As terrestrial animals cannot afford to spend more water for excretion, they excrete less toxic nitrogenous wastes like urea and uric
Uric acid
Uric acid is a heterocyclic compound of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen with the formula C₅H₄N₄O₃. It forms ions and salts known as urates and acid urates, such as ammonium acid urate. Uric acid is a product of the metabolic breakdown of purine nucleotides, and it is a normal compone…
What do animals excrete from their environment?
Animals excrete a variety of nitrogen waste products, but ammonia, urea and uric acid predominate. A major factor in determining the mode of nitrogen excretion is the availability of water in the environment. Generally, aquatic animals excrete mostly ammonia, whereas terrestrial animals excrete either urea or uric acid.
How are nitrogenous wastes excreted in terrestrial animals?
As terrestrial animals cannot afford to spend more water for excretion, they excrete less toxic nitrogenous wastes like urea and uric acid. Ammonia produced by metabolism is converted into urea by the ornithine cycle in the liver of these animals and released into the blood, which is filtered and excreted out by the kidneys.
How do plants and animals get nitrogen?
These chemicals are obtained by animals through their consumption of plants. When plants and animals die, or when animals excrete waste, the nitrogen compounds in the organic matter re-enter the soil, where they are broken down by microbes known as decomposers, which are beneficial to the soil’s fertility. How do animals get nitrogen * Your answer?
What are the functions of nitrogen end products in animals?
There are diverse physiological functions of nitrogen end products in different animal groups, including excretion, acid-base regulation, osmoregulation and buoyancy. Animals excrete a variety of nitrogen waste products, but ammonia, urea and uric acid predominate.

What happens to the nitrogen excreted by animals?
Excess nitrogen is excreted from the body. Nitrogenous wastes tend to form toxic ammonia, which raises the pH of body fluids. The formation of ammonia itself requires energy in the form of ATP and large quantities of water to dilute it out of a biological system.
Why do terrestrial animals excrete urea?
Terrestrial animals need to conserve water. They lose a great amount of water because of evaporation. So, they try to get rid of their metabolic waste (urea) with a minimal amount of water lost. Hence, they excrete hypertonic urine.
What are three forms in which animals excrete nitrogenous wastes?
1: Nitrogen excretion: Nitrogenous waste is excreted in different forms by different species. These include (a) ammonia, (b) urea, and (c) uric acid.
What is the main source of nitrogen-containing wastes in animals?
Urea serves an important role in the metabolism of nitrogen-containing compounds by animals. It is the main nitrogen-containing substance in the urine of mammals.
Why terrestrial organisms excrete lesser toxic nitrogenous waste?
Answer: Terrestrial adaptation necessitated the production of lesser toxic nitrogenous wastes like urea and uric acid for the conservation of water. Mammals and many terrestrial amphibians mainly excrete urea and are called uriotelic animals.
In what form is nitrogen excreted in animals?
Animals excrete a variety of nitrogen waste products, but ammonia, urea and uric acid predominate. A major factor in determining the mode of nitrogen excretion is the availability of water in the environment.
What are the three main modes of excretion in animals?
They are: Ammonotelism (Type of excretion- ammonia) Ureotelism (Type of excretion – urea) Uricotelism (Type of excretion – uric acid)
Where is nitrogenous waste produced?
Nitrogen wastes They are ammonia, urea, uric acid, and creatinine. All of these substances are produced from protein metabolism. In many animals, the urine is the main route of excretion for such wastes; in some, it is the feces.
How do animals excrete waste?
Besides carbon dioxide, compounds of nitrogen arise from metabolism and are eliminated, chiefly by the kidney, in the urine (excretion). Food not digested is eliminated through the anus (defecation). These processes are characteristic of animals in general, but not of plants.
What is nitrogen excretion?
The removal of unusable or excess nitrogen from a cell or a living organism.
What is the advantage of excreting urea rather than ammonia as waste?
Ammonia is toxic in part because it raises the pH of the bodily fluids. Urea actually requires far less energy to produce than uric acid, but uric acid has the advantage of reducing water loss and is less toxic.
What animal excretes uric acid?
Birds, reptiles and desert dwelling animals excrete uric acid as a semi-solid material in their gut excreta, by a complicated, high energy-demanding process. Yet this has the advantage of conserving much-needed water. Interestingly, birds' manure known as “guano” is known as high-quality plant fertilizers [3].
Where does the waste product urea come from?
Urea is produced in the liver and is a metabolite (breakdown product) of amino acids. Ammonium ions are formed in the breakdown of amino acids. Some are used in the biosynthesis of nitrogen compounds. Excess ammonium ions are converted to urea.
Which of the following is an advantage of excreting nitrogenous wastes as urea rather than as ammonia?
African lungfish, which are often found in small, stagnant pools of fresh water, produce urea as a nitrogenous waste. What is the advantage of this adaptation? A) Urea takes less energy to synthesize than ammonia.
Where does meat get its nitrogen?
Meat eating animals get their nitrogen from the amino part of the amino acid constituent of protein. There is probably more in some proteins. Its probably the same for herbivores. Beef farmers and mutton farmers used to introduce dehydrated meat powder and urine derivatives. A lot of this was stopped after CJD.
How do plants get nitrogen?
Plants get nitrogen two ways. By extracting it out of organic matter in the soil and from lightning. The atmosphere is 78% N and lightning strikes convert that N into a usable form for plants.
What is the process of nitrifying bacteria?
Nitrifying bacteria in the soil convert ammonia into nitrite (NO2-) and then into nitrate (NO3-). This process is called nitrification. Compounds such as nitrate, nitrite, ammonia and ammonium can be taken up from soils by plants and then used in the formation of plant and animal proteins.
What does lightning do to soil?
Through lightning: Lightning converts atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia and nitrate (NO3) that enter soil with rainfall.
How does denitrification complete the nitrogen cycle?
Denitrification completes the nitrogen cycle by converting nitrate (NO3-) back to gaseous nitrogen (N2). Denitrifying bacteria are the agents of this process. These bacteria use nitrate instead of oxygen when obtaining energy, releasing nitrogen gas to the atmosphere.
What is the nitrogen gas in soil?
Biologically: Nitrogen gas (N2) diffuses into the soil from the atmosphere, and species of bacteria convert this nitrogen to ammonium ions (NH4+), which can be used by plants. Legumes (such as clover and lupins) are often grown by farmers because they have nodules on their roots that contain nitrogen-fixing bacteria. (Learn more about this process in the article The role of clover .)
How is nitrogen added to fertilizer?
Nitrogen is added mainly as a liquid or solid fertilizer, either naturally through animal manure (like cattle, sheep or horse), or man-made as highly concentrated pellets or in liquid form (as a powder or pellet mixed with water or another liquid-based fertilizer). Urea (as around 40 to 46% N with a lot of other filler, making a 40-0-0 or 46-0-0) is one of the more common means of adding nitrogen, since ammonia nitrate is now so heavily regulated it's almost outlawed because it's a simple bomb-making material when combined with diesel. Nitrogen also comes in other combined forms with other nutrients like phosphorus (mono-ammonium phosphate, for example) or sulphur (ammonium sulphate).
How do animals get rid of waste?
Excretion in Animals: Have you ever wondered how animals get rid of waste matter from their body? Are they toxic in nature? What are the nitrogenous wastes that animals eliminate from their body? Yes, animals excrete waste from their body through various specific excretory organs based on their adaptation and body features. Maintenance of a steady-state or constant internal environment, called homeostasis, is the essential requirement for normal life processes. Animals accumulate uric acid, carbon dioxide, ammonia, urea, water, and ions like K+, Cl-, Na+, sulphate, phosphate, etc., either by metabolic activities or by other means like excess ingestion. Animals must regulate water and salt balance in the body and eliminate nitrogenous wastes. All these functions are interrelated.
What is the elimination of ammonia as the chief nitrogenous waste material?
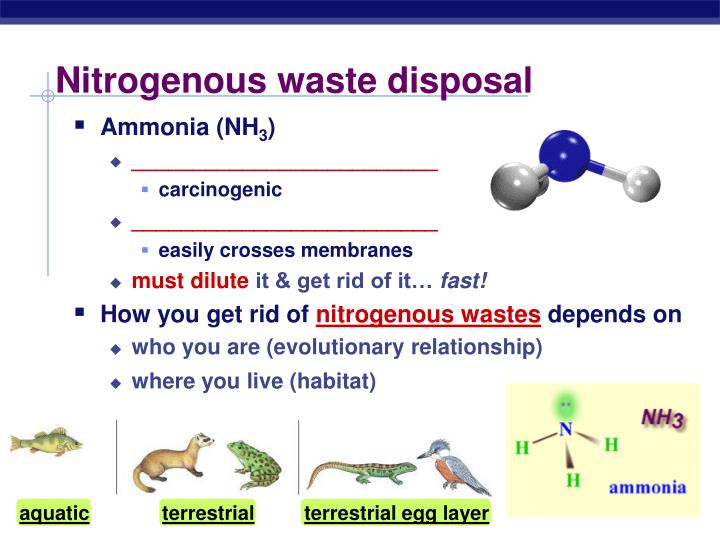
1. Ammonotelism: The elimination of ammonia as the chief nitrogenous waste material is termed ammonotelism. Ammonia is formed by the oxidative deamination of amino acids. Ammonia is extremely poisonous and readily dissoluble in water. Hence it should be removed from the body quickly and in the form of a very dilute solution. In many invertebrates, ammonia is excreted through the surface of the body. In fishes, most of the ammonia is lost as NH₂+ across the epithelium of the gills, and kidneys excrete only minor amounts of nitrogenous wastes.
What are some examples of aminotelic animals?
Examples of Aminotelic Animals: Echinoderms and molluscs are the best examples of aminotelic.
How many modes of excretion are there in animals?
Based on the excretory product, five modes of excretion are known in animals. They are:
Where is excretion carried out?
Excretion in humans is carried out through kidneys, lungs and skin.
What are some examples of excretory products?
Excretion Examples & Structures 1 All vertebrates have kidneys – Excretory product is urea 2 Flame cells in planaria 3 Earthworms have Nephridia 4 Cockroaches have malpighian tubules 5 Prawns have antennal glands or green glands
How is urea excreted?
In some mammals and amphibians, urea is excreted as the metabolic waste products. Such organisms are called ureotelic. In these organisms, ammonia that is produced is converted to urea in the liver of animals and is released back into the blood. The kidneys filter the urea and are expelled outside the body. Some of the urea is retained in the matrix of the kidney to maintain a desired osmolarity in the organisms. Humans are ureotelic as we expel the urea through urine. Moreover, urea is comparatively less toxic than ammonia.
What are the most common metabolic wastes?
Nitrogenous wastes are formed as a result of metabolic cellular activities. The most common metabolic wastes are ammonia, urea, and uric acid.
What is the process of eliminating ammonia from the body?
The process of eliminating ammonia from the body is known as ammonotelism, and the organisms which exhibit this nature are called ammonotelic. Most fish, protozoans, echinoderms, poriferans and crustaceans fall into this category. Aquatic animals excrete ammonia directly into the environment; where the compound is quickly diluted.
Why is urea retained in the kidney?
Some of the urea is retained in the matrix of the kidney to maintain a desired osmolarity in the organisms. Humans are ureotelic as we expel the urea through urine. Moreover, urea is comparatively less toxic than ammonia.
