
Why does a hormone affect only a target cell?
The hormones dissolve in plasma and travel the circulatory pathways through various body tissues. So why do hormones affect only their target cells in particular tissues? Because only those target cells have receptors for that particular hormone. Some hormones bind to receptors on the surface of target cells.
What is the relationship between a hormone and target cell?
Most hormones circulate in blood, coming into contact with essentially all cells. However, a given hormone usually affects only a limited number of cells, which are called target cells. A target cell responds to a hormone because it bears receptors for the hormone. In other words, a particular cell is a target cell for a hormone if it contains functional receptors for that hormone, and cells which do not have such a receptor cannot be influenced directly by that hormone.
Why do hormones attach to specific target cells?
Unlike steroid hormones, lipid insoluble hormones do not directly affect the target cell because they cannot enter the cell and act directly on DNA. Binding of these hormones to a cell surface receptor results in activation of a signaling pathway; this triggers intracellular activity and carries out the specific effects associated with the hormone.
What makes a cell a target of a particular hormone?
What makes a cell a target of a particular hormone? the presence of a receptor for that particular hormone. The neurohypophysis (posterior pituitary) secrets. ... ___ has more target cells in the body than any of the others. Growth hormone (GH) Target organs most often regulate the pituitary gland via.
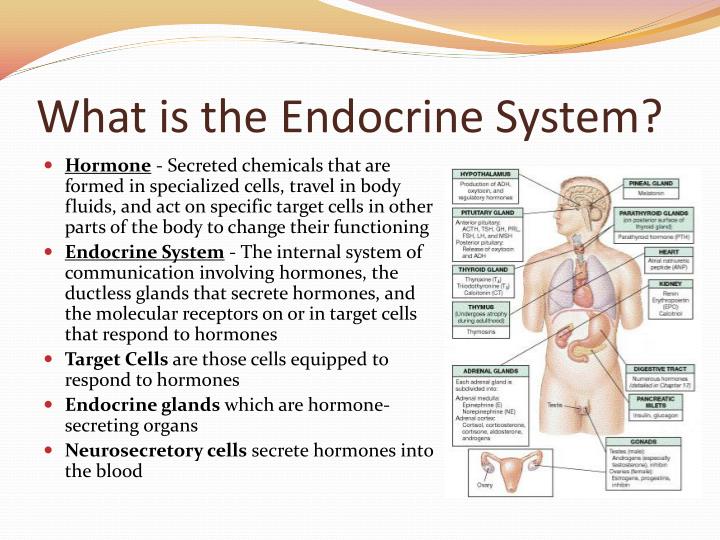
How do hormones effect target cells?
Hormones influence gene expression by binding DNA in a cell's nucleus. That is, hormones turn on certain genes that are preprogrammed to make specific proteins. These proteins cause a cell to respond in a new way (grow, secrete, metabolize, etc.).
What are the three basic ways hormones act on their target cells?
List the three basic ways hormones act on their target cells.Alter the rate of enzymatic reactions,control transport of molecules into and out of cells, or.change gene expression and protein synthesis in target cells.
How do hormones act on specific target cells quizlet?
-a given hormone affects only specific target cells. -Hormones, like neurotransmitters, influence their target cells by chemically binding to specific protein receptors. Phenomenon in which there is a decrease in the number of receptors in response to an excess of a hormone or neurotransmitter.
How do hormones control cells?
Endocrine glands release hormones into the bloodstream. This lets the hormones travel to cells in other parts of the body. The endocrine hormones help control mood, growth and development, the way our organs work, metabolism , and reproduction. The endocrine system regulates how much of each hormone is released.
What are the three ways hormones can interact?
The three most common types of interaction are as follows:The permissive effect, in which the presence of one hormone enables another hormone to act. ... The synergistic effect, in which two hormones with similar effects produce an amplified response. ... The antagonistic effect, in which two hormones have opposing effects.
What are 3 hormones and their functions?
Endocrine system hormonesHormoneSecreting gland(s)Functionglucagonpancreashelps increase levels of blood glucose (blood sugar)insulinpancreashelps reduce your blood glucose levelsluteinizing hormone (LH)pituitarycontrols estrogen and testosterone production as well as ovulationmelatoninpinealcontrols sleep-wake cycles12 more rows
What are the three 3 classes of hormones and be able to provide an example for each?
There are three major types of hormones. Protein hormones (or polypeptide hormones) are made of chains of amino acids. An example is ADH (antidiuretic hormone) which decreases blood pressure. Steroid hormones are derived from lipids. ... Amine hormones are derived from amino acids.
What are 3 examples of bodily functions that hormones regulate quizlet?
Hormones control chemical reactions, help regulate water balance, growth, reproductive cycles, and digestive processes. Endocrine glands secrete chemicals called hormones into the blood.
What happens when a receptor becomes bound to a hormone?
More specifically, when a receptor becomes bound to a hormone, it undergoes a conformational change which allows it to interact productively with other components of the cells, leading ultimately to an alteration in the physiologic state of the cell.
How do hormones affect the cell?
Many hormones affect their target cells by inducing such transitions, usually causing an activation of one of more enzymes. Because enzymes are catalytic and often serve to activate additional enzymes, a seemingly small change induced by hormone-receptor binding can lead to widespread consequences within the cell.
What are chemical messengers that invoke profound changes within target cells?
Hormones are chemical messengers that invoke profound changes within target cells. How is this accomplished? There are two fundamental mechanisms by which such changes occur:
How does stimulation of gene expression affect a cell's phenotype?
Modulation of gene expression: Stimulating transcription of a group of genes clearly can alter a cell's phenotype by leading to a burst of synthesis of new proteins. Similarly, if transcription of a group of previously active genes is shut off, the corresponding proteins will soon disappear from the cell.
How does receptor binding affect the body?
Receptor binding alters cellular activity and results in an increase or decrease in normal body processes. Depending on the location of the protein receptor on the target cell and the chemical structure of the hormone, hormones can mediate changes directly by binding to intracellular hormone receptors and modulating gene transcription, ...
What are intracellular hormone receptors?
Intracellular Hormone Receptors. Lipid-derived (soluble) hormones such as steroid hormones diffuse across the membranes of the endocrine cell. Once outside the cell, they bind to transport proteins that keep them soluble in the bloodstream.
How do hormones work?
Discuss the role of different types of hormone receptors. Hormones mediate changes in target cells by binding to specific hormone receptors. In this way, even though hormones circulate throughout the body and come into contact with many different cell types, they only affect cells that possess the necessary receptors.
Why are heat shock proteins called HSP?
Heat shock proteins (HSP) are so named because they help refold misfolded proteins. In response to increased temperature (a “heat shock”), heat shock proteins are activated by release from the NR/HSP complex. At the same time, transcription of HSP genes is activated.
What is the term for the increase in the number of receptors in response to rising hormone levels?
When the number of receptors decreases in response to rising hormone levels, called down-regulation, cellular activity is reduced.
What is the second messenger of a hormone?
One very important second messenger is cyclic AMP (cAMP). When a hormone binds to its membrane receptor, a G-protein that is associated with the receptor is activated; G-proteins are proteins separate from receptors that are found in the cell membrane. When a hormone is not bound to the receptor, the G-protein is inactive and is bound to guanosine diphosphate, or GDP. When a hormone binds to the receptor, the G-protein is activated by binding guanosine triphosphate, or GTP, in place of GDP. After binding, GTP is hydrolysed by the G-protein into GDP and becomes inactive.
How do receptors affect hormones?
The number of receptors that respond to a hormone determines the cell’s sensitivity to that hormone, and the resulting cellular response.
