong life of heating and cooling systems.
How does a peristaltic pump work?
Peristaltic Pumps are simple, but can be expensive. They consist of a continuous tube wrapped around a rotating squeegee that pushes fluid through the tube. A motor controls the rotating squeegee. The fluid flow rate is controlled by changing the motor speed.
How is a diaphragm pump controlled?
Diaphragm Pumps are more expensive. They consist of an flexible Diaphragm controlled by a motor through an adjustable stroke rod. The fluid flow rate is controlled by changing motor speed (Diaphragm Stroke Frequency) and changing the Diaphragm Stroke Length (amount of Chemical delivered per Stroke)
What is a solenoid pump?
Solenoid Pumps are the simplest and least expensive type of Metering Pump. They consist of a spring return piston controlled by an electric solenoid. Each time the pump is stroked (solenoid On – Off) a fixed amount fluid is pushed out by the piston. The fluid flow rate is controlled by increasing the stroke frequency.
How are chemicals added to a process?
In a process control application, chemicals are usually added in liquid form at a controlled rate using positive displacement metering pumps. The required chemical pumps are selected based on the strength of the chemicals and the required flow rate.
Can you buy a chemical feed system?
Chemical feed systems can be purchased complete, but they’ re usually purchased as separate components; chemical storage tank, piping, pumps, etc.. Sometimes the system comes on a chemical feed skid. Chemical Feed Pumps are used in many applications with one of three types of positive displacement pumps.
What is a chemical feed system?
Chemical/Mineral feed systems are among the most effective, versatile, and cost-efficient of water treatment devices. Depending on the chemical agent used, the same equipment can treat bacteria, iron, manganese, low pH, hydrogen sulfide (rotten egg smell), and many other water problems. Multiple problems may even be addressed with ...
Why do we need filters?
Filters are sometimes needed to remove the “precipitated” contaminant (iron, for example), or to remove an injected chemical and its by-products after it has done its work. Chlorine, for example, can create some very undesirable spin-off chemicals.
Is chemical feeder system a guarantee?
Below is a brief summary of problems that you might treat with a chemical feeder system. This is not an exhaustive list and it is not a performance guarantee. Here, as with any water treatment strategy, results can depend on many variables. It's often best to get advice before ordering.
Can a Stenner pump feed hydrogen peroxide?
And equipment purchased for one purpose can be easily converted to another. The high quality Stenner peristaltic pump can be used to feed chlor ine or soda ash, for example , but is also capable of feeding hydrogen peroxide without losing its prime. Feed systems are simple to install and to operate.
What is the delivery system in a chemical feed system?
Delivery systems are the heart of a chemical feed system. The delivery system most often used is the chemical metering pump. Nearly 95% of all feed systems use metering pumps. However, gravity feed is gaining popularity in cooling water systems. Eductors are also used occasionally.
Where are chemical feed points in boiler water?
Chemical feed points are usually selected as far upstream in the boiler water circuit as possible. For chemical feed beyond the feedwater pump or into the steam drum, the pump must be matched to the boiler pressure. For high-pressure boilers, proper pump selection is critical.
Why do polymers cak?
Dry Polymers. Dry polymers are susceptible to caking if stored under highly humid conditions. Caking is undesirable because it interferes with the polymer make-down and dilution process. Therefore, dry polymers should be kept in areas of low humidity, and opened containers of dry material should be sealed prior to restorage. In general, polymer products begin to lose their activity after 1 year of storage. Although this process is gradual, it ultimately affects the cost of chemical treatment. It is highly recommended that polymers be used before their expiration dates.
What is a water jet eductor?
The water-jet eductor harnesses the kinetic energy of a moving liquid under pressure. An eductor entrains another liquid, gas, or gas-solid mixture, mixes it with the liquid under pressure, and discharges the mixture against a counterpressure, as shown in Figure 35-10. Application of water-jet eductors is limited by the amount of lift or suction necessary, available motive pressure, and discharge pressure. Generally, a motive-to-discharge pressure ratio of at least 3.5:1 is necessary.
What is feedforward control?
Feedforward control systems are designed to detect changes in chemical demand and compensate for them to keep the system under control. In contrast, feedback control systems react only after a system error is detected. Feedforward control is typically used to adjust corrosion inhibitor feed rate (based on changes in water temperature), chelant feed rate (based on a hardness tests), and coagulant feed rate (based on influent turbidity readings).
What are the components of a steam generator?
As shown in Figure 35-17, a steam generating system includes three major components for which treatment is required: the deaerator, the boiler, and the condensate system. Oxygen scavengers are usually fed to the storage section of the deaerator. The boiler internal treatment is fed to the feedwater pump suction or discharge, or to the steam drum. Condensate system feed points also vary, according to the chemical and the objective of treatment. Typical feed points include the steam header or other remote steam lines. Chemical feed may also be fed directly in combination with internal treatment chemicals or oxygen scavengers.
How are treatment chemicals stored?
Treatment chemicals are usually delivered and stored in one of three ways: bulk, semibulk, and drums. The choice among these three depends on a number of factors, including usage rate, safety requirements, shipping regulations, available space, and inventory needs.
What is metering pump?
But metering pumps are specialty pumps: They’re designed for precision-injection of chemicals, acids, bases, corrosives or viscous liquids and slurries.
What is the driver of a pump?
Driver: The pump is usually driven by an AC constant speed motor. Variable speed, pneumatic, and hydraulic drivers are also utilized. Smaller pumps use solenoid coils as an economic drive mechanism.
What is a series G metering pump?
Available in two motor driven models – the SD and the SG – the Series G Metering Pumps feature rugged aluminum construction specifically engineered to handle higher output and higher pressure applications in harsh environments.
What is the diaphragm connected to?
Sometimes a diaphragm is hydraulically connected. The piston's pumping motion is applied to hydraulic fluid, which causes the diaphragm to flex back and forth as the piston reciprocates. The movement of the piston flexes the diaphragm – the more the diaphragm flexes, the higher the flow rate for the pump.
How does a diaphragm pump work?
They operate by admitting the liquid in and out of the chamber. The driving mechanism is what activates the diaphragm into operation. There are a number of different driving mechanisms that diaphragm pumps may use. The two most common are air operated and motor driven. Air operated diaphragm metering pumps use compressed air to drive ...
How does a peristaltic pump work?
However, they operate quite differently. Peristaltic pumps use rotating rollers to squeeze a flexible tube to move the liquid in a pressurized flow. As the tube is constricted and the low-pressure volume increases, it creates a vacuum that pulls the liquid into the tube. The liquid is then pushed through the tubing as the tubing is constricted at several points by the rollers. With each oscillating or rotating motion, the fluid flows through the tubing. Peristaltic metering pumps are designed as either circular (rotary) or linear.
What is the most commonly used metering pump?
Diaphragm and peristaltic pumps are the most commonly used metering pumps, and they are found to be effective, safe, accurate, and versatile in meeting the needs of the industries where they are used.
Why are diaphragm pumps so reliable?
They are found to be very reliable because they don’t have internal parts that rub together, creating friction and leading to wear and tear. Additionally, because they don’t require seals or lubrication in the pump head, there isn’t a chance of oil vapor contamination or leakage of the media being pumped.
What is an air operated diaphragm pump?
Air operated diaphragm metering pumps use compressed air to drive a double diaphragm (two diaphragms) alternatively. A shuttle valve alternates the air flow between the two diaphragms.
What is a dosing pump?
Metering pumps, also called dosing pumps, are pumps that are designed to dispense specific amounts of fluid and measured flow control. They use expanding and contracting chambers to move the liquids.
How does a vacuum tube work?
As the tube is constricted and the low-pressure volume increases, it creates a vacuum that pulls the liquid into the tube. The liquid is then pushed through the tubing as the tubing is constricted at several points by the rollers. With each oscillating or rotating motion, the fluid flows through the tubing.