- Tectonic plates are 62 miles thick and are made up of the continental crust and the oceanic crust.
- Slab pull is the most relevant force that affects the movement of tectonic plates.
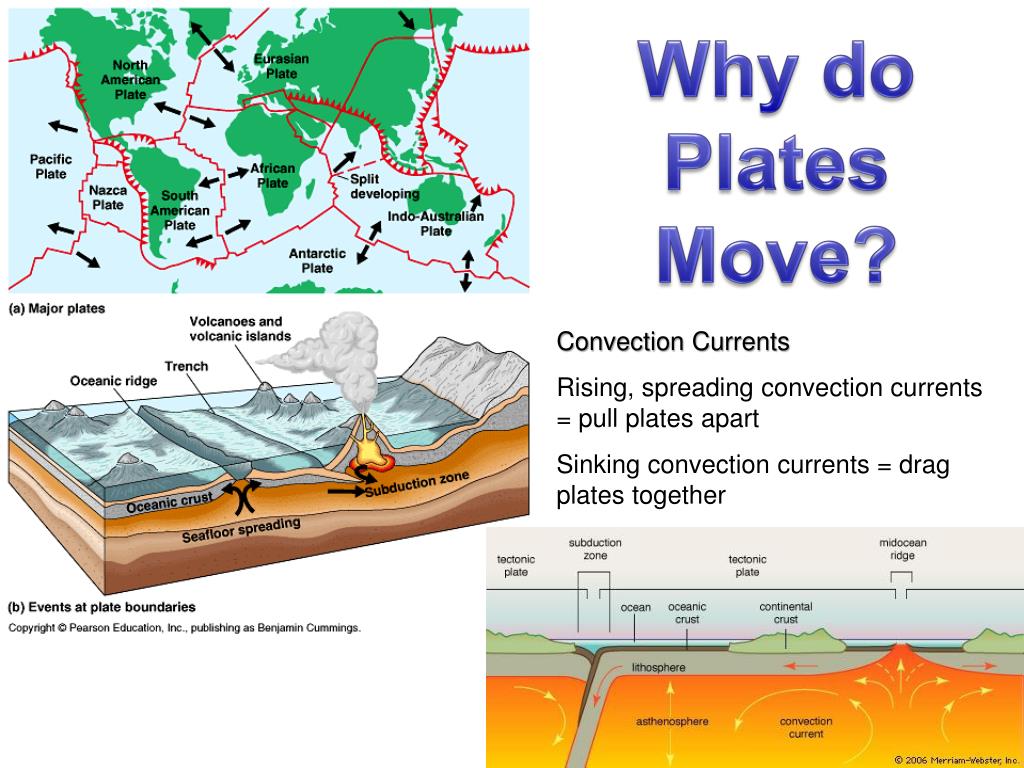
- Convection refers to specific cells within the Earth’s mantle that create heat. The heat makes the solid rocks move upwards while the colder rocks move downwards.
What are convection currents and how do they happen?
Convection currents are flowing fluid that is moving because there is a temperature or density difference within the material. Because particles within a solid are fixed in place, convection currents are seen only in gases and liquids. A temperature difference leads to an energy transfer from an area of higher energy to one of lower energy.
How do convection currents cause the plates to move?
Similarly, why do convection currents cause plates to move? Plates at our planet's surface move because of the intense heat in the Earth's core that causes molten rock in the mantle layer to move. It moves in a pattern called a convection cell that forms when warm material rises, cools, and eventually sink down. As the cooled material sinks down, it is warmed and rises again.
What are some examples of convection currents?
Everyday Examples of Convection
- boiling water - When water boils, the heat passes from the burner into the pot, heating the water at the bottom. ...
- radiator - A radiator puts warm air out at the top and draws in cooler air at the bottom.
- steaming cup of hot tea - The steam you see when drinking a cup of hot tea indicates that heat is being transferred into the air.
What do convection currents do with plate tectonics?
What is the role of convection currents in plate tectonics? Convection currents in the magma drive plate tectonics . Large convection currents in the aesthenosphere transfer heat to the surface, where plumes of less dense magma break apart the plates at the spreading centers, creating divergent plate boundaries.

Where does convection occur on Earth?
In the Earth, this happens in the magma in the mantle. The core heats up the magma and causes a convection current.
What happens when the plates move?
The movement of the plates can lead to volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, tsunamis and mountain-range formation . However, it does take a huge amount of movement in the mantle to move literally the heaviest rocks on Earth, so it's a very slow process, even if the consequences - volcanic eruptions, for example - seem very quick.
What happens when hot molecules move up?
As the hot molecules move up, they cool down and begin to drop. As the cool molecules move down, they heat up and begin to rise. This cycle goes on over and over again, as is known as a convection current. In the Earth, this happens in the magma in the mantle. The core heats up the magma and causes a convection current.
What is the process of rising magma?
Rising magma pushes against and along tectonic plates, which eventually moves the plates together, apart, or along each other.