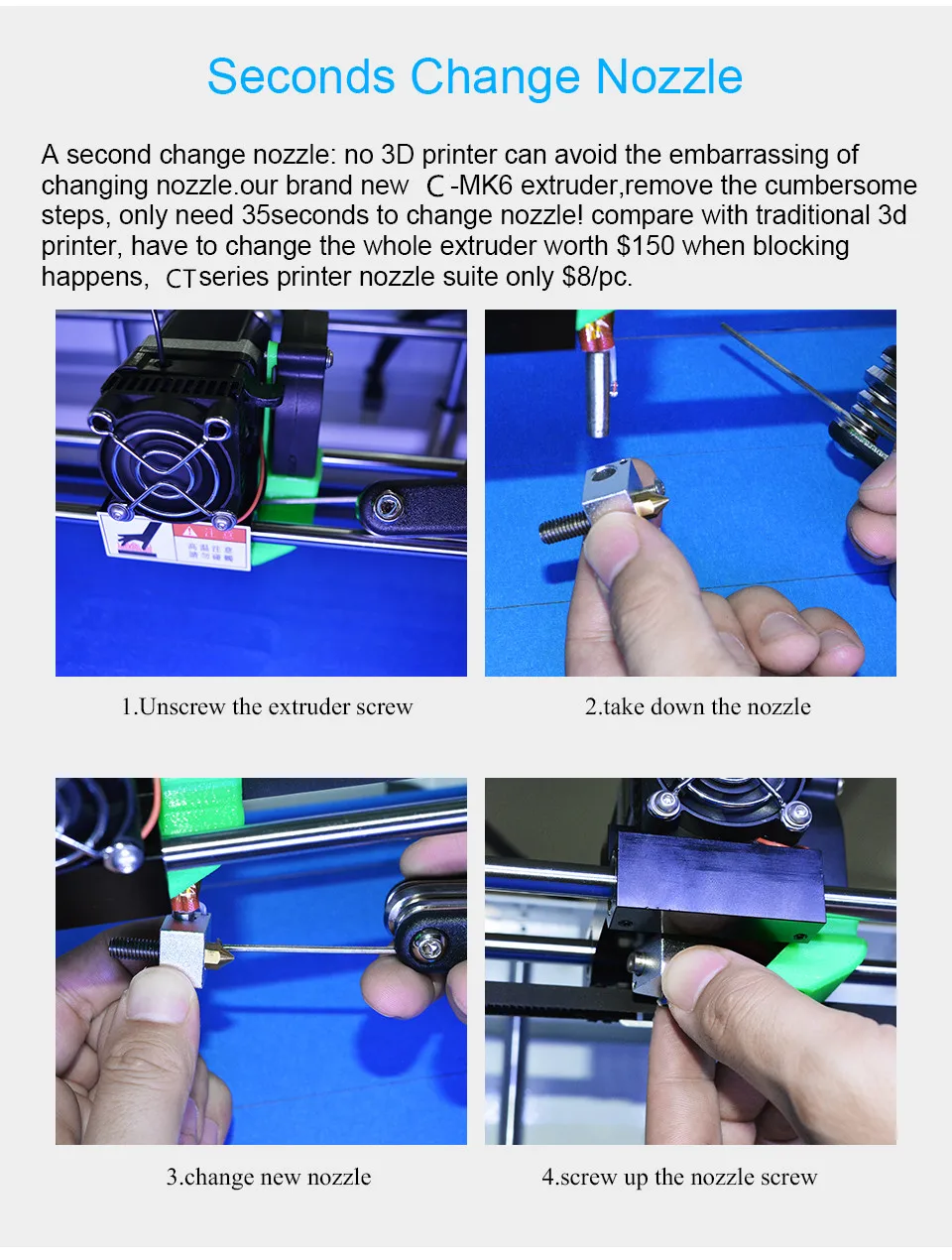
What can you do with metal 3D printing?
Support in metal 3D printing serves 3 different functions:
- They offer a suitable platform for the next layer to be built upon.
- They anchor the part to the build plate and they prevent warping.
- They act as a heat sink drawing heat away from the part and allowing it to cool at a more controlled rate.
What are the advantages of metal 3D printing?
Advantages of Metal 3D Printing. One of the main benefits of metal 3D printing is that it can shorten product development cycles and generate more revenue. While product development is a continuous process, the more iteration a product goes through, the better it gets. However, the process of iteration can be quite expensive and can lead to ...
Can 3D printers be used to make metal hardware?
Yes you can. Metal printers are very expensive though (+$500,000) so the best thing would be to order parts from a service. There are three popular metal 3D printing processes Prometal, DMLS and EBM.
How to make my own 3D printer?
What are The Steps to Make Your Own 3D Printer?
- Define the Design and Specs. As you want to make your own 3D printer, you may have a look and feel of the design in your head. ...
- List and Buy Parts. You will find many online websites listing the parts required to build the 3D printer. ...
- Take it Slow. You must understand that the project won’t complete in a week. ...
- Test it. Now comes the testing phase. ...
How does a 3D printer use metal?
The metal 3D printing process involves sintering or melting metal powders directly, or combining them with a second material to allow delivery through a nozzle. It is used for both rapid prototyping and finished production parts for aerospace, mechanical engineering, tooling and more.
Is metal 3D printing a thing?
Metal 3D printing, or selective laser melting (SLM), combines the design flexibility of 3D printing with the mechanical properties of high-performance metal alloys to create unique, strong, and lightweight parts, even for the most complex applications.
Are metal 3D printed parts strong?
Tests showed that under certain conditions the final 3D printed stainless steels were up to three times stronger than steels made by conventional techniques and yet still ductile, the scientists report today in Nature Materials .
What metal do metal 3D printers use?
Titanium. This metal is strong, incredibly lightweight, and heat and chemical resistant. Normally, titanium is extremely challenging to machine (contributing to its high cost), making it a great metal 3D printing material.
Is metal 3D printing expensive?
The cost of metal 3D printing today is very high when compared to traditional manufacturing methods. A typical DMLS/SLM part will cost you approximately $5,000 to $10,000 to 3D print and finish.
Can you 3D print a gun?
In 2013 a Texas company, Solid Concepts, demonstrated a 3D printed version of an M1911 pistol made of metal, using an industrial 3D printer. In 2014, a New Zealand company, Oceania Defence, demonstrated 3D printed titanium suppressors that are 50% lighter than conventional ones. The Grizzly is a 3D printed .
How long do 3D printed items last?
In short, when you place PLA under normal room temperature, it can last for a very long time – say 12 to 18 years. Depending on where and how you store it, 3D printed objects made from PLA can last from a month, to 2 years and up to many years. It can break down at different rates depending on its environment.
How much power does a metal 3D printer use?
The average 3D printer with a hotend at 205°C and heated bed at 60°C draws an average power of 70 watts. For a 10-hour print, this would use 0.7kWh which is around 9 cents. The electric power your 3D printer uses depends mainly on the size of your printer and the temperature of the heated bed and nozzle.
Is 3D printed metal stronger than forged?
The most common question when it comes to 3D-printed steel is: “Is it as strong as forged or cast steel.” The short answer is yes … and no. 3D printed steel parts can be as strong or stronger than steel parts made with traditional manufacturing.
Can u make money with a 3D printer?
Yes, you can make money with a 3D printer. And there are a lot of ways that you can do it, whether that's selling 3D printed items, digital goods, or even offering a 3D printing service in your local area.
Can 3D printers print glass?
Glass 3D Printing 2 (G3DP 2) enables an entirely unique means of digital design and fabrication with glass. It is a high fidelity, large-scale, additive manufacturing technology for 3D printing optically transparent glass structures at architectural dimensions.
How is steel 3D printed?
The most widely used method for metal 3D printing is SLM, which is also called direct metal laser sintering (DMLS) or laser powder bed fusion (LPBF). LPBF 3D printers use high-powered lasers to selectively melt a metal powder.
Is 3D printing only plastic?
Plastic is still the most popular material used for 3D printing. As the 3D-printing market value increases, the list of what materials can be used also grows. Raw materials such as metal, graphite, and carbon fiber are commonly used for 3D printing, though at-home use is mostly limited to PLA for now.
When was 3D metal printing invented?
The origins of direct metal 3D printing can be traced back to 1994, when EOS first introduced its EOSINT M250 machine. This machine was based on direct metal laser sintering (DMLS) technology.
How is steel 3D printed?
The most widely used method for metal 3D printing is SLM, which is also called direct metal laser sintering (DMLS) or laser powder bed fusion (LPBF). LPBF 3D printers use high-powered lasers to selectively melt a metal powder.
What material is not used in 3D printing?
Materials such as wood, cloth, paper and rocks cannot be 3D printed because they would burn before they can be melted and extruded through a nozzle.
What can you manufacture with metal 3D printing?
Metal 3D printing is a suitable manufacturing process for making complex, custom parts that are difficult or very costly to manufacture with more t...
Is metal 3D printing expensive?
As opposed to most of the other additive manufacturing processes, metal 3D printing is quite expensive. For example, you can pay upwards of $450 fo...
How do you reduce the cost of metal 3D printing?
Reducing the material required is key to lowering the overall price of metal 3D printing. Two ways to do this are to minimize the part volume and g...
What is metal 3D printing commonly used for?
You’ll likely see metal 3D printing commonly used for prototyping in production-grade materials and producing functional, end-use parts. It’s also...
Are support structures required for metal 3D printing?
Support structures are always required when manufacturing parts with metal 3D printing. This is due to the extremely high processing temperature. U...
What are the best alternatives for metal 3D printing?
While metal 3D printing can produce impressively complex and robust parts, the high cost may have you searching for a viable alternative. One recom...
Can you 3D print aluminum parts?
For the most part, aluminum is the primary alloy used in metal 3D printing. This is due to its high flexibility, strength and impressive thermal pr...
Can you 3D print with stainless steel?
Similarly to aluminum (and also titanium), you can use stainless steel to 3D print complex and often much larger parts, thanks to the material’s st...
How does metal 3D printing work?
The basic fabrication process for SLM and DMLS are very similar. Here is how it works:
What is the difference between SLM and DMLS?
Essentially: SLM produces parts from a single metal, while DMLS produces parts from metal alloys. Both SLM and DMLS are used in industrial applications to create end-use engineering products. In this article, we use the term metal 3D printing to refer to both processes in general and we describe the basic mechanisms of the fabrication process ...
How does SLM work?
Here is how it works: The build chamber is first filled with inert gas (for example argon) to minimize the oxidation of the metal powder and then it is heated to the optimal build temperature.
How to make a DMLS?
The basic fabrication process for SLM and DMLS are very similar. Here is how it works: 1 The build chamber is first filled with inert gas (for example argon) to minimize the oxidation of the metal powder and then it is heated to the optimal build temperature. 2 A thin layer of metal powder is spread over the build platform and a high power laser scans the cross-section of the component, melting (or fusing) the metal particles together and creating the next layer. The entire area of the model is scanned, so the part is built fully solid. 3 When the scanning process is complete, the build platform moves downwards by one layer thickness and the recoater spreads another thin layer of metal powder. The process is repeated until the whole part is complete.
What is SLM in 3D printing?
Selective Laser Melting (SLM) and Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) are two metal additive manufacturing processes that belong to the powder bed fusion 3D printing family. The two technologies have a lot of similarities: both use a laser to scan and selectively fuse (or melt) the metal powder particles, bonding them together and building a part layer-by-layer. Also, the materials used in both processes are metals that come in a granular form.
How high is the layer height in 3D printing?
In SLM and DMLS almost all process parameters are set by the machine manufacturer. The layer height used in metal 3D printing varies between 20 to 50 microns and depends on the properties of the metal powder (flowability, particle size distribution, shape etc).
Why is topology optimization important in metal printing?
Since the cost of metal printing is very high, simulations are often used to predict the behavior of the part during processing. Topology optimization algorithms are also used not only to maximize the mechanical performance and create lightweight parts but also to minimize the need of support structure and the likelihood of warping.
How does DMP work?
DMP is a powerful 3D Printing technology that shapes any desired metal part geometry by melting metal powder layer by layer. This technology is applied to build up material in layers instead of removing it in different steps. The metal powder particles pinpointed by the laser quickly and fully melt so that the new material properly attaches to the previous layer, without glue or binder liquid. A powerful fiber laser with high energy intensity operates in the inert area inside the machine. This guarantees that the metal parts being built exhibit a dense and homogenous material structure. The CAD design of the parts directly drives the DMP production machines without the need for programming, clamping or tooling.
What is a DMP 3D printer?
But the difference is in the detail and experience. DMP printers from 3D Systems have been used to manufacture over 500k metal parts. This experience has been designed into robust metal 3D Printers for repeatability, part quality, productivity and a low total cost of operation (TCO). Removable Print Modules (RPMs) allow change-over times of 1 hour and 24/7 uptime. The vacuum chamber enables Oxygen (O 2) content of <25ppm for consistent part properties and full powder usage keeping waste to a minimum. When part quality, volume and efficiency matter - DMP is the best choice for 3D Printing metal.
What is powder bed fusion?
Powder Bed Fusion (PBF) is a term that summarizes all technologies that selectively melt and fuse metal and plastic powder to build up complex parts directly from CAD files. PBF methods use either a laser (DMP/DMLS/SLS) or an electron beam (EBM) and different approaches to spreading or applying the powder with rollers or blades. Direct Metal Printing (DMP) is a laser-based metal 3d Printing technology that applies the material in both directions (bi-directional re-coating), counts on a vacuum chamber for oxygen exposure of consistently <25ppm for repeatable high part properties and uses a Removable Print Module (RPM) for short changeover times and 24/7 uptime.
What is DMP in metal?
Direct Metal Printing (DMP), also commonly known as Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS), is an additive manufacturing technology that builds high quality complex metal parts from 3D CAD data. In the machine, a high precision laser is directed to metal powder particles to selectively build up thin horizontal metal layers one after the other. This cutting edge technology allows for the production of metal parts with challenging geometries, not possible using traditional subtractive or casting technologies. A variety of functional metals are available to print designs, from prototypes to production series of up to 20,000 units.
What is DMP in aerospace?
DMP is an ideal technology for aerospace and defense applications. It allows for the production of small and extremely complex shapes with no need for tooling, and it permits dramatically different part design than conventional processes like machining, stamping or die casting will allow.
Does DMP meet DMLS requirements?
DMP not only meets the needs for DMLS requirements, it exceeds them.
How to reduce assembly time and cost?
Reduce assembly time and cost by eliminating the need of sub-assembly labor and jigs and fixtures
From plastic to metal
Since the first 3D printers appeared in the 1980s, its applications have continued to grow. Initially, the technology was relatively unknown, according to Live Science, but gained popularity in the 21st century. In the early years of 3D printing, it was used mainly for speedy prototyping and the filament available was limited to plastics.
Space application
Metal printing is favoured by many engineers tasked with making space-based components such as metal parts for rockets. Because rocket engines need to be able to withstand very high temperatures, an Inconel copper superalloy powder is often chosen.
Melting metal
From digital file to metal part, follow the steps of the metal printing process in the following interactive image.
Additional resources
What's next for metal 3D printing in space? You can read about the progression towards autonomous 3D printing in space in this article by NASA. Or, learn more about how 3D printing can assist Space Station Research.
How does EBM work?
EBM uses an electron beam of around 6kW to melt the powder bed. Also, the powder particles are much bigger in size compared to DMLS powder. The printing data is prepared by slicing the 3D Cad model along with supports into numerous layers. The slicing is done with a much higher layer thickness compared to that of DMLS.
How does a ceramic nozzle work?
A heating element is present just before the nozzle to soften the material helping in easier deposition. The nozzle moves along the x and y axes to deposit heated material on the build plate. After printing a layer, the build platform goes down by a layer thickness and the nozzle again deposits materials as per the details of the next layer. This repeats until the final layer is printed. Ceramic media is printed in between the support and the part for easier support removal during post-processing.
What is a recoater?
A recoater uniformly spreads metal powder on the build platform. The inkjet head having numerous tiny nozzles selectively deposits droplets of a binding agent over the metal powder. The binding agent containing wax and polymer, fills in the void between the metal particles, thus creating a bond. Once this is done, the build platform moves downward by a layer thickness and the process is repeated until the final layer is printed. The printed part is in a fragile green state and needs further post-processing to strengthen the part.
How thick is a 3D CAD model?
These slices have specific thickness ranging from 20microns to 100 microns and provide the necessary data for printing each layer.
What is direct energy deposition?
Direct Energy Deposition uses either metal powder or wire as the raw material and laser beam or electron beam as the melting source for printing metal layer by layer.
What is 3D printing?
3D printing, in general, is a revolutionary technology which uses just the 3D CAD data of a component to create the physical component layer by layer.
Why is the build chamber closed?
The build chamber is closed and vacuum is created in the entire build chamber to minimize oxidation. A layer of powder is spread on the build platform and the Electron Beam first heats the entire powder bed to an optimal temperature and then selectively melts the metal powder.
SLM (Selective Laser Melting) process
SLM is the abbreviation of Selective Laser Melting, which is a process that creates products additively as it fuses metal powder particles together. With this process, the metal part will be created layer by layer. Eventually your 3D design will be created because of this, which is also the case for other additive manufacturing techniques.
DMLS (Direct Metal Laser Sintering) technology
DMLS, or Direct Metal Laser Sintering, can be used as well. 3D printers used in DMLS technology additively manufactured parts by sintering fine particles of metal powder to fuse them locally. Because of this, it is very similar to the SLS process, which can be used to produce plastic parts with the help of a 3D printer.
Additive manufacturing process: Binder jetting
Binder Jetting is another additive manufacturing process that can create metal parts as well. This method works with a binding agent, as its name already suggests. This liquid binder is deposited on the powder, depending on the 3D file you want to make.
