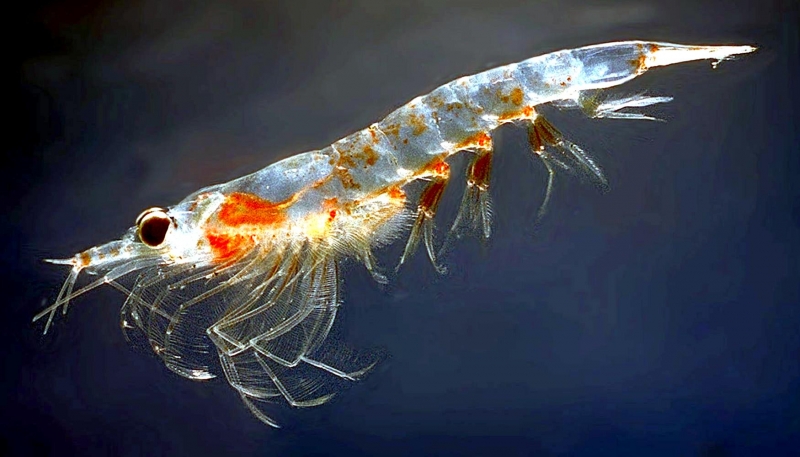

Who eats phytoplankton in an aquatic food web?
Phytoplankton and algae form the bases of aquatic food webs. They are eaten by primary consumers like zooplankton, small fish, and crustaceans.
What is a plankton food web?
Structure and Function of Plankton Food Webs in Florida Aquatic Ecosystems - UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA Plankton are a primary source of food for economically important fish and comprise the base of a food web that supports many other aquatic biota.
What do plankton do in the ocean?
They drift about in the water, allowing tides, currents, and other factors determine where they go. There are two main types of plankton: phytoplankton, which are plants, and zooplankton, which are animals. Zooplankton and other small marine creatures eat phytoplankton and then become food for fish, crustaceans, and other larger species.
How do phytoplankton make their energy?
Phytoplankton make their energy through photosynthesis, the process of using chlorophyll and sunlight to create energy. Like other plants, phytoplankton take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen. Phytoplankton account for about half of the photosynthesis on the planet, making them one of the world’s most important producers of oxygen.
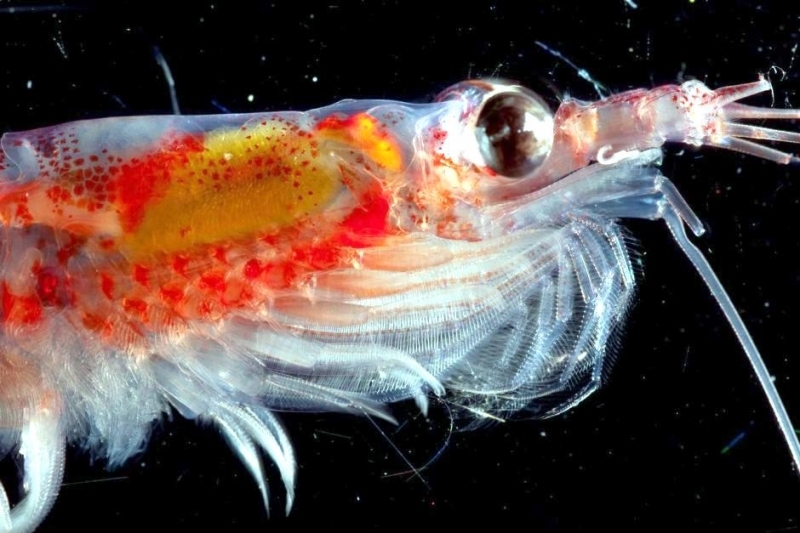

Why are plankton at the base of the food web?
Producers. Primary producers — including bacteria, phytoplankton, and algae — form the lowest trophic level, the base of the aquatic food web. Primary producers synthesize their own energy without needing to eat. Many photosynthesize, using the sun's energy to build carbohydrates.
What forms the base of the ocean food web?
At the base of the ocean food web are single-celled algae and other plant-like organisms known as phytoplankton. Phytoplankton are a group of microscopic autotrophs divided into a diverse assemblage of taxonomic groups based on morphology, size, and pigment type.
What is the role of plankton in the ocean?
Phytoplankton are microscopic plants, but they play a huge role in the marine food web. Like plants on land, phytoplankton perform photosynthesis to convert the sun's rays into energy to support them, and they take in carbon dioxide and produce oxygen.
How does plankton produce food?
Most of the plankton in the ocean are plants. Phytoplankton produce their own food by lassoing the energy of the sun in a process called photosynthesis. So for sunlight to reach them, they need to be near the top layer of the ocean.
Is plankton a producer?
In the marine food web, special producers are found. They are tiny microscopic plants called phytoplankton. Since the water is the home for these special tiny plants; it is also the home for tiny microscopic animals called zooplankton. And of course, zooplankton eat phytoplankton.
What does phytoplankton feed on?
Phytoplankton rely on nutrients found in their surroundings, such as phosphate, nitrate, and calcium, to thrive. In addition to phytoplankton and zooplankton, two even smaller kinds of plankton can be found floating in the sea. Bacterioplankton are bacteria and virioplankton are viruses.
How does phytoplankton tiny plants obtain energy from the ocean ecosystem?
Like land plants, phytoplankton have chlorophyll to capture sunlight, and they use photosynthesis to turn it into chemical energy. They consume carbon dioxide, and release oxygen. All phytoplankton photosynthesize, but some get additional energy by consuming other organisms.
Where do plankton live in the ocean?
They are mostly found in the sunlit zone of the water column, less than 200 metres deep, which is sometimes called the epipelagic or photic zone. Ichthyoplankton are planktonic, meaning they cannot swim effectively under their own power, but must drift with the ocean currents.
What would happen if there was no plankton?
Plankton are the base of the marine food web, without them all larger organisms will probably die. No plankton=no fish= no food for millions of people. Without ocean life millions (if not billions) of people will start to starve.
What are plankton considered in the food chain?
(singular: plankton) microscopic aquatic organisms. organism that eats producers; herbivores. organism on the food chain that can produce its own energy and nutrients. Also called an autotroph.
How do plankton reproduce?
Brooding of eggs on the body in a sac or release of egg cases into the plankton aids in the development of several invertebrates. Asexual reproduction can also occur in planktonic forms but seems to be less common in marine invertebrates. Asexual reproduction usually occurs through fission, or budding.
What animal is plankton Spongebob?
copepodsDid you know that the character Plankton from Spongebob is based on a real planktonic animal - the Copepod (shown above)? There are even specific group of copepods with one eye, just like Plankton, called Cyclops! There are two main types of plankton and most of them are microscopic.
What is at the bottom of the ocean food chain?
Phytoplankton are tiny plants that obtain their energy from the sun as they move around in the ocean. This group is at the bottom of the food web because they are a large producer for all living organisms within the ocean.
What is a food web in the ocean?
Many species consume more than one type of species, creating a complex web of interactions known as a food web. In the visual below, you can see an example of a food web in the open ocean ecosystem and also one food chain that is a part of that food web.
What is the food chain of the ocean?
A food chain in the ocean begins with tiny one-celled organisms called diatoms, which make their own food from sunlight. Shrimplike creatures eat the diatoms. Small fish eat the shrimplike creatures, and bigger fish eat the small fish.
What are the main producers of the ocean?
The principal marine primary producers are cyanobacteria, algae and marine plants.
What is plankton?
Plankton are a collection of tiny organisms that live at and beneath the surface of lakes, rivers, ponds, and oceans across the planet. They’re named for the Greek word planktos, meaning to drift or float. Plankton don’t swim on their own—they’re carried by tides, currents, and other forces, which determine where they go.
Different types of plankton
The two most prominent types of plankton in the ocean are zooplankton, which are tiny animal organisms, and phytoplankton, which are plantlike. (Other forms of plankton include bacterial and fungal.
Threats to plankton
Ocean acidification, caused by excess carbon dioxide dissolving in seawater, poses a significant threat to phytoplankton. A more acidic ocean will cause some types to grow slower, some to grow faster, and the balance among them to change, which could have big ripple effects for the higher levels of the food web.
Threats from plankton
When environmenmental conditions change, often triggered by too much of a nutrient—such as nitrogen or phosphorus from fertilizer runoff—populations of some types of phytoplankton can grow rapidly, in what’s called a “bloom.” Some blooms can be harmful, depleting oxygen in the water, blocking sunlight, and secreting toxins.
What are the primary consumers of aquatic food webs?
Primary consumers are in turn eaten by fish, small sharks, corals, and baleen whales.
What are the primary producers of the food web?
Primary producers — including bacteria, phytoplankton, and algae — form the lowest trophic level, the base of the aquatic food web. Primary producers synthesize their own energy without needing to eat. Many photosynthesize, using the sun’s energy to build carbohydrates. However, some primary producers can create energy without sunlight using chemosynthesis to metabolize chemicals released from hydrothermal vents, methane seeps, and other geological features.
How does changing the food web affect organisms?
However, changes in one part of the food web may cause a trophic cascade that affects organisms across multiple trophic levels. For instance, removing a top predator may cause its prey to become more abundant, as fewer individuals are eaten. But with more prey around, the organisms that it eats may become scarcer.
Why are humans important to the food web?
It is our responsibility to ensure that our fisheries are sustainable and that we are not polluting the ocean with toxins that bioaccumulate in food webs.
What is the food web?
education. Food webs describe who eats whom in an ecological community. Made of interconnected food chains, food webs help us understand how changes to ecosystems — say, removing a top predator or adding nutrients — affect many different species, both directly and indirectly. Phytoplankton and algae form the bases of aquatic food webs.
What animals graze on algae?
Larger animals, including some marine snails, fish, reptiles, and mammals, graze on algae. Filter feeders strain their food (plankton and detritus) directly from the water.
What animals are fed by filter feeders?
Filter feeders strain their food (plankton and detritus) directly from the water. Filter feeding animals include animals like bivalves, tube worms, sponges, and even large animals like baleen whales and manta rays. Predators more actively feed on other animals. There are many kinds of predators that feed on many kinds of prey.
What is the role of plankton in the ocean?
Plankton are an essential component of life on Earth. Marine plankton, found in all ocean ecosystem s, play a critical role in maintaining the health and balance of the ocean and its complex food web s. The oxygen, nutrient s, and biomass they produce also sustain terrestrial life—from the food we eat to the air we breathe.
What is the function of plankton?
Plankton—derived from the Greek root planktos, meaning “wanderer” or “drifter”—are unable to swim against current s, tide s, or wave s.
What is the name of the organisms that are found in the aquatic ecosystem?
The word refers to the numerous organisms floating throughout aquatic ecosystems. Phytoplankton are the tiny, plant-like producer s of the plankton community. They include bacteria and algae that form the base of aquatic food webs. Common phytoplankton include diatom s, dinoflagellate s, cyanobacteria (blue-green algae), and green algae.
What is the primary consumer of plankton?
Zooplankton are the animal-like primary consumer s of plankton communities. In turn, zooplankton then become food for larger, secondary consumer s such as fish. Zooplankton include microscopic and macroscopic organisms.
What are radiolarians and foraminifera?
This makes them an important part in the regulation of climate change. Foraminifera (forams) and radiolarians are microscopic zooplankton. The tests, or shells, of these plankton are so abundant that they form the majority of seafloor sediment in many parts of the ocean.
What are some examples of zooplankton?
Zooplankton include microscopic and macroscopic organisms. Some zooplankto—such as copepod s, krill, and arrow worm s—will drift the ocean as plankton for their entire lives. Other zooplankton live only a portion of their lives as ocean drifters. These include oysters, crabs, and some fish.
What is the substance an organism needs for energy, growth, and life?
substance an organism needs for energy, growth, and life. composed of living or once-living material. process by which plants turn water, sunlight, and carbon dioxide into water, oxygen, and simple sugars. microscopic organism that lives in the ocean and can convert light energy to chemical energy through photosynthesis.
What Is Plankton?
- Plankton are a collection of tiny organisms that live at and beneath the surface of lakes, rivers, ponds, and oceans across the planet. They’re named for the Greek word planktos, meaning to drift or float. Plankton don’t swim on their own—they’re carried by tides, currents, and other forces, which determine where they go. Plankton are an important ...
Different Types of Plankton
- The two most prominent types of plankton in the ocean are zooplankton, which are tiny animal organisms, and phytoplankton, which are plantlike. (Other forms of plankton include bacterial and fungal. Plankton are also not strictly aquatic; there is a wide assortment of aeroplankton that float through the atmosphere, just as their better-known counterpart float in the ocean.) Many phytopl…
Threats to Plankton
- Ocean acidification, caused by excess carbon dioxide dissolving in seawater, poses a significant threat to phytoplankton. A more acidic ocean will causesome types to grow slower, some to grow faster, and the balance among them to change, which could have big ripple effects for the higher levels of the food web. Warming water because of climate change can have the same effects. Pl…
Threats from Plankton
- When environmenmental conditions change, often triggered by too much of a nutrient—such as nitrogen or phosphorus from fertilizer runoff—populations of some types of phytoplankton can grow rapidly, in what’s called a “bloom.” Some blooms can be harmful, depleting oxygen in the water, blocking sunlight, and secreting toxins. Harmful algae blooms, some of which are also kn…