- Use an Earth Fault Loop Tester or select the Earth Fault Loop Test option on a multifunctional tester such as the Megger 1553.
- Test on the incoming side of the installation. Connect one test lead to the Line terminal, the second test lead to the Neutral terminal and the third (usually ...
- Press the TEST button. The measurement should be a low reading ohm value.
How do I test the earth fault loop impedance?
The means of earthing will be isolated from the installation’s earthing system (earth rods) bonding during the test. The Ze measurement will confirm the earth fault loop impedance as the sum of the resistances. Step 1: Use an Earth Fault Loop Tester or select the Earth Fault Loop Test option on a multifunctional tester such as the Megger 1553.
What is the best method for loop impedance testing?
As it stands today, most contractors will use one of 5 different test techniques when loop impedance testing: This is the traditional loop impedance test. Using a test current of up to 20 A and a simple 2 wire connection, it is by and large the fastest, most accurate test available on a day to day basis.
What is earth loop impedance?
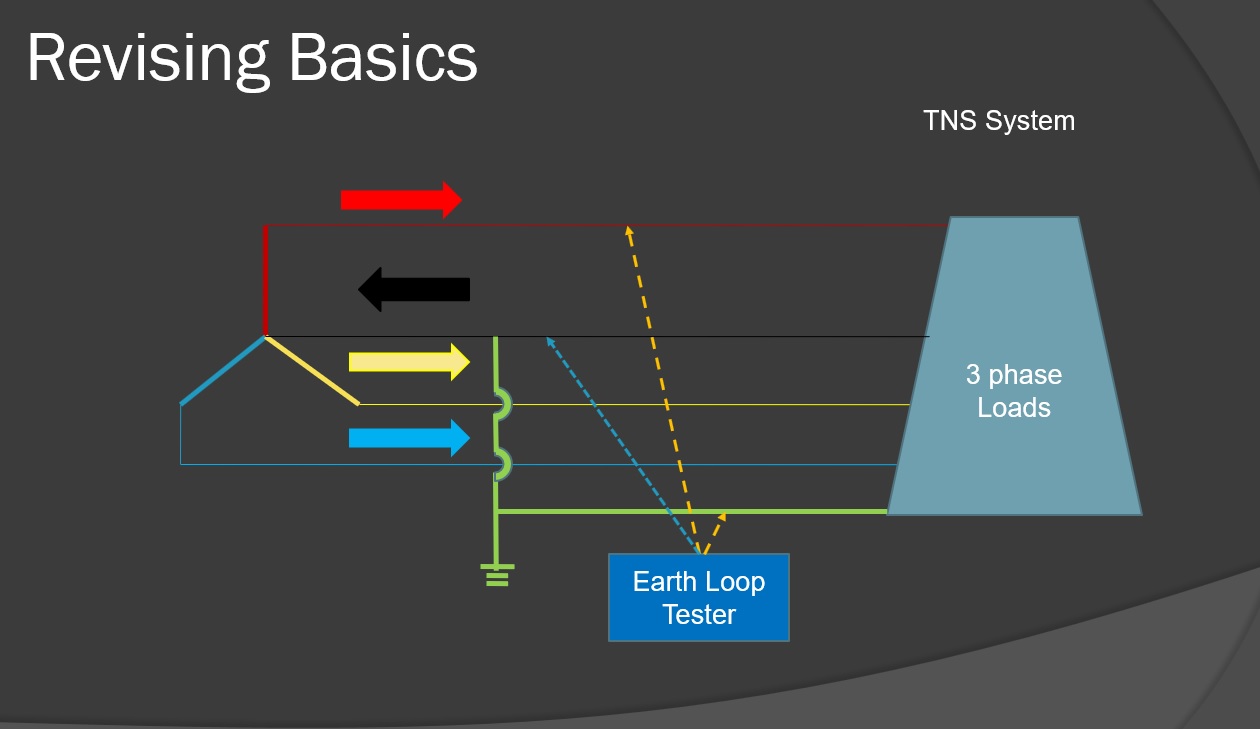
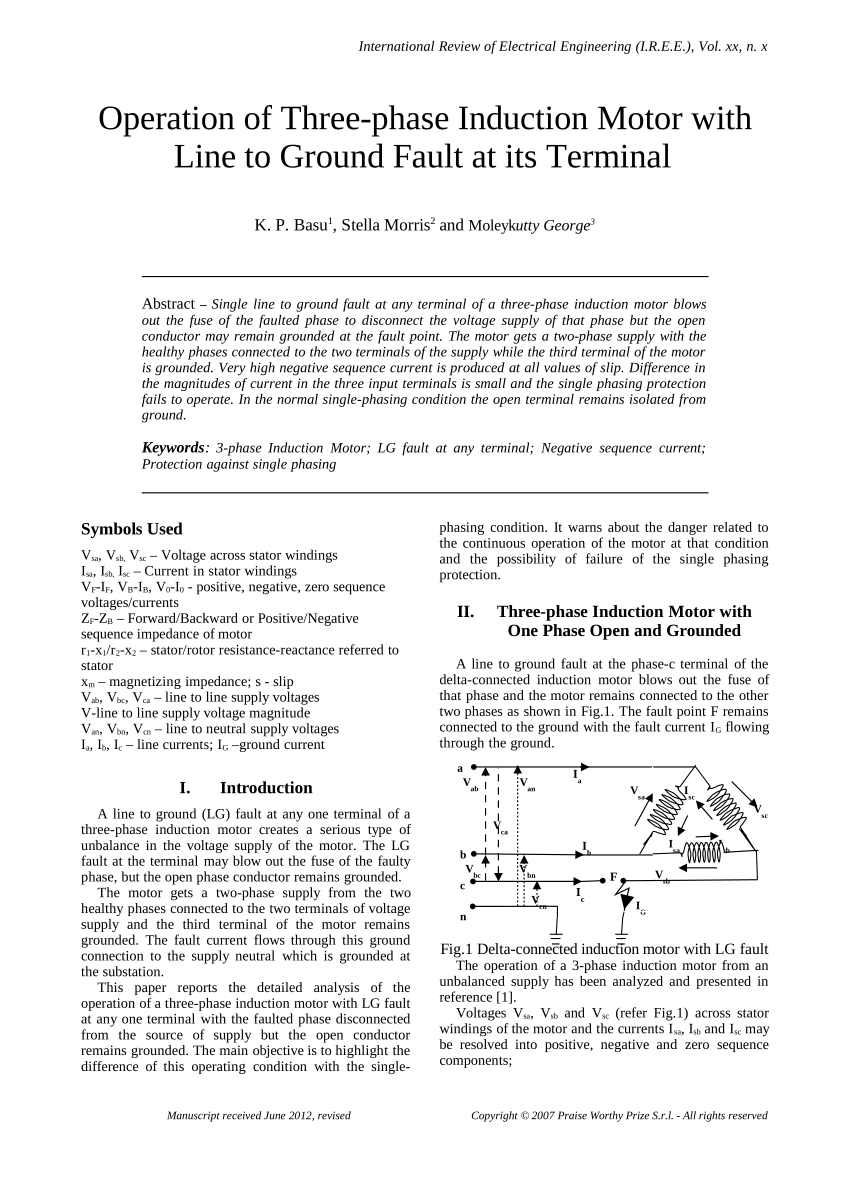
What is Earth Loop Impedance? During an electrical fault on a circuit, a current will flow from the Line conductor towards Earth and in to the Neutral point of the supply company transformer.
What is a good earth loop impedance?
The value of external earth loop impedance (Ze) measured or otherwise determined in accordance with Regulation 313.1 may differ from the applicable typical maximum value declared by the electricity distributor, which is usually: 0.8 Ω for TN-S system. 0.35 Ω for a TN-C-S system.
How do you do a ZS test?
0:292:19Earth Fault Loop Impedance Test On a Circuit Zs 1 - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd then all I need to do is a very very simple procedure is to plug the instrument into the socketMoreAnd then all I need to do is a very very simple procedure is to plug the instrument into the socket switch it on now I've got the result. Which is 0.37 of an ohm.
What is the purpose of an earth loop impedance test?
The main reason for earth loop impedance testing – which is often simply called loop testing – is to verify that, if a fault occurs in an electrical installation, sufficient current will flow to operate the fuse or circuit breaker protecting the faulty circuit within a predetermined time.
What is ground loop impedance?
Earth fault loop impedance is the path followed by fault current when a low impedance fault occurs between the phase conductor and earth, i.e. “earth fault loop”. Fault current is driven round the loop by the supply voltage.
What happens if earth fault loop impedance is too high?
What if the earth loop impedance be too high? However should the resistance is too high, the circuit protection may not operate at all. As a user of electrical items you may not notice any issues, however over a period of time your equipment around you my start to deteriorate (stop working or catch fire).
What is the maximum ZS permitted by BS 7671?
IET Forums - Maximum ZS Permitted By BS7671. Is the correct value to be entered for a RCBO Type B 0.57 Ohms or 1333 Ohms (80%) or 1667 Ohms.
How do you measure earth loop impedance with a multimeter?
12:0316:50Earth Fault Loop Impedance Test & Prospective Fault Current TestYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd put a probe on and now test between the incoming. Live tails of the line and the neutral comingMoreAnd put a probe on and now test between the incoming. Live tails of the line and the neutral coming in so this is how much current would flow in the event of a short-circuit.
How do you perform a loop test?
External loopback test—Tests the hardware of Ethernet interfaces. To perform an external loopback test on an Ethernet interface, connect a loopback plug to the Ethernet interface. The device sends test packets out of the interface, which are expected to loop over the plug and back to the interface.
What is the maximum earth loop impedance?
Tables of maximum earth fault loop impedance 3 gives the maximum Zs value of 1.37 ohms at a nominal voltage (U0) of 230 V. This compares with 1.44 ohms in the same table of the previous version of BS 7671.
How do you find the fault in a loop?
How to calculate earth fault loop impedance value (Zs) ? Get to know the voltage to earth (Uo) Determine Ia, see the breaker tripping curve, to find the cuurent needed to trip in 5 seconds (see example on the attached file “Earth Fault Loop Impedance Summary.ppt”, slide 2 and 3) Calculate Zs = Uo / Ia.
How can earth fault loop impedance be improved?
Increase the size of the PE or PEN conductors and/or the phase conductors, to reduce the loop impedance.
How do you test Zs on a distribution board?
3:2216:50Earth Fault Loop Impedance Test & Prospective Fault Current TestYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWe want to make sure that there is an earth connection to the installation. And secondly that theMoreWe want to make sure that there is an earth connection to the installation. And secondly that the value the Z value is equal to or less than the value determined by the designer.
What is the 80% ZS rule?
The 80% rule of thumb is only intended to be applied to a test result taken from an impedance test. You have to ensure that the tested value does not exceed 80% of the tabulated value.
How do you find the Zs of a circuit?
4:0512:11WHAT IS Zs? Why is it important to test Zs. - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWe can say that zs equals ze plus r1 plus r2.MoreWe can say that zs equals ze plus r1 plus r2.
What is the difference between Zs and Ze?
Zs is the total impedance of the complete circuit and it is made up of: The impedance of the supply cables and transformer windings, Ze. The resistance of our circuit line conductor, R1. The resistance of our circuit cpc, R2.
How to test earth fault loop?
Locate the furthest point on the circuit to be tested (such as the furthest socket) Step 2. With the appropriate Earth Fault Loop Tester, connect the test leads to the Line, Neutral and Earth terminals. Step 3.
How to test the highest Earth Fault Loop Impedance (Zs)?
Having obtained the `Ze` value for the installation, the value of `Zs` can be easily calculated for every circuit. During the City and Guilds 2391 practical assessment it is allowed to test each and every circuit for the value of `Zs`; however, because of the limited time at hand it is advised to calculate the value of `Zs` instead of direct measurement.
How to test a Megger 1553?
Step 1. Use an Earth Fault Loop Tester or select the Earth Fault Loop Test option on a multifunctional tester such as the Megger 1553. Step 2. Test on the incoming side of the installation.
What happens to the current in a circuit if there is a fault?
During an electrical fault on a circuit, a current will flow from the Line conductor towards Earth and in to the Neutral point of the supply company transformer. This circuit (loop), which consists of all the elements within the loop (supply transformer winding , supply company phase conductor, main fuse, main switch, protective device, ...
Is it better to test every circuit for Zs?
However in real life situation it is better to test every circuit for Zs individually instead of calculation. The measured value will almost never be exactly the same as the calculated one. This is because other factors such as parallel paths of earthing within the installation.
Do you have to replace earth connections before reclosing a main switch?
DO NOT FORGET to replace the earth connections for the installation before reclosing the Main Switch and energising the circuits!
How to measure earth fault loop impedance?
In most cases the circuit breaker needs to be bridged out. The total earth fault loop impedance is measured by plugging a loop tester into a socket outlet, or in some cases with an external earth probe. The value of the earth fault loop impedance is the sum of the resistances. When using an external earth probe, the earth fault loop impedance is measured by touching an external probe directly to an earth bar, collector and connection point of an earth bar. The same measurement can be done by touching the earth probe to exposed, conductive parts of equipment in the circuits and exposed metal parts.
Why do you need to conduct a loop impedance test?
According to the current national safety standards, you are required to conduct loop impedance test on your premises to ensure the safety of all guests and employees. The electrical earth of all your electrical installations and power points has to be tested to discover any faults within your electric circuit. Having a functional earth return circuit will allow the detection of circuit faults and facilitate a reaction from your MCB (miniature circuit breaker). Carelabs technician will detect the resistance level in your earth return circuit and notify you if it is at the wrong level – it needs to be low enough to allow the circuit breaker to function correctly. Carelabs will inspect and test your electrical wiring and by asking us to test you are protecting both your employees and your liability. It is important to adhere to national legislation to avoid harsh penalties.
Why should a loop tester be repeated?
Since the test result is dependent on the supply voltage, small variations will affect the reading. Thus, the test should be repeated several times to ensure consistent results. Anyone on site must avoid shock hazard while establishing contact and while doing the test. When buying a loop tester ask for distribution board test leads so that Ze and Zs measurements can be done.
Why is an RCD protected circuit important?
A circuit protected by an RCD will need special attention, because the earth-fault loop test will draw current from the phase which returns through the protective system. Thus testing of circuits protected by RCDs has presented instrument manufacturers’ with difficulties in providing test results similar to that of the testing of non-RCD protected circuits, without tripping the RCDs during the tests. Therefore, any RCDs must be bypassed by short circuiting connections before earth-fault loop tests are carried out. It is, of course, of the greatest importance to ensure that such connections are removed after testing.
What is the most accurate loop impedance test?
This is the traditional loop impedance test. Using a test current of up to 20 A and a simple 2 wire connection , it is by and large the fastest, most accurate test available on a day to day basis. Most standard loop impedance testers will incorporate this type of test. Because of the relatively high test current, the readings are not generally influenced by external factors and will return repeatable, stable readings in most scenarios.
How does the RCD test method overcome the need to by-pass even the new electronic protection devices?
This test method overcame the need to by-pass even the new electronic protection devices by utilising a low current Line-Earth test current, whilst still returning a degree of accuracy. Not having to by-pass the RCD/RCBO obviously introduced a time saving factor. In addition, by having the requirement of connecting to Line, Neutral and Earth, the testers were now able to confirm the presence of all three as well as indicate if there was a reverse polarity at the test point and, due to the limited test current, there was no issue with tripping the MCB.
Does the impedance change depending on the type of installation?
The required values of impedance and time will change dependent upon the type of installation (TN/TT etc.) and the type of protection, whether it be a miniature circuit breaker (MCB), cartridge fuse or re-wireable fuse for example. The fault current can either be in the Line-Neutral or Line-Earth circuit, so there is a need to confirm the loop impedance of each
How to determine earth loop impedance?
Therefore, where reliable measured values are available for the external earth loop impedance (Ze) and for the loop resistance of the line and protective conductors (R₁ + R₂) of the circuit, it is permissible to derive the loop impedance of a circuit by using the following formula: Zs = Ze + (R₁ + R₂).
What would happen if an RCD was used to test an earth fault loop?
Inadvertent disconnection of a circuit, group of circuits, distribution board or even a whole installation could occur if an RCD operates when an earth fault loop impedance test is carried out. As a result, a number of methods have been developed to minimise the likelihood of an RCD operating during such a test.
Does a loop test cause a RCD to operate?
Further, as the loop test is being performed on the supply side of any RCD protecting the circuit in question, it should not, in most cases, cause the RCD to operate when the measurement of Ze or Zdb is taken. However, persons using this method should satisfy themselves that there is no other RCD upstream of the circuit under test, protecting for example a sub-main circuit.
Why do we test earth loop impedance?
Testing an earth loop impedance involves having your power points and electric installations tested to prevent electric shocks and harm at your home or workplace. That is performed by ensuring the impedance of the electric circuit is producing enough fault current to run a device.
What is a Fault Loop Impedance, by the way?
A fault loop impedance is what its name tells—it’s the impedance (resistance) of the loop (circuit) under fault circumstances. A fault condition is normally categorized as a short circuit at the end of the cable run or the terminal’s load.
What is loop in electrical?
The term loop here talks about the whole path the current will flow in the circuit under fault conditions. You will find two opportunities for a short circuit at the end of the cable run.
Why does a phase to earth circuit have more resistance than a phase to phase fault?
Take note that the impedance of the phase-to-earth circuit is utilized in such calculations. That’s because the earth wire is normally smaller than active wires. Therefore, it will have more resistance than a phase-to-phase fault.
What is the impedance of a circuit?
The impedance on the circuit identifies the amount of current if there’s a short circuit. The cable path efficiently functions as a resistor, which has been placed across the circuit breaker. Simply put, if the impedance is high, less current will flow.
What is the earth return circuit?
Such electrical earth wiring arrangements in buildings are often linked to the ground. In electrical terms, that’s also known as the earth return circuit. The earthing rods or earthing cables are there for electrical current to pass through if a short circuit occurs.
What is the next step after you acquire the value of Zs for each circuit?
After you acquire the value of Zs for each circuit, the next step is to confirm those values are within the specified limits designated by NEC.
Why conduct an earth loop impedance test?
Conducting the earth loop impedance testing can ensure that your devices have enough current to operate during an electrical surge. To have the complete picture before you, we have this guide.
How to test earth impedance?
You will plug the loop tester into the socket-outlet or with an external earth probe for this test. The external earth probe then measures the impedance, and it measures either by touching the earth bar, conductive, or exposed metal parts of the equipment. Keep in mind that the process is hazardous and may lead to shock hazards.
How to test a circuit with a Megger 1553?
Take an earth fault tester or choose the loop testing option on the multifunctional tester like Megger 1553. Test the supply side of the electrical circuit. Place the one test probe on the line terminal, the second on the neutral, and the third on the earth conductor.
How does a loop tester work?
The tester will measure the unloaded voltage between conductors and provide some resistance in the link to prevent a fault. Then it will calculate the voltage drop across the resistor. Always remember that the supply voltage will be dependent upon the impedance of the loop.
Why do you need to test every circuit?
Thus, you need to test every circuit to ensure no loop impedance drives the excess current in a loop. Also, you will check that if resistance does exist, it is not causing the current not to blow out the fuse. To explain, the loop test contains whether sufficient current passes through the protective devices such as fuse or circuit breakers. That way, you will ensure that fault currents are strong enough to operate the circuit breaker within a short period.
Why is the wind stuck in a loop?
Often, the wind is stuck into a loop because of the supply voltage with a high impedance; the higher the fault current, the more time the circuit breakers will take to operate.
What happens if you leave a wire unchecked?
If you leave the wirings unchecked, you will be evacuating people from your building due to the fire that broke out. Loop impedance testing or loop testing might be a good investment option if you opt for preventive measures.
