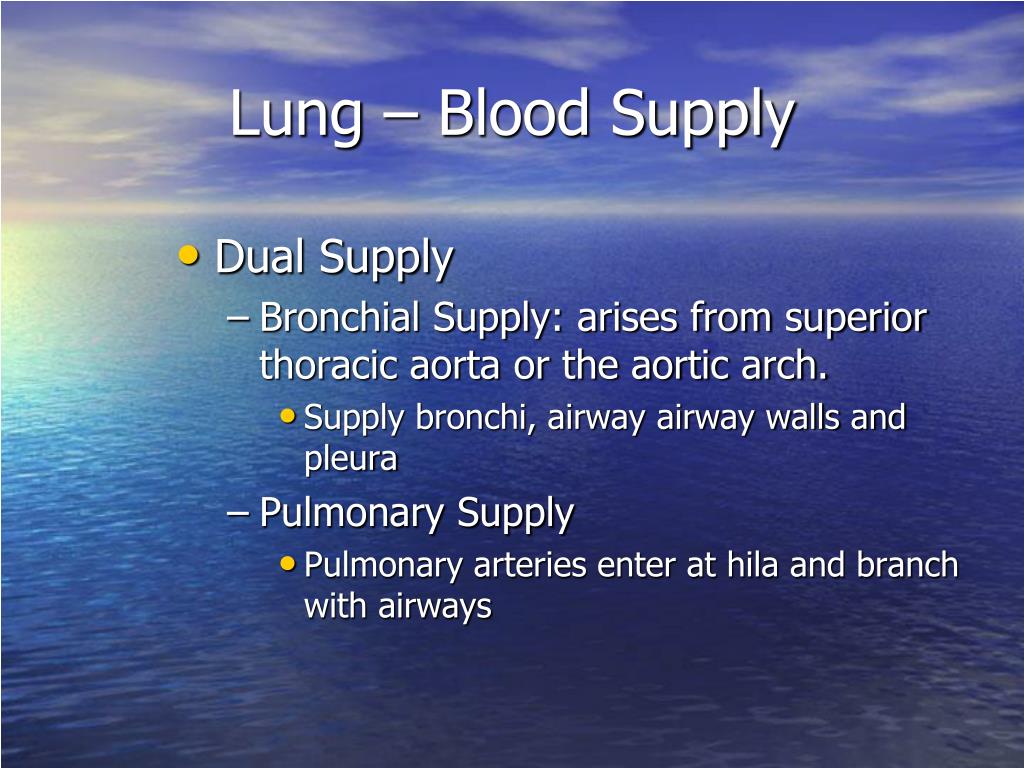
Blood Supply to the Lungs The lungs receive blood via two sets of arteries : pulmonary arteries and bronchial arteries. Deoxygenated blood passed through the pulmonary trunk, which divides into a left pulmonary artery that enters the left lung and a right pulmonary artery that enters the right lung.
Why do the lungs need a very good blood supply?
- Thin lining: the lining of the alveoli is very thin so that gases can quickly diffuse through it.
- Large surface area: human lungs contain about 500 million alveoli, which creates a surface area around half the size of a tennis court. ...
- Good blood supply: the alveoli have a dense capillary network so that large volumes of gases can be exchanged.
Which blood vessel carries blood to the lungs?
pulmonary artery. a blood vessel that carries oxygen poor blood from heart to lungs. systole. contraction phase of heartbeat. mitral valve. located between the left upper and lower chambers of the heart. pericardium. saclike membrane surrounding the heart. SA node sinoatrial node.
Why does the blood flow through the lungs?
Blood flow through the capillary beds reaches almost every cell in the body and is controlled to divert blood according to the body’s needs. After oxygen is removed from the blood, the deoxygenated blood flows to the lungs, where it is reoxygenated and sent through the veins back to the heart. Key Terms. arteriole: ...
How does blood flow through the body and lungs?
What are the steps of blood flow?
- The blood first enters the right atrium.
- The blood then flows through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle.
- When the heart beats, the ventricle pushes blood through the pulmonic valve into the pulmonary artery.
See more
Do the lungs have a blood supply?
Vasculature. The lungs have dual blood supplies. The bronchial circulation is part of the systemic circulation and has a high pressure and high oxygen content. Bronchial arteries most often arise from the descending aorta and “feed” the bronchial tree as far as the respiratory bronchiole.
What blood vessels feed the lungs?
In human anatomy, the bronchial arteries supply the lungs with nutrition and oxygenated blood.
How many blood vessels are in the lungs?
There are 4 total pulmonary veins—with 2 pulmonary veins coming from each lung, left and right—that empty into the left atrium of the heart. Two pulmonary veins emerge from the hilus of each lung, and each pulmonary vein receives blood from 3-4 bronchial veins apiece before draining into the left atrium.
Which artery takes the blood to the lungs for oxygenation?
The pulmonary arteryThe pulmonary artery carries oxygen-poor blood from the right ventricle into the lungs, where oxygen enters the bloodstream. The pulmonary veins bring oxygen-rich blood to the left atrium.
What system does the lungs work with?
Although they are the primary site of gaseous exchange, the lungs work in conjunction with the musculoskeletal system of the thorax ( ribs, sternum, diaphragm, and other accessory muscles) to facilitate inhalation and exhalation. Key facts about the lungs. Surfaces.
What are the lungs?
The human lungs are a pair of spongy organs within the thoracic cavity that facilitate gaseous exchange. They are a part of the respiratory system, which also includes the nose, nasal sinuses, mouth, pharynx, larynx, and trachea.
What are the stages of development of the pulmonary plexus?
Pulmonary plexus (vagus nerve, cervical cardiac nerves) Embryology. Four stages of development - pseudoglandular, canalicular, terminal sac, alveolar stages. The goal of this article is to explore the embryology and anatomy of the human lungs. It will also include a brief review of the respiratory tract.
How many segments does the left lung have?
The lobes are then further subdivided into bronchopulmonary segments; such that the left lung has 9 – 10 segments, while the right lung has 10. Between lobes are interlobar surfaces of lungs which are separated by fissures of the lungs. The apex is the highest point of the lung, extending into the thoracic inlet.
Why is the left lung different from the heart?
In order to accommodate the left-sidedness of the heart, the left lung has less tissue in the anteromedial region of the organ. Consequently, the left lung appears morphologically different from the lung such that it has one less fissure and one less lobe. The oblique fissure of the left lung divides the organ into the superior and inferior lobes.
How many surfaces does the lung have?
Alternatively, we can describe the lung as having three surfaces ( costal, medial and diaphragmatic) which are divided by three borders ( anterior, posterior and inferior ). The organs are roughly conical in shape and are divided by fissures into lobes.
How much does the left lung weigh?
The morphological difference between the left and right lungs is also reflected in the weight of the organs; as the left (565 g) weighs less than the right (625 g). They also tend to be heavier in men than they are in women; although this feature is dependent on the height of the individuals.
Which system supplies the lungs with oxygenated blood?
There are two sets of arteries. The transport system needs a relatively small amount of oxygenated blood and the bronchial system is supplied by the bronchial arteries, while the exchange system has needs to supply a tennis court sized surface are and is supplied by the larger pulmonary arterial system.
Where does blood flow from the pulmonary artery?
At the capillary level, all the blood supplied by the pulmonary artery drains into the alveolar capillaries where they become oxygenated and then drain into the pulmonary venules within the interlobular septa, and finally back to the left atrium.
What is the RPA in the chest?
The right pulmonary artery (RPA) takes almost a 140-degree turn from the main pulmonary artery. It rests on the top of the left atrium (LA) and has a straight shot in the direction of the midaxillary line. Thus on a lateral examination of the chest the LPA has the shape of an umbrella handle and the RPA is seen as an ovoid or rounded structure as we look down its barrel. The pulmonary veins are all inferior to the pulmonary arteries at the hilum.
How many veins are in the pulmonary artery?
At the most central portion of each hilum there are usually 2 veins, one artery and one bronchus. This is because the length of the bronchus and artery prior to division is relatively long, while the confluence of the veins is close to the entrance into the left atrium. Thus the superior veins from the upper lobes are anterior and the veins to the inferior lobes are posterior. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD 31592
What is the lateral examination of the right pulmonary artery?
The lateral examination serves to demonstrate the ovoid appearance of the right pulmonary artery (*) as it courses above the LA to the right midaxillary line, together with the more cranially placed arching shape of the LPA (**) which courses posteriorly. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD 30398c04
What are the two bronchial arteries?
There are usually two bronchial arteries. The left artery arises from the aorta, and the right arises either from the 3rd intercostal artery (30%), with the 3rd intercostal as a common origin (intercostobronchial artery), from the thoracic aorta, or from one of the other proximal intercostal arteries. It is not uncommon to have 3 or 4 intercostal arteries.#N#The bronchial arteries supply the bronchi and the tissue of the lungs with oxygenated blood. As systemic vessels their pressure is at systemic levels, with a mean pressure that is 5-6 times higher than the mean pulmonary pressure (15mmHg.).
Which bronchus can you jump over?
If you recall the LPA has the ability to high jump over the left mainstem bronchus, while the RPA has to be satisfied with a jump between bronchus intermedius below and the RUL bronchus above.
How do lungs work?
How do my lungs work? Your lungs make oxygen available to your body and remove other gases, such as carbon dioxide, from your body. This process takes place 12 to 20 times per minute. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center.
Which tube leads to the left lung?
One bronchial tube leads to the left lung, the other to the right lung. For the lungs to perform their best, the airways need to be open during inhalation and exhalation and need to be free from inflammation (swelling) and abnormal amounts of mucus.
How many lobes does the right lung have?
The right lung has 3 sections called lobes and is a little larger than the left lung, which has 2 lobes. The bronchial tubes divide into smaller air passages called bronchi, and then into bronchioles. The bronchioles end in tiny air sacs called alveoli, where oxygen is transferred from the inhaled air to the blood.
What is the name of the tube that leads to the right lung?
Your trachea is divided into 2 air passages called bronchial tubes. One bronchial tube leads to the left lung, the other to the right lung.
Why do lungs lose elasticity?
Healthy lungs are elastic so they can expand when you exhale. In contrast, a disease like emphysema causes the lungs to lose their elasticity. When a person's lung can no longer expand properly or transfer oxygen to the blood, that person has difficulty breathing and tires easily.
What happens to the body after you absorb oxygen?
After absorbing oxygen, the blood leaves the lungs and is carried to the heart. The blood then is pumped through your body to provide oxygen to the cells of your tissues and organs. When cells use oxygen, carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) is produced and transferred to the blood. Your blood carries the CO 2 back to your lungs and it is removed when you exhale.
Friday, April 24, 2009
The lungs receive blood via two sets of arteries : pulmonary arteries and bronchial arteries. Deoxygenated blood passed through the pulmonary trunk, which divides into a left pulmonary artery that enters the left lung and a right pulmonary artery that enters the right lung.
Blood Supply to the Lungs
The lungs receive blood via two sets of arteries : pulmonary arteries and bronchial arteries. Deoxygenated blood passed through the pulmonary trunk, which divides into a left pulmonary artery that enters the left lung and a right pulmonary artery that enters the right lung.
How do the lungs produce oxygenated blood?
The Lungs CREATE oxygenated blood by allowing the transfer of gasses at the molecular level through our alveoli, the tiny air sacs that are surrounded by capillaries.
Why does blood travel to the lungs?
Blood travels to the lungs because it is not oxygenated and it will become oxygenated in the lungs, since that is what the lungs are for. The pulmonary artery takes blood to t…he lungs, and the pulmonary vein takes blood from the lungs back to the heart, from whence it is pumped throughout the body.
How do the airways work in the lungs?
Think of your lung airway passages as a system of tubes being built sort of like a tree, only upside-down. The trachea is the trunk and the bronchi are the first “fork”. At the ends of the smallest branches are the alveoli—tiny little sacs with walls only one or two cells thick. The heart pumps blood that it has received from the veins into the lungs. This blood travels from the heart to the lungs via the pulmonary arteries. These arteries branch repeatedly, until the blood is running through very thin-walled capillaries that run between the alveolar air sacs. Gases diffuse easily across the air sac membranes. Oxygen we breathe in flows into the blood, and carbon dioxide flows out and we exhale it.
What makes blood oxygenated?
The lungs make oxygenated blood. In other words, the lungs facilitate the transfer of oxygen from inspired air to the deoxygenated blood thus making it oxygenated.
Where does oxygen come from in the lungs?
From the bronchial arteries. The alveoli get oxygen directly from the atmosphere so only the conducting portion of the lungs actually needs oxygenated blood.
How does oxygen move through the alveoli?
Even with the cells lining the alveoli and capillaries these small distances support diffusion of O2 and CO2. By bringing blood and air into close approxim ation oxygen can move rapidly into blood and carbon dioxide move the other direction .
Which veins supply oxygenated blood to the rest of the body via the heart?
The pulmonary veins supply oxygenated blood to the rest of the body via the heart.