How does plate tectonics affect the mantle?
Thus, the ability of the Earth to deflect the solar wind when it strikes the Earth’s magnetic field has meant that the planet has been able to protect its atmosphere and sustain life on Earth. Although, this is only possible as a result of plate tectonics, which enables the upper layers of the mantle to cool efficiently.
What causes convection cells in the mantle?
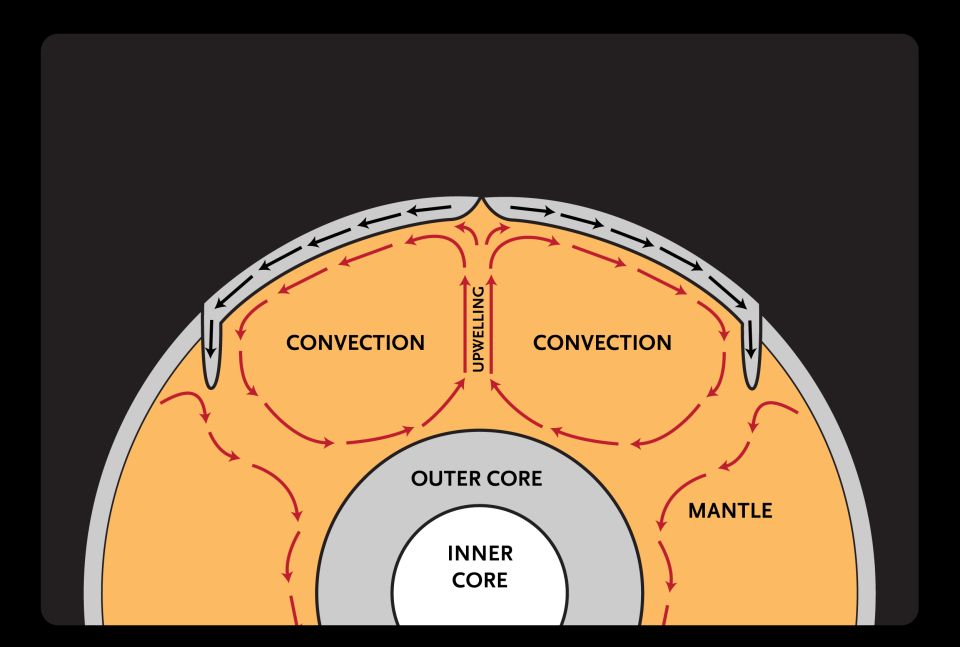
The mantle is heated from below (the core), and in areas that are hotter it rises upwards (it is buoyant), whereas in areas that are cooler it sink down. This results in convection cells in the mantle, and produces horizontal motion of mantle material close to the Earth surface.
What role does the mantle play in plate tectonics?
This flow, called mantle convection, is an important method of heat transport within the Earth. Mantle convection is the driving mechanism for plate tectonics, which is the process ultimately responsible for producing earthquakes, mountain ranges, and volcanos on Earth. What happens when convection currents occur?
What happens during mantle convection?
Mantle convection is the process by which the excess heat in the Earth’s deep interior is transferred to its surface through the fluid-like motions of the rocks in the mantle. Convection occurs in the Earth’s mantle because it is the most efficient way for the Earth to cool or dispose of its deep-seated heat content.

How can convection currents move tectonic plates?
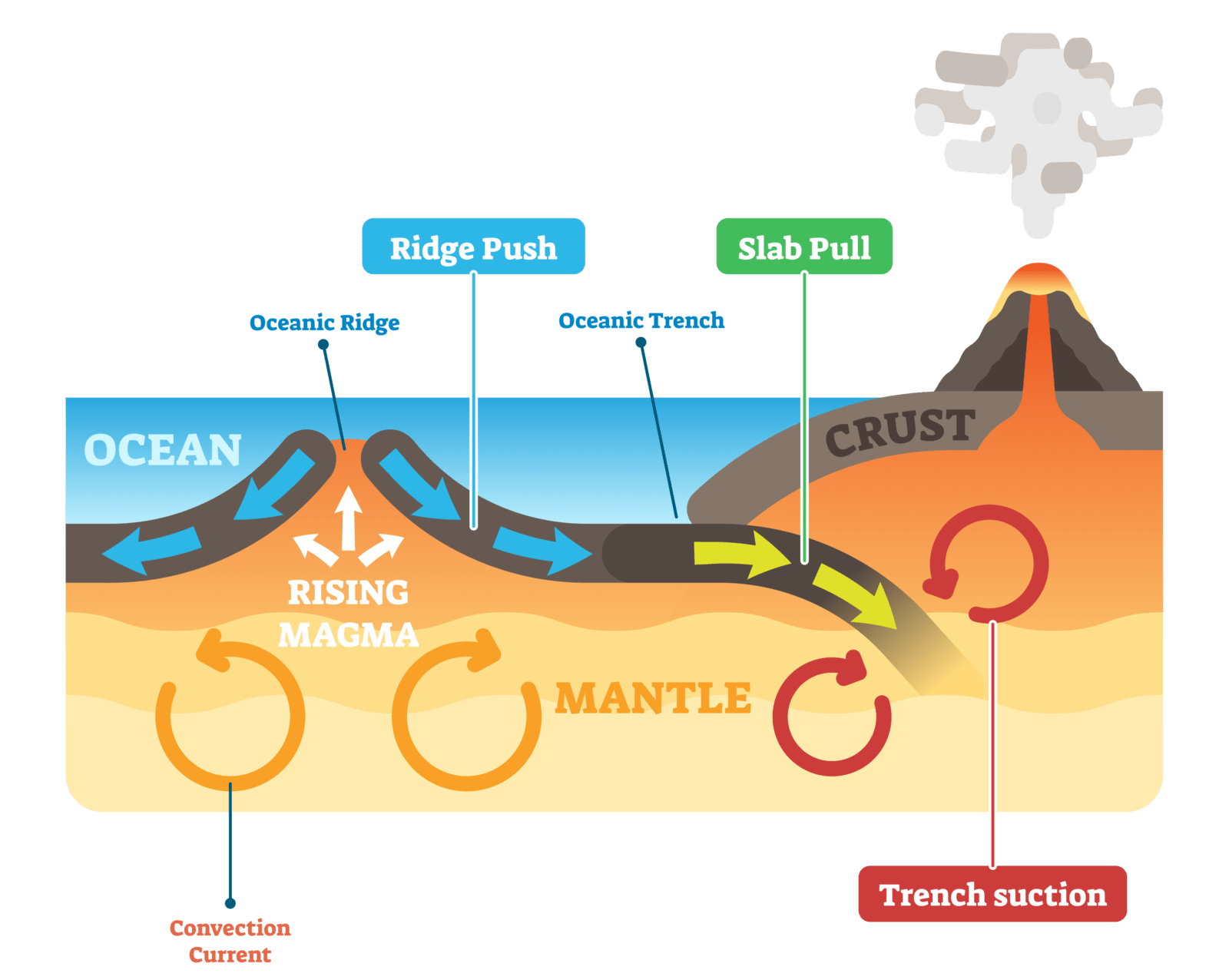
Convection currents drive the movement of Earth's rigid tectonic plates in the planet's fluid molten mantle. In places where convection currents rise up towards the crust's surface, tectonic plates move away from each other in a process known as seafloor spreading (Fig. 7.21).
How do convection currents in the mantle move?
Convection Currents The core's heat energy is transferred to the mantle, causing it to rise towards the Earth's surface, which is cooler. As the heated mantle transfers its heat energy to the lithosphere, it becomes more dense than the surrounding magma and sinks back down towards the core.
What causes tectonic plates to move?
The heat from radioactive processes within the planet's interior causes the plates to move, sometimes toward and sometimes away from each other. This movement is called plate motion, or tectonic shift.
How does a convection current work?
How does convection work? Convection works by areas of a liquid or gas heating or cooling greater than their surroundings, causing differences in temperature. These temperature differences then cause the areas to move as the hotter, less dense areas rise, and the cooler, more dense areas sink.
How does the convection currents within the asthenosphere of the Earth move?
Heat from deep within Earth is thought to keep the asthenosphere malleable, lubricating the undersides of Earth's tectonic plates and allowing them to move. Convection currents generated within the asthenosphere push magma upward through volcanic vents and spreading centres to create new crust.
Do convection currents move oceanic and continental plates?
Complete answer: Convection flows drive the development of Earth's inflexible tectonic plates in the planet's liquid mantle. In spots where convection flows ascend towards the crust surface, tectonic plates move away from one another in a cycle known as seafloor spreading.
What causes mantle convection?
Heat driving the mantle convection comes from two sources—(1) the excess heat from the Earth's formation and (2) heat generated by unstable isotopes such as uranium-238, thorium-232, and potassium-40. These sources produce internal heating, heat from the bulk of the fluid and the base near the Earth's core.
Why are convection currents in the mantle important?
This flow, called mantle convection, is an important method of heat transport within the Earth. Mantle convection is the driving mechanism for plate tectonics, which is the process ultimately responsible for producing earthquakes, mountain ranges, and volcanos on Earth.
Where does convection occur on Earth?
In the Earth, this happens in the magma in the mantle. The core heats up the magma and causes a convection current.
What happens when the plates move?
The movement of the plates can lead to volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, tsunamis and mountain-range formation . However, it does take a huge amount of movement in the mantle to move literally the heaviest rocks on Earth, so it's a very slow process, even if the consequences - volcanic eruptions, for example - seem very quick.
What is the process of rising magma?
Rising magma pushes against and along tectonic plates, which eventually moves the plates together, apart, or along each other.
What happens when hot molecules move up?
As the hot molecules move up, they cool down and begin to drop. As the cool molecules move down, they heat up and begin to rise. This cycle goes on over and over again, as is known as a convection current. In the Earth, this happens in the magma in the mantle. The core heats up the magma and causes a convection current.
How does mantle convection drive plate tectonics?
As mantle convection rises, it breaks apart the Earth to form mid-oceanic ridges (tensional force). When it sinks down, it breaks it apart (com pressional force).
Where does mantle convection occur?
For liquids and gases, the convection cycle can happen because particles can freely flow. But in our rigid lithosphere which is a solid, particles cannot freely move.
Why do convection cells have a circular movement?
Now that we have a source of heat, we know systems always try to go into an equilibrium. For example, hot water will mix with cold water. Actually, this happens in the atmosphere with air temperature.
How does this relate to continental drift?
We know that plate tectonics are moving because of mantle convection. You also know that plates can diverge, converge, or slide across one another.
How does plate tectonics activate volcanoes and earthquakes?
Plate tectonics helps answer what we didn’t know about volcanoes, mountains, and earthquakes.
What causes the greatest mountains in the world?
All the greatest mountains in the world are the result of continents crashing into each other. It’s the tensional and compressional forces from mantle convection that drives plate tectonics. Each continent rides on plate tectonics like a colossal conveyor belt. And they move about 5 to 10 centimeters per year.
What forces break apart the lithosphere?
These tensional and compressional forces are what drives plate tectonics. They break apart the whole lithosphere into 7 major plate tectonics and 12 or so minor ones. Now, that we know mantle convection tears the brittle lithosphere apart which is also called “slab pull”.
What is the term for the movement of the plates and the activity inside the Earth?
Where convection currents converge, plates move towards each other. The movement of the plates, and the activity inside the Earth, is called plate tectonics. Plate tectonics cause earthquakes and volcanoes. The point where two plates meet is called a plate boundary. Earthquakes and volcanoes are most likely to occur either on or near plate ...
Why does the Earth's crust move?
The crust moves because of movements deep inside the earth. Heat rising and falling inside the mantle creates convection currents generated by radioactive decay in the core. The convection currents move the plates. Where convection currents diverge near the Earth's crust, plates move apart.