
To configure a DNS zone for secure zone transfer, change the zone transfer setting to the option to allow zone transfers to specific IP addresses by performing the following actions:
- In the DNS Manager, right-click the name of the DNS zone and click Properties.
- On the Zone Transfers tab, click Allow zone transfer.
- Select Only to the following servers.
- Click Edit, then in the IP addresses of the secondary servers list, enter the IP addresses of the servers you wish to specify.
- When you have entered all the required IP addresses, click OK.
- In the DNS Manager, right-click the name of the DNS zone and click Properties.
- On the Zone Transfers tab, click Allow zone transfer.
- Select Only to the following servers.
- Click Edit, then in the IP addresses of the secondary servers list, enter the IP addresses of the servers you wish to specify.
What is DNS zone and how does it work?
A DNS zone is an administrative space which allows for more granular control of DNS components, such as authoritative nameservers. The domain name space is a hierarchical tree, with the DNS root domain at the top. A DNS zone starts at a domain within the tree and can also extend down into subdomains so that multiple subdomains can be managed by one entity.
How to create a DNS forward lookup zone?
Create a New Forward Lookup Zone
- Open the Bind configuration file into a text editor. nano /etc/named.conf
- Define a new domain. ...
- The options set in the above configuration do the following: type Defines the role of this server for the zone. ...
- Save your changes and exit the text editor.
- The next step is to create the database file. ...
How to create new Windows DNS zone?
- Open the Server Manager.
- Click DNS
- Right-Click on your server and then click DNS Manager.
- Inside of DNS Manager... Expand your server. Right-Click on Forward Lookup Zones and click New Zone... In the New Zone Wizard... On the Welcome screen, click Next. ...
Do not use ISP DNS?
Why You Shouldn’t Use Your ISP’s Default DNS Server Your computers, phones, and other devices normally use the Domain Name System (DNS) server with which the router is configured. Unfortunately, this is often the one provided by your Internet Service Provider (ISP). These lack privacy features and also might be slower than some alternatives.
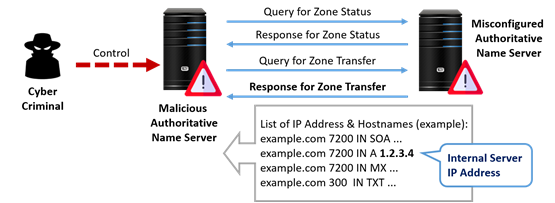
What is allow transfer in DNS?
allow-transfer defines a match list e.g. IP address(es) that are allowed to transfer (copy) the zone information from the server (master or slave for the zone). The default behaviour is to allow zone transfers to any host.
How do you trigger a zone transfer?
To perform a zone transfer, type set q = any and then ls –d targetdomain. This will output the records that were received by the zone transfer. With all of the DNS information, it is possible to determine a lot about the network that uses that domain.
How do I restrict DNS zone transfers?
Restricting DNS Zones TransferGo to Tools & Settings > DNS Settings.On the Transfer Restrictions Template tab, you can view all hosts to which DNS zone transfers for all zones are allowed.Click Add IP Address.Specify the registrar's IP or network address and click OK.
Which tool can be used to perform a DNS zone transfer?
NSlookupNSlookup is a Windows tool which can be used to initiate a DNS zone transfer that sends all the DNS records to a hacker's system.
How often does DNS zone transfer occur?
By default, the DNS service polls Active Directory for changes every 180 seconds (3 minutes).
How do I check my zone transfer?
The tool starts by discovering all the name servers associated with your target domain. Then, to each name server, it sends a Zone Transfer (AXFR) DNS request and checks if it is successful or not. In case of success, the entire zone file is displayed.
How do I disable DNS blocking?
iOS: Open Settings, select Wi-Fi, and tap the i button beside your network name. Tap the DNS field and delete any text there. Android: Open Settings, select Wi-Fi, and long-press on your network name then tap Modify Network. There, delete any text in the DNS field.
Why would you want to limit and regulate zone transfers?
The less information you provide to outsiders, the less they have to work with when attempting to gain unauthorized access to the network. One way to protect this information is by restricting DNS zone transfers.
Can VPN prevent DNS spoofing?
Instead of connecting your devices to your internet provider's local server, a VPN connects to private DNS servers around the world that use end-to-end encrypted requests. This prevents attackers from intercepting traffic and connects you to DNS servers that are better protected from DNS spoofing.
Are DNS zone transfers illegal?
In most countries, including the United States, it IS ILLEGAL to attempt unauthorized zone transfers.
What are the three types of zone transfers?
There are three types of zone transfer to consider: Full zone transfer. Incremental zone transfer. AD replication.
What are the 3 types of DNS zones?
Broadly speaking, there are five types of DNS zones.Primary zone.Secondary zone.Active Directory-integrated zone.Stub zone.Reverse lookup zone.
Where are zone transfers initiated?
Zone transfers are always initiated by the secondary server (that is, they are 'requested' or 'pulled'). While there are mechanisms in place to alert secondaries that they should check to see if a zone transfer is needed, the transfer itself is always started by the secondary.
Is a zone transfer push or pull?
pullThe zone transfer is performed through a "pull" mechanism rather than a "push." This means that the secondary servers initiate the zone transfer.
What is the purpose of forcing a zone transfer?
A zone transfer usually occurs when you bring up a new DNS server as a secondary DNS server. A full transfer of all the zone information will take place in order to replicate the already existing records for that zone. This a time-consuming and resource-intensive process. Thus, incremental DNS transfers were developed.
What are three types of zone transfers?
There are three types of zone transfer to consider: Full zone transfer. Incremental zone transfer. AD replication.
What is a DNS Zone?
A DNS zone is a distinct part of the domain namespace which is delegated to a legal entity— a person, organization or company, who are responsible for maintaining the DNS zone. A DNS zone is also an administrative function, allowing for granular control of DNS components, such as authoritative name servers.
What is SOA record?
Start of Authority (SOA) record —specifies the primary authoritative name server for the DNS Zone. After these two records, the zone file can contain any number of resource records, which can include: Name Server records (NS)— specifies that a specific DNS Zone, such as “example.com” is delegated to a specific authoritative name server.
What is DNS lookup?
When a web browser or other network device needs to find the IP address for a hostname such as “example.com”, it performs a DNS lookup - essentially a DNS zone check - and is taken to the DNS server that manages the DNS zone for that hostname. This server is called the authoritative name server for the domain. The authoritative name server then resolves the DNS lookup by providing the IP address, or other data, for the requested hostname.
What is the name server in DNS?
At each hierarchical level of the DNS system, there is a Name Server containing a zone file, which holds the trusted, correct DNS records for that zone.
What is a name in DNS?
Name is an alphanumeric identifier of the DNS record. It can be left blank, and inherits its value from the previous record.
How many servers are in the DNS root zone?
The DNS root zone is operated by 13 logical servers, run by organizations like Verisign, the U.S. Army Research Labs and NASA. Any recursive DNS query (learn more about DNS query types) starts by contacting one of these root servers, and requesting details for the next level down the tree—the Top Level Domain (TLD) server.
What is a CNAME?
Canonical Name records (CNAME)— points a hostname to an alias. This is another hostname, which the DNS client is redirected to
What is the preamble portion of a zone transfer?
The preamble portion of zone transfer relies on the serial number, and only the serial number, to determine whether a zone's data have changed, and thus whether the actual data transfer is required. For some DNS server packages, the serial numbers of SOA resource records are maintained by administrators by hand. Every edit to the database involves making two changes, one to the record being changed and the other to the zone serial number. The process requires accuracy: the administrator may forget to change the serial number or change it incorrectly (reduce it). RFC 1912 (section 2.2 SOA records) recommends using the value YYYYMMDDnn as the number (YYYY=year, MM=month, DD=day, nn=revision number). This won't overflow until the year 4294.
What is the preamble of a DNS transfer?
The preamble portion of zone transfer relies on the serial number, and only the serial number, to determine whether a zone's data have changed , and thus whether the actual data transfer is required. For some DNS server packages, the serial numbers of SOA resource records are maintained by administrators by hand. Every edit to the database involves making two changes, one to the record being changed and the other to the zone serial number. The process requires accuracy: the administrator may forget to change the serial number or change it incorrectly (reduce it). RFC 1912 (section 2.2 SOA records) recommends using the value YYYYMMDDnn as the number (YYYY=year, MM=month, DD=day, nn=revision number). This won't overflow until the year 4294.
How does data transfer work?
The actual data transfer process begins by the client sending a query (opcode 0) with the special query type AXFR (value 252) over the TCP connection to the server. The server responds with a series of response messages, comprising all of the resource records for every domain name in the "zone". The first response comprises the SOA resource record for the zone apex. The other data follows in no specified order. The end of the data is signaled by the server repeating the response containing the SOA resource record for the zone apex.
Why is DNS sensitive?
This is because information such as server hostnames may become public knowledge, which can be used to discover information about an organization and even provide a larger attack surface. In June 2017 the registrar responsible for Russian top-level-domains accidentally enabled DNS zone transfers via AXFR which led to 5.6 million records being accidentally exposed.
What is DNS zone transfer?
DNS zone transfer, also sometimes known by the inducing DNS query type AXFR, is a type of DNS transaction. It is one of the many mechanisms available for administrators to replicate DNS databases across a set of DNS servers .
What does SOA resource record do in IXFR?
The client sends the SOA resource record for the zone apex that it currently has, if any, in the IXFR message, letting the server know which version of the "zone" it believes to be current.
What is serial number comparison?
Serial number comparisons are intended to use Serial Number Arithmetic as defined in RFC 1982. However, this was not clearly specified in RFC 1034, resulting in not all clients perform the serial number check, in the preamble, in the same way. Some clients check merely that the serial number supplied by the server is different from that known by the client, or non-zero. Other clients check that the serial number supplied by the server is within a given range of the serial number already known by the client. Yet other clients still perform the latter check and additionally check that the serial number supplied by the server is not zero.
Is it necessary to configure a separate DNS replication topology that uses ordinary DNS zone transfers?
I go with Ace, since it is not necessary to configure a separate DNS replication topology that uses ordinary DNS zone transfers because all zone data is replicated automatically by means of Active Directory replication.
Is conditional forwarder better than secondaries?
I think a conditional forwarder is a better choice than creating Secondaries on your domain for the partner, and vice versa. This way you do not need zone transfers to be allowed. Here's more on it that explains your options:
Does DC1 allow zone transfers?
Currently only DC1 has "Allow Zone Transfers" enabled, and only on one Forward Lookup zone (our main domain name). DC2-4 do not have Zone Transfers enabled.
Do you need zone transfers for AD integrated zones?
Zone transfers are not required for AD integrated zones because the zone is stored in the actual AD database and gets replicated to all DC/DNS servers in the replication scope of the zone (DomainNC partition, DomanDnsZones or ForestDnsZones application partitions). Ace. Ace Fekay.
Do you need zone transfers for AD?
Zone transfers are not required for AD integrated zones because the zone is stored in the actual AD database and gets replicated to all DC/DNS servers in the replication scope of the zone (DomainNC partition, DomanDnsZones or ForestDnsZones application partitions).
Can I disable zone transfers on all servers?
By default, IIRC, Zone transfers are not enabled with AD integrated zones. If you don't have any Secondary zones on any non-DCs pulling a copy of the zone (for whatever purpose), then no, I would disable it on all DC/DNS servers.
Do conditional forwarders work?
Even trusted domains - conditional forwarders work, less hassle to setup , no additional requirements to change settings on the Master when setting up a secondary.
Can pfSense see DNS records?
With the configuration you have in place, your pfSense box will still see them.
Is PfSense free?
The pfSense Book is free of charge!
Can you use unbound on multiple interfaces?
It appears you can configure unbound to listen on multiple interfaces, and with a different listening port on each interface. However, I'm not sure you can do that within the pfSense GUI. You might can pull something like that off using the Custom Options section, but I'm doubtful because the settings you need there are also put into the configuration file by the GUI code (interfaces and port). You could wind up with duplicate settings in the configuration file and unbound may not like that.
What port does the GUI use?
The GUI lets you choose multiple interfaces to listen on, but when you choose a port (either 53 or 853), it uses that port for all interfaces.
Is logging in and creating mapping in Windows the same as pfSense?
In terms of effort, logging in and creating the mapping in Windows versus doing the same on pfSense seems the same. Maybe I'm missing something critical in what you want to do.
Can I use secondary DNS for AD?
If you really want a secondary DNS for AD, I would suggest biting the bullet and standing up another Windows server. It can be a virtual machine (just not on the same physical host as your current Windows server if you want real redundancy).
Is it correct to delete forward lookup zone?
Deleting that forward lookup zone is correct. It should never have been there.
What is DNS zone transfer?
A DNS zone transfer is a procedure that lets two DNS servers exchange their zones. This is needed for redundancy. There are several zone transfer methods but the most common one uses the AXFR protocol. Learn about the AXFR protocol.
How to secure zone transfers?
The simplest way to secure zone transfers is to restrict AXFR requests to trusted IP addresses. You can do it in your DNS server configuration or on your firewall. You can additionally use transaction signatures.
What is DNS in the Internet?
DNS (Domain Name System) is like an Internet phonebook. It is responsible for resolving human-readable hostnames into machine-readable IP addresses. The system includes authoritative DNS servers that provide information and DNS caches that store that information temporarily for client lookups. A typical DNS query is very simple: a client provides a human-readable hostname and in response receives an IP address. However, the system assumes that the querying client knows the hostname.
Why is DNS transfer needed?
DNS is a critical service. If a DNS server for a zone is not working and cached information has expired, the domain is inaccessible to all services (web, mail, and more). Therefore, each zone should have at least two DNS servers. For more critical zones, there may be even more.
What is DNS query?
A typical DNS query is very simple: a client provides a human-readable hostname and in response receives an IP address. However, the system assumes that the querying client knows the hostname. DNS servers host zones. A DNS zone is a portion of the domain name space that is served by a DNS server.
Why should DNS servers be configured to only allow zone transfers from trusted IP addresses?
In order to prevent this vulnerability from occurring, the DNS server should be configured to only allow zone transfers from trusted IP addresses. The following is an example of how this can be accomplished in the BIND DNS server.
How many DNS servers are needed for each zone?
Therefore, each zone should have at least two DNS servers. For more critical zones, there may be even more. However, a zone may be large and may require frequent changes. If you manually edit zone data on each server separately, it takes a lot of time and there is a a lot of potential for a mistake. This is why DNS zone transfer is needed.

Overview
DNS zone transfer, also sometimes known by the inducing DNS query type AXFR, is a type of DNS transaction. It is one of the many mechanisms available for administrators to replicate DNS databases across a set of DNS servers.
A zone transfer uses the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) for transport, and takes the form of a client–server transaction. The client requesting a zone transfer may be a secondary server requ…
Operation
Zone transfer consists of a preamble, followed by the actual data transfer. The preamble comprises a lookup of the Start of Authority (SOA) resource record for the "zone apex", the node of the DNS namespace that is at the top of the "zone". The fields of this SOA resource record, in particular the "serial number", determine whether the actual data transfer need to occur at all. The client compares the serial number of the SOA resource record with the serial number in the last …
Limitations
Though it is standardized, full-zone transfer being described as one of the possible database replication mechanisms in RFC 1034 and RFC 5936 (incremental zone transfer described in RFC 1995), zone transfer is the most limited of those database replication mechanisms. Zone transfer operates in terms of "wire format" resource records, i.e. resource records as they are transferred using the DNS protocol. However, the schema of wire format resource records may not be identi…
Operational problems
The preamble portion of zone transfer relies on the serial number, and only the serial number, to determine whether a zone's data have changed, and thus whether the actual data transfer is required. For some DNS server packages, the serial numbers of SOA resource records are maintained by administrators by hand. Every edit to the database involves making two changes, one to the record being changed and the other to the zone serial number. The process requires a…
See also
• List of DNS record types
External links
• CAPEC-291 DNS Zone Transfers
• CVE-1999-0532 A DNS server allows zone transfers.
• CWE-16 Configuration
• CWE-276 Incorrect Default permissions