What is the mechanism of action of echinocandins?
Mechanism of action. Echinocandins noncompetitively inhibit beta-1,3-D-glucan synthase enzyme complex in susceptible fungi to disturb fungal cell glucan synthesis. Beta-glucan destruction prevents resistance against osmotic forces, which leads to cell lysis.
What are echinocandins made of?
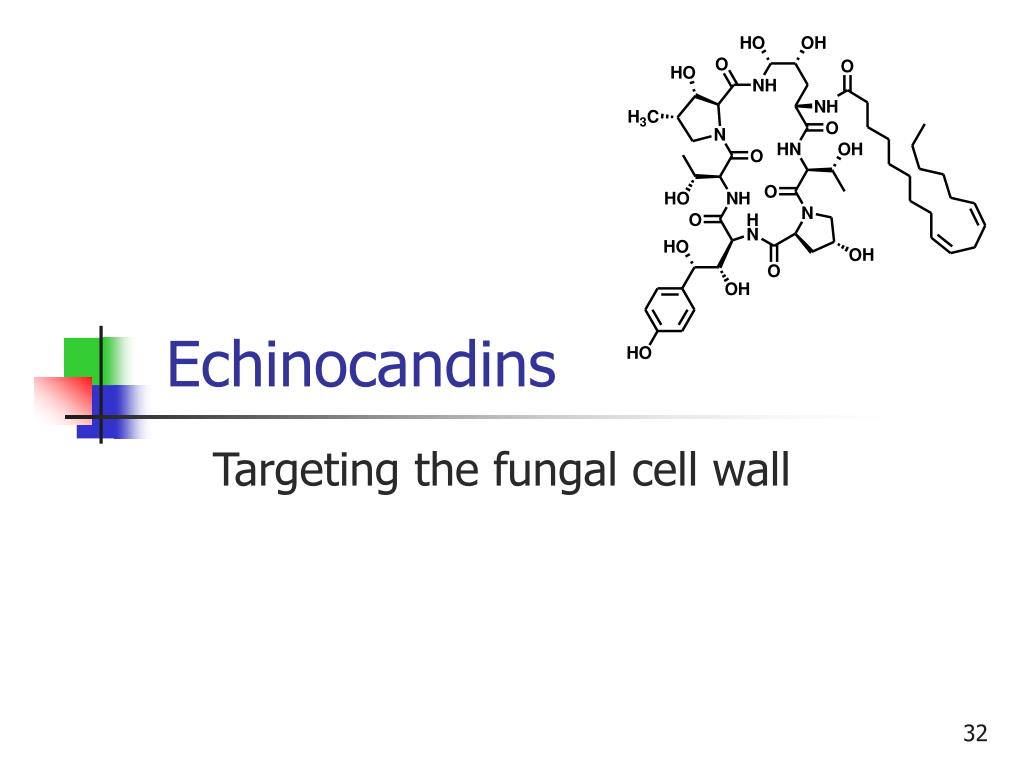
Echinocandins are a group of semisynthetic, cyclic lipopeptides with an N-linked acyl lipid side chain. The drugs in the class are: caspofungin, micafungin and anidulafungin.
Are echinocandins excreted from the kidneys?
All echinocandins have poor oral bioavailability and are administered only by the intravenous route. Since none of the drugs are excreted solely by the kidneys, the dose need not be altered in renal impairment.
Is echinocandin a penicillin?
Echinocandin. The class has been termed the " penicillin of antifungals," along with the related papulacandins, as their mechanism of action resembles that of penicillin in bacteria. β-glucans are carbohydrate polymers that are cross-linked with other fungal cell wall components, equivalent to bacterial peptidoglycan.

How do echinocandins work to fight off fungal infections?
The echinocandins are a new class of antifungals, developed in response to the need for safe and effective antifungals for the treatment of invasive fungal infections. These agents work by inhibiting 1,3-beta-d-glucan synthase, an enzyme essential for production of cell walls in select fungi.
What is the mechanism of action of echinocandins?
The echinocandins have a unique mechanism of action, inhibiting beta-(1,3)-D-glucan synthase, an enzyme that is necessary for the synthesis of an essential component of the cell wall of several fungi. The echinocandins display fungistatic activity against Aspergillus spp.
How are echinocandins administered?
Pharmacokinetics. Oral absorption of echinocandins is limited and they are given only by intravenous infusion. They have high affinity for plasma proteins and their distribution into the CSF is poor. Elimination is by hepatic metabolism or slow spontaneous degradation with very long half-lives up to 40–50 hours.
What are examples of echinocandins?
Echinocandins are a group of semisynthetic, cyclic lipopeptides with an N-linked acyl lipid side chain. The drugs in the class are: caspofungin, micafungin and anidulafungin.
What is the mode of action of terbinafine?
Mechanism: Terbinafine has a fungicidal effect by inhibiting the enzyme squalene monooxygenase which is involved in the synthesis of sterol in fungi. This inhibits fungal sterol biosynthesis by decreasing ergosterol levels.
How does amphotericin B work?
Amphotericin B injection is used to treat serious and potentially life-threatening fungal infections. Amphotericin B injection is in a class of medications called antifungals. It works by slowing the growth of fungi that cause infection.
What are the side effects of echinocandins?
Side effects of echinocandin antifungals may include:Facial flushing (temporary reddening of the skin because of dilation of blood vessels beneath the skin)Severe rash.Itching.Fever.Thrombophlebitis (inflammation of a vein, usually in the leg)Hepatitis (inflammation of the liver)
Are echinocandins oral?
The chains act as anchors on the fungal cell membrane to facilitate antifungal activity. Due to their limited oral bioavailability, echinocandins are administered through intravenous infusion.
Is echinocandins a fungicide?
The major advantage of echinocandins relative to other antifungal agents is their fungicidal activity against Candida spp, including fluconazole-resistant C. glabrata and C.
Is itraconazole an antibiotic?
Itraconazole is an antifungal medication that is used in adults to treat infections caused by fungus. This includes infections in any part of the body including the lungs, mouth or throat, toenails, or fingernails.
What is the mechanism of action of griseofulvin?
Griseofulvin is fungistatic, however the exact mechanism by which it inhibits the growth of dermatophytes is not clear. It is thought to inhibit fungal cell mitosis and nuclear acid synthesis. It also binds to and interferes with the function of spindle and cytoplasmic microtubules by binding to alpha and beta tubulin.
Is griseofulvin an antifungal?
Griseofulvin belongs to the group of medicines called antifungals. It is used to treat fungus infections of the body, feet, groin and thighs, scalp, skin, fingernails, and toenails.
What are some examples of echinocandins?
Examples. List of echinocandins: Pneumocandins (cyclic hexapeptides linked to a long-chain fatty acid) Echinocandin B not clinically used, risk of hemolysis. Cilofungin withdrawn from trials due to solvent toxicity. Caspofungin (trade name Cancidas, by Merck) Micafungin (FK463) (trade name Mycamine, by Astellas Pharma.)
What is echinocandin B?
Jump to navigation Jump to search. Group of chemical compounds. Echinocandin B. Echinocandins are a class of antifungal drugs that inhibit the synthesis of β-glucan in the fungal cell wall via noncompetitive inhibition of the enzyme 1,3-β glucan synthase.
What is caspofungin used for?
Caspofungin is used in the treatment of febrile neutropenia and as "salvage" therapy for the treatment of invasive aspergillosis. Micafungin is used as prophylaxis against Candida infections in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation patients.
What is the penicillin of antifungals?
The class has been termed the " penicillin of antifungals," along with the related papulacandins, as their mechanism of action resembles that of penicillin in bacteria. β-glucans are carbohydrate polymers that are cross-linked with other fungal cell wall components, the fungal equivalent to bacterial peptidoglycan.
Does Caspofungin interfere with ciclosporin?
Caspofungin has some interference with ciclosporin metabolism, and micafungin has some interference with sirolimus (rapamycin), but anidulafungin needs no dose adjustments when given with ciclosporin, tacrolimus, or voriconazole.
Is caspofungin linear or triphasic?
Caspofungin has triphasic nonlinear pharmacokinetics, while micafungin (hepatically metabolized by arylsulfatase, catechol O-methyltransferase, and hydroxylation) and anidulafungin (degraded spontaneously in the system and excreted mostly as a metabolite in the urine) have linear elimination.
Does Candida spp have echinocandin resistance?
Echinocandin resistance is rare among Candida spp. However, case studies have shown some resistance in C. albicans, C. glabrata, C. lusitaniae, C. tropicalis, and C. parapsilosis. Resistance patterns include alterations in the glucan synthase (Fks1-Fks2 complex), overexpression of efflux pumps, strengthening of cell wall by increased chitin production, upregulation of stress-response pathways, and dysregulation of mismatch repair pathways. In addition a few species and strains of Candida spp. and Aspergillus spp. show a "paradoxic effect", i.e., they are susceptible to low concentrations but resistant to high concentrations in broth microdilution studies.
What is the role of echinocandin in fungi?
The echinocandin antifungal agents act by inhibiting the synthesis of 1,3-β-d -glucan. Along with 1,6-β- d -glucan, chitin (a polymer of N -acetyl glucosamine), and cell wall proteins, 1,3-β- d -glucan is one of the fibrillar and interwoven macromolecules that form the fungal cell wall. 189 1,3-β- d -glucans are the predominant component of the cell wall of the ascomycetous fungi, provide much of the rigidity of the wall, and are synthesized by a transmembrane glucan synthase complex. Although the precise mechanism of action is unknown, the echinocandins inhibit the functioning of this complex (see Fig. 39-2 ). Disruption of 1,3-β- d -glucan synthesis leads to reduced wall integrity, abnormal cell morphology, and finally cell rupture and death. To date, in studies of echinocandins as therapy for candidiasis, the principal pharmacodynamic driver of in vivo response has been the ratio of the peak achieved concentration to the MIC. 9
What is the drug used for candidiasis?
The echinocandin antifungal agents, caspofungin , micafungin, and anidulafungin, inhibit the synthesis of 1,3-β-d-glucan in the fungal cell wall.218-222 Caspofungin has been used effectively for treatment of candidiasis and invasive aspergillosis refractory to other antifungal drugs. 218,222 The echinocandins have activity against species of Candida that are resistant to fluconazole and other azoles, but are not active against Cryptococcus. 218-222 Caspo fungin , micafungin, and anidulafungin are currently available only in an intravenous formulation and are generally well tolerated. Although initial studies suggested an increased risk for hepatotoxicity when caspofungin is used concomitantly with cyclosporine, subsequent clinical experience suggests that the drug can be safely used with cyclosporine or tacrolimus. 219,220 Although the pharmacokinetics of caspofungin is unaltered by coadministration of tacrolimus, caspo fungin may reduce tacrolimus concentrations by up to 20%. Additionally, caspofungin concentrations may be increased by cyclosporine up to 35%. Thus additional monitoring of cyclosporine and tacrolimus is warranted with coadministration of caspofungin. These interactions have not been reported with micafungin or anidulafungin. 221,222
Is echinocandin an antifungal?
This echinocandin antifungal is the first of its kind to be approved and is only available for intravenous use. It can be used by itself or with liposomal amphotericin B, or with voriconazole for refractory invasive aspergillosis and candidiasis in immunosuppressed patients282,292-294; however, it is not an effective agent in the treatment of cryptococcus infection. The drug inhibits fungal cell wall β- (1,3)-glucan synthesis. It appears to be metabolized by hepatic P450s and may inhibit CYP3A4. 295 Caution is therefore required when it is used with cyclosporin A 296 and other calcineurin inhibitors. However, nelfinavir did not alter its pharmacokinetics. 297 Because of a paradoxic loss of efficacy against Candida spp. at high concentrations, 295 it may best be used for complicated infections in combination with other drugs. Because phase 1 and 2 trials commonly reported elevated levels of liver enzymes, 292 its long-term safety and incidence of hepatotoxicity are still to be determined.
Is echinocandin a class C drug?
The echinocandins as a group have been classified as pregnancy class C drugs (Drugs@FDA, n.d. ). For each, this designation is largely based on animal studies demonstrating that fetal harm may occur; and for each, there is a lack of sufficient data in pregnant women to adequately establish and/or inform the risk of adverse effects to human embryo and fetal development. Each of the echinocandins is secreted in the milk of lactating rats, but data does not exist to confirm this in humans. Even if present, echinocandins are not absorbable through the gastrointestinal tract, and thus would not be expected to produce a systemic exposure in a breast-feeding infant. That being said, local effects on the infant׳s gastrointestinal microbiome are plausible. Therefore, a risk: benefit analysis based on the benefits of breastfeeding, the mother׳s clinical need for echinocandin therapy, potential alternative therapies, and risk of echinocandin gastrointestinal exposure by the infant should be considered.
Is caspofungin a monotherapy?
Several case series and additional retrospective observational reports show that caspofungin may be effective as “salvage” therapy either as monotherapy, or in combination with other agents in patients with Pneumocystis pneumonia who are not responding to, or who are intolerant of, first-line therapy ( Armstrong-James et al., 2010; Zhang et al., 2018a) There are no prospective evaluations of caspofungin monotherapy against TMP-SMX, clindamycin with primaquine, or other regimens as first-line therapy for HIV-associated or non-HIV-associated Pneumocystis pneumonia. The efficacy of other echinocandins (i.e. micafungin and anidulafungin) against Pneumocystis is currently unknown, but case reports of successful treatment have been described ( Chang et al., 2018 ).
What are Echinocandins?
Echinocandins are a class of antifungal drugs that target the fungal cell wall. They are lipopeptide molecules that noncompetitively inhibit (1,3) beta-d-glucan synthase enzyme. This enzyme forms glucan, a major component of the fungal cell wall therefore by inhibiting its synthesis fungal cell walls are damaged.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
What are some examples of echinocandins?
They inhibit an enzyme that’s involved in the making of the fungal cell wall. Some examples of echinocandins are: Anidulafungin: mucosal and invasive Candida infections. Caspofungin: mucosal and invasive Candida infections, aspergillosis.
What are the structures that are commonly targeted by antifungal drugs?
Two structures that are commonly targeted are the fungal cell membrane and the fungal cell wall.
What is the antifungal drug that prevents the growth of fungal cells?
There are also some other types of antifungal medications. These have mechanisms different from the types we’ve discussed above. Flucytosine is an antifungal that prevents the fungal cell from making nucleic acids and proteins. Because of this, the cell can no longer grow and thrive.
How are antifungal drugs given?
Antifungal drugs are very diverse. They can be given orally, as a topical treatment, or via IV. How an antifungal drug is given depends on factors like the specific drug, the type of infection you have, and the severity of your infection. Antifungal drugs are classified by their chemical structure as well how they work.

Overview
Echinocandins are a class of antifungal drugs that inhibit the synthesis of β-glucan in the fungal cell wall via noncompetitive inhibition of the enzyme 1,3-β glucan synthase. The class has been termed the "penicillin of antifungals," along with the related papulacandins, as their mechanism of action resembles that of penicillin in bacteria. β-glucans are carbohydrate polymers that are cross-linke…
Medical uses
Drugs and drug candidates in this class are fungicidal against some yeasts (most species of Candida, but not Cryptococcus, Trichosporon, and Rhodotorula). Echinocandins also have displayed activity against Candida biofilms, especially in synergistic activity with amphotericin B and additive activity with fluconazole. Echinocandins are fungistatic against some molds (Aspergillus, but not Fusarium and Rhizopus), and modestly or minimally active against dimorphic …
Side effects
All three agents are well-tolerated, with the most common adverse effects being fever, rash, nausea, and phlebitis at the infusion site. They can also cause a histamine-like reaction (flushing) when infused too rapidly. Toxicity is uncommon. Its use has been associated with elevated aminotransferases and alkaline phosphatase levels.
Chemistry
The present-day clinically used echinocandins are semisynthetic pneumocandins, which are chemically lipopeptide in nature, consisting of large cyclic hexapeptoids. Caspofungin, micafungin, and anidulafungin are similar cyclic hexapeptide antibiotics linked to long modified N-linked acyl fatty acid chains. The chains act as anchors on the fungal cell membrane to facilitate an…
Mechanism of action
Echinocandins noncompetitively inhibit beta-1,3-D-glucan synthase enzyme complex in susceptible fungi to disturb fungal cell glucan synthesis. Beta-glucan destruction prevents resistance against osmotic forces, which leads to cell lysis. They have fungistatic activity against Aspergillus species. and fungicidal activity against most Candida spp., including strains that are resistant to fluconazole. In vitro and mouse models show echinocandins may also enhance hos…
Resistance
Echinocandin resistance is rare among Candida spp. However, case studies have shown some resistance in C. albicans, C. glabrata, C. lusitaniae, C. tropicalis, and C. parapsilosis. Resistance patterns include alterations in the glucan synthase (Fks1-Fks2 complex), overexpression of efflux pumps, strengthening of cell wall by increased chitin production, upregulation of stress-response pathways, and dysregulation of mismatch repair pathways. In addition a few species and strain…
Pharmacokinetics
Due to the large molecular weight of echinocandins, they have poor oral bioavailability and are administered by intravenous infusion. In addition, their large structures limit penetration into cerebrospinal fluid, urine, and eyes. In plasma, echinocandins have a high affinity to serum proteins. Echinocandins do not have primary interactions with CYP450 or P-glycoprotein pumps. Caspofungin has triphasic nonlinear pharmacokinetics, while micafungin (hepatically metaboliz…
Interference
Caspofungin has some interference with ciclosporin metabolism, and micafungin has some interference with sirolimus (rapamycin), but anidulafungin needs no dose adjustments when given with ciclosporin, tacrolimus, or voriconazole.