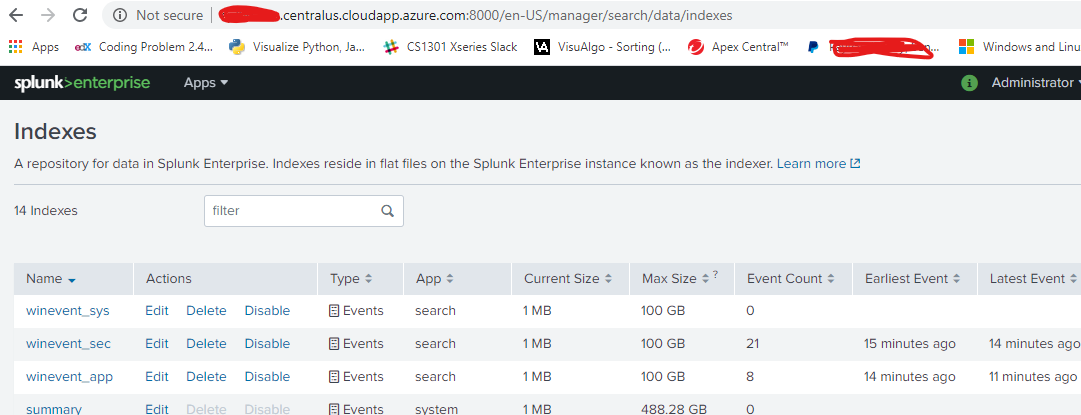
Checking Indexes We can have a look at the existing indexes by going to Settings → Indexes after logging in to Splunk. The below image shows the option. On further clicking on the indexes, we can see the list of indexes Splunk maintains for the data that is already captured in Splunk.
Full Answer
How to create a new index in Splunk?
We can create a new index with desired size by the data that is stored in Splunk. The additional data that comes in can use this newly created index but better search functionality. The steps to create an index is Settings → Indexes → New Index. The below screen appears where we mention the name of the index and memory allocation etc.
What types of data can Splunk Enterprise Index?
Splunk Enterprise can index any type of time-series data (data with timestamps ). When Splunk Enterprise indexes data, it breaks it into events, based on the timestamps. The indexing process follows the same sequence of steps for both events indexes and metrics indexes.
What is an indexer in Splunk?
An indexer is a Splunk Enterprise instance that indexes data. For small deployments, a single instance might perform other Splunk Enterprise functions as well, such as data input and search management. In a larger, distributed deployment, however, the functions of data input and search management are allocated to other Splunk Enterprise components.
What is defaultdb in Splunk?
By default, all events will go to the index specified by defaultDatabase, which is called main but lives in a directory called defaultdb. In this tutorial, we put focus to index structures, need of multiple indexes, how to size an index and how to manage multiple indexes in a Splunk environment.
See more

How can I see all indexes in Splunk?
Checking Indexes We can have a look at the existing indexes by going to Settings → Indexes after logging in to Splunk. The below image shows the option. On further clicking on the indexes, we can see the list of indexes Splunk maintains for the data that is already captured in Splunk.
How do I find Splunk index?
Control index access using Splunk WebNavigate to Settings > Roles.Click the role that the User has been assigned to.Click on "3. Indexes".Control the indexes that particular role has access to, as well as the default search indexes.
What indexes are in Splunk?
"A Splunk index is a repository for Splunk data." Data that has not been previously added to Splunk is referred to as raw data. When the data is added to Splunk, it indexes the data (uses the data to update its indexes), creating event data. Individual units of this data are called events.
What is index in Splunk search query?
INDEX: an index in Splunk is like a repository of data. There are default indexes that can be used when uploading data, but it is better to create your own. To create a new Index go to Settings > Indexes > New index.
What is the default index in Splunk?
_internal : This index includes Splunk Enterprise internal logs and metrics. _introspection : Instrumentation data about your Splunk instance and environment and writes that data to log files to aid in reporting on system resource utilization and troubleshooting problems with your Splunk Enterprise deployment .
What are the basic commands in Splunk?
List of search commandsCommandDescriptiontimechartCreate a time series chart and corresponding table of statistics. See Functions for stats, chart, and timechart in the Splunk Enterprise Search Reference.topDisplays the most common values of a field.transactionGroups search results into transactions.112 more rows•Sep 17, 2021
What is a Splunk summary index?
A special index that stores the results of a scheduled report, when you enable summary indexing for the report. Summary indexing lets you run fast searches over large data sets by spreading out the cost of a computationally expensive report over time.
What is index and bucket in Splunk?
Splunk indexed data is located in database directories, divided into subdirectories called buckets. As time goes by, Splunk performs storage tiering, moving data through several types of buckets, which represent four tiers—hot, warm, cold and frozen.
How do I check my Splunk Sourcetype?
Using index="test" | stats dc(sourcetype) as sourcetypes only shows the total number of sourcetypes but does not list them individually. To list them individually you must tell Splunk to do so. If this reply helps you, Karma would be appreciated. To list them individually you must tell Splunk to do so.
How do you check logs in Splunk?
Application logs can be accessed through Splunk. To start a new search, open the Launcher menu from the HERE platform portal and click on Logs (see menu item 3 in Figure 1). The Splunk home page opens and you can begin by entering a search term and starting the search.
How do I use Splunk queries?
0:225:20Basic Searching in Splunk 6.X - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipApplication the app includes a search bar for entering our searches. A time range picker for theMoreApplication the app includes a search bar for entering our searches. A time range picker for the search links to the search documentation. And tutorial.
How do I filter Splunk logs?
Filter logs by fieldNavigate to Log Observer. ... Click the Index selector next to Saved Queries, then select the indexes you want to query. ... Click Add Filter.On the Fields tab, type the name of the field you want to filter on, then click the field you want.More items...
How do I search Splunk?
You can search by typing keywords in the search bar, like Error, Login, Logout, Failed, etc. After Logging in into your Splunk instance, you can see the Search & Reporting app on the left side. Click on the Search & Reporting app to get into the app. You can see Search bar with time range picker.
How do I create a Splunk index?
Use Splunk Web to create an indexIn Splunk Web, go to Settings > Indexes.On the Indexes page, click New Index.On the New Index page, in the Index Name field, enter devtutorial. Keep the other default settings.Click Save.
Where is Splunk stored?
indexesIn Splunk, you store data in indexes made up of file buckets. These buckets contain data structures that enable Splunk to determine if the data contains terms or words. Buckets also contain compressed, raw data.
Where are Splunk logs stored?
Splunk software keeps track of its activity by logging to various files located in /opt/$SPLUNK_HOME/var/log/splunk.
How to look at indexes in Splunk?
We can have a look at the existing indexes by going to Settings → Indexes after logging in to Splunk. The below image shows the option.
How to create index in Splunk?
The additional data that comes in can use this newly created index but better search functionality. The steps to create an index is Settings → Indexes → New Index. The below screen appears where we mention the name of the index and memory allocation etc.
What is Splunk indexing?
Indexing is a mechanism to speed up the search process by giving numeric addresses to the piece of data being searched. Splunk indexing is similar to the concept of indexing in databases. The installation of Splunk creates three default indexes as follows.
What is audit index?
audit − This index contains events related to the file system change monitor, auditing, and all user history.
Does Splunk have local storage?
If all of your disks are local, then you do not need to be concerned with the following details. If your Splunk system has a non-local partition that is utilized for long-term storage, then you will need to manage the settings for where Splunk puts older data.
Does Splunk freeze the cold bucket?
Now that we have the Local storage sorted out, we must tune the total index size. Since we have already tuned the hot and warm buckets, Splunk will automatically ‘freeze’ (aka – delete or archive) the oldest cold bucket. Here is the equation to calculate the maximum index size.
Where is the index located in Splunk?
Each index occupies a set of directories on the disk. By default, these directories live in $SPLUNK_DB, which, by default, is located in $SPLUNK_HOME/var/lib/splunk.
What is index in Splunk?
An index in Splunk is a storage pool for events, capped by size and time. By default, all events will go to the index specified by defaultDatabase, which is called main but lives in a directory called defaultdb.
Why do you need to put indexes on different devices?
If you have access to multiple storage devices, placing indexes on different devices can help increase the performance even more by taking advantage of different hardware for different queries. Likewise, placing homePath and coldPath on different devices can help performance.
Why do we need to put different source types in different indexes?
Placing different source types in different indexes can help increase performance if those source types are not queried together. The disks will spend less time seeking when accessing the source type in question.
What is an index made of?
An index is made up of buckets, which go through a specific life cycle. Each bucket contains events from a particular period of time.
How to change storage location in Splunk?
To change your storage location, either modify the value of SPLUNK_DB in $SPLUNK_HOME/etc/splunk-launch.conf or set absolute paths in indexes.conf.
Can you use test indexes in Splunk?
If you do not have a test environment , you can use test indexes for staging new data. This then allows you to easily recover from mistakes by dropping the test index. Since Splunk will run on a desktop, it is probably best to test new configurations locally, if possible.