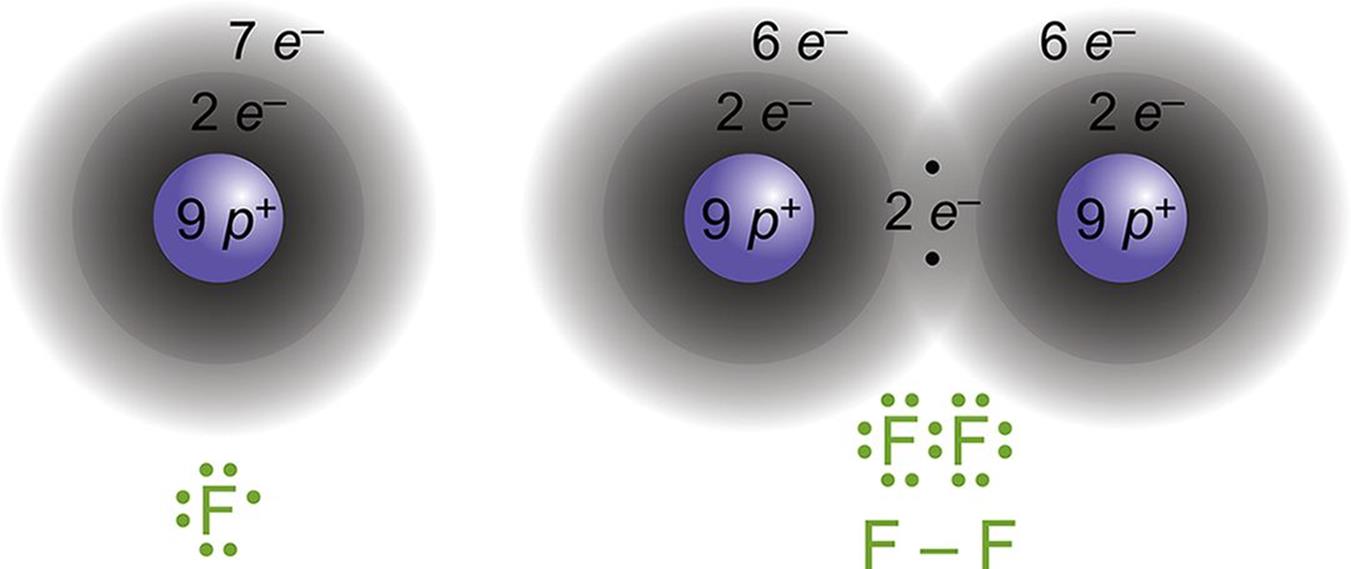
The nature of the covalent bond (ESABU) By overlapping orbitals, the outer energy shells of all the bonding atoms are filled. The shared electrons move in the orbitals around both atoms. As they move, there is an attraction between these negatively charged electrons and the positively charged nuclei.
What elements are involved in covalent bonds?
Some of the properties of covalent bonds are:
- Covalent bonding does not result in the formation of new electrons. ...
- They are very powerful chemical bonds that exist between atoms.
- A covalent bond normally contains the energy of about ~80 kilocalories per mole (kcal/mol).
- Covalent bonds rarely break spontaneously after it is formed.
Why do covalent bonds have a low melting point?
Why does covalent bonding have low melting point? Covalent molecular They have low melting points and boiling points because the attractions between molecules are easy to overcome. They do not conduct electricity because there are no free charges to move. Some covalent molecular compounds have higher melting points than expected.
Which Bond is stronger ionic or covalent?
Ionic bonds are stronger than covalent bonds, because there is a stronger attraction between ions that have opposite charges, which is why it takes a lot of energy to separate them. Covalent bonds are bonds that involve the sharing of electron pairs between atoms.
Why are covalent bonds the strongest?
Ionic bond examples include:
- LiF - Lithium Fluoride.
- LiCl - Lithium Chloride.
- LiBr - Lithium Bromide.
- LiI - Lithium Iodide.
- NaF - Sodium Fluoride.
- NaCl - Sodium Chloride.
- NaBr - Sodium Bromide.
- NaI - Sodium Iodide.

How do electrons move in ionic bonding?
In ionic bonding, electrons are completely transferred from one atom to another. In the process of either losing or gaining negatively charged electrons, the reacting atoms form ions. The oppositely charged ions are attracted to each other by electrostatic forces, which are the basis of the ionic bond.
How do electrons move in a molecule?
As a rule, electrons will flow from atomic centers high in electron density to atomic centers low in electron density. This dependence on polarity is similar to the way that electricity flows in an electric circuit. If there is no difference in electrical potential between the ends of a wire, electricity will not flow.
Do shared electrons revolve?
Electrons do not revolve; rather, they occupy certain atomic orbitals. To put it simply, they just stay there, delocalized over some space around the nucleus, everywhere at once.
Do electrons move from negative to positive?
Electron Flow is what actually happens and electrons flow out of the negative terminal, through the circuit and into the positive terminal of the source.
How do electrons actually move around the nucleus?
Like gravity acting on planets, an electromagnetic force attracts the orbiting electron to the nucleus. Classical physicists wondered that the electron didn't run out of energy. Niels Bohr solved this mystery by introducing quanta, discrete energy states in which electrons may stably persist.
How do electrons spin in an orbital?
3:329:15Understanding Electron Spin in an Orbital - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo make sure you this idea is clear that if two electrons have opposite spins or opposite magneticMoreSo make sure you this idea is clear that if two electrons have opposite spins or opposite magnetic fields. The two electrons can possibly attract each other if they have the same spin then the Fields.
Why do electrons revolve?
Solution : The electrostatic force between electrons and nucleus provides the centripetal force to the electron to make it move around the nucleus.
What keeps electrons in orbit around the nucleus?
Electrons are kept in the orbit around the nucleus by the electromagnetic force, because the nucleus in the center of the atom is positively charged and attracts the negatively charged electrons.
What causes movement of electrons during chemical reaction?
Snapshot of an electron The first weak ultraviolet pulse sets the electrons in motion. The second strong infrared pulse then removes an electron from the molecule, accelerates it and drives it back to the molecule.
Why are electrons always moving?
Because an electron is a quantum object with wave-like properties, it must always be vibrating at some frequency.
What are moving electrons called?
The directional movement of electrons between atoms is called electrical current. Amperage is a term used to describe the number of electrons moving past a fixed point in a conductor in one second. Current is measured in units called amperes or amps.
How can electrons in an atom move from one energy level to another?
How can electrons in an atom move from one energy level to another? To move from one energy level to another, an electron must gain or lose just the right amount of energy. Electrons are said to be quantized because they need a quantum of energy to move to a different sublevel.
How many electrons do atoms need to form a covalent bond?
Atoms form covalent bonds as a result of the Octet Rule. The Octet Rule states that all atoms in a molecule need to have eight electrons in their valence shell. This rule can be satisfied by sharing, losing or gaining electrons. A covalent bond allows atoms to satisfy the Octet Rule via sharing.
Why do atoms share electrons?
Atoms share their electrons in order to completely fill up their outer-most layer — the valence shell. Two atoms that are covalently bonded have less energy than the individual atoms, making the bonded atoms more stable. Atoms form covalent bonds as a result of the Octet Rule.
What is the measure of the tendency of an atom to attract electrons?
Electronegativity measures the tendency of an atom to attract electrons. Atoms with similar electronegativities are more willing to share electrons than those with different electronegativities . Up to three covalent bonds can form at one time in a molecule. In a single bond, one pair of electrons is shared between two atoms.
Which type of bond is the least stable?
A double bond shares two pairs of electrons; it is stronger than a single bond, but it also creates a less stable molecule because it is more reactive. The triple bond shares three pairs of electrons, making it the least stable covalent bond. ADVERTISEMENT.