
What is DLM SAS? DLM= The dlm= option can be used to specify the delimiter that separates the variables in your raw data file. For example, dlm=','indicates a comma is the delimiter (e.g., a comma separated file,. csv file).
How do you use DLM in a CSV file?
Feb 12, 2020 · How do I use DLM in SAS? The dlm= option can be used to specify the delimiter that separates the variables in your raw data file. For example, dlm=','indicates a comma is the delimiter (e.g., a comma separated file, . csv file). Or, dlm='09'x indicates that tabs are used to separate your variables (e.g., a tab separated file). Click to see full answer.
Do I need to license SAS/access to read from DBMS files?
Apr 23, 2020 · What is DLM SAS? DLM= The dlm= option can be used to specify the delimiter that separates the variables in your raw data file. For example, dlm=','indicates a comma is the delimiter (e.g., a comma separated file, . csv file). Or, dlm='09'x indicates that tabs are used to separate your variables (e.g., a tab separated file).
What is the difference between DSD and DLM?
your computer uses EBCDIC (IBM mainframes) instead of ASCII, then use DLM=’05’X. DATA reading; INFILE ’c:\MyRawData\Books.txt’ DLM = ’09’X; INPUT Name $ Week1 Week2 Week3 Week4 Week5; RUN; By...
When does SAS Go to a new line?
Jan 30, 2015 · DSD does 3 things: 1. dlm=','. 2. if there are two comma in a row, it sees a missing value. 3. if there are quotes around data elements, it removes them. dlm is just dlm. When using dlm= and dsd together, the value defined by dlm= overrides comma.
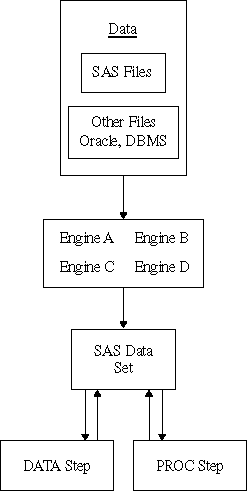
What is the difference between DLM and DSD in SAS?
What is the use of DSD in SAS?
specifies that when data values are enclosed in quotation marks, delimiters within the value are treated as character data. The DSD option changes how SAS treats delimiters when you use LIST input and sets the default delimiter to a comma.
How do you use delimiter in SAS?
What are Infile options in SAS?
- BLKSIZE=block-size. specifies the block size of the input file. ...
- COLUMN=variable. names a variable that SAS uses to assign the current column location of the input pointer. ...
- DELIMITER= delimiter(s) ...
- DLMSTR= delimiter. ...
- DLMSOPT= 'options' ...
- DSD (delimiter-sensitive data) ...
- ENCODING= 'encoding-value' ...
- END=variable.
What is input buffer and PDV in SAS?
What does Truncover mean in SAS?
How do I import a delimited file into SAS?
- Start the PROC IMPORT procedure with the PROC IMPORT keywords.
- Define the location and filename of the text file with the FILE=-argument.
- Define the name of the SAS output dataset with the OUT=-argument.
- Use the DBMS=tab to import text files.
What does Lrecl mean in SAS?
What does a delimiter do?
What is the difference between input and Infile in SAS?
How do I use OBS and Firstob in SAS?
proc print data=study(firstobs=20); run; This SET statement uses FIRSTOBS= and OBS= to read only observations 5 through 10 from the data set STUDY. The data set NEW contains six observations.
What is format and informat in SAS?
What does DSD do in SAS?
When you specify DSD , SAS treats two consecutive delimiters as a missing value and removes quotation marks from character values. Whereas the default functionality of DLM=',' is to treat consecutive commas as a single comma, DSD will assign missing values between consecutive commas. Here's an example: data work.
What is a dataline in SAS?
What are Datalines in SAS? The DATALINES statement is the last statement in the DATA step and immediately precedes the first data line. Use a null statement (a single semicolon) to indicate the end of the input data. You can use only one DATALINES statement in a DATA step.
What is a delimited file?
A delimited file is a plain text file that contains a separator between the data fields. For example, to read Comma Separated Value (CSV) files in SAS 6, you had to preprocess the files in order for SAS to recognize that there were missing values between consecutive commas.
How many delimiters does SAS use?
By default, SAS interprets two or more delimiters in a row as a single delimiter. If your file has
Can you read data files with any delimiter?
common delimiters found in data files, but you could read data files with any delimiter character
Comparisons
Modified list input has a scanning feature that can use informats to read data which are not aligned in columns. Formatted input causes the pointer to move like that of column input to read a variable value. The pointer moves the length that is specified in the informat and stops at the next column.
Comparisons
Modified list input has a scanning feature that can use informats to read data which are not aligned in columns. Formatted input causes the pointer to move like that of column input to read a variable value. The pointer moves the length that is specified in the informat and stops at the next column.
What does length= mean in SAS?
specifies a variable that SAS sets to the length of the current input line. SAS does not assign the variable a value until an INPUT statement executes. Like automatic variables, the LENGTH= variable is not written to the data set.
When does SAS set a variable to 1?
specifies a variable that SAS sets to 1 when the first record in a file in a series of concatenated files is read. The variable is set only after SAS encounters the next file. Like automatic variables, the EOV= variable is not written to the data set.
What is end= in SAS?
Until SAS processes the last data record, the END= variable is set to 0. Like automatic variables, this variable is not written to the data set.
What is the START variable in SAS?
specifies a variable whose value SAS uses as the first column number of the record that the PUT _INFILE_ statement writes. Like automatic variables, the START variable is not written to the data set.
When data is read from the job stream, must you use a DATALINES statement?
When data is read from the job stream, you must use a DATALINES statement. However, to take advantage of certain data-reading options that are available only in the INFILE statement, you can use an INFILE statement with the file-specification DATALINES and a DATALINES statement in the same DATA step.
What is the format modifier in SAS?
The & (ampersand) format modifier enables you to read character values that contains one or more embedded blanks with list input and to specify a character informat. SAS reads until it encounters two consecutive blanks, the defined length of the variable, or the end of the input line, whichever comes first.
How to separate input values in SAS?
Input values must be separated by at least one blank (the default delimiter) or by the delimiter specified with the DLM= or DLMSTR= option in the INFILE statement . If you want SAS to read consecutive delimiters as if there is a missing value between them, specify the DSD option in the INFILE statement.
What is a colon in SAS?
SAS reads until it encounters a blank column, the defined length of the variable (character only), or the end of the data line, whichever comes first.
What is an input in SAS?
The INPUT statement reads raw data from instream data lines or external files into a SAS data set. You can use the following different input styles, depending on the layout of data values in the records:
What is modified list input?
A more flexible version of list input, called modified list input, includes format modifiers. The following format modifiers enable you to use list input to read nonstandard data by using SAS informats:
When an equal sign follows a variable in an input statement, SAS expects that data remaining on the input line contains
Note: When an equal sign follows a variable in an INPUT statement, SAS expects that data remaining on the input line contains only named input values. You cannot switch to another form of input in the same INPUT statement after using named input.
Can you use informats to read data that is not aligned in columns?
Note: You can also use informats to read data that is not aligned in columns. See Modified List Input for more information.
Why do we use colons in DSD?
The colon modifier helps when the actual value is shorter than the informat's width, but it also helps by moving the pointer PAST the delimiter so that the NEXT variable is read correctly. This is what makes it important when using formatted input statements with the DSD infile option.
How does input behave when it sees a delimiter?
The real issue how the input statement behaves when it sees a delimiter when it starts to read a variable. With the DSDoption it will set the value to missing and move the pointer past the delimiter. Without the DSD option it will skip over the delimiter (or multiple adjacent delimiters) before reading the value. You can confirm this by reading a line that starts with a delimiter.
