
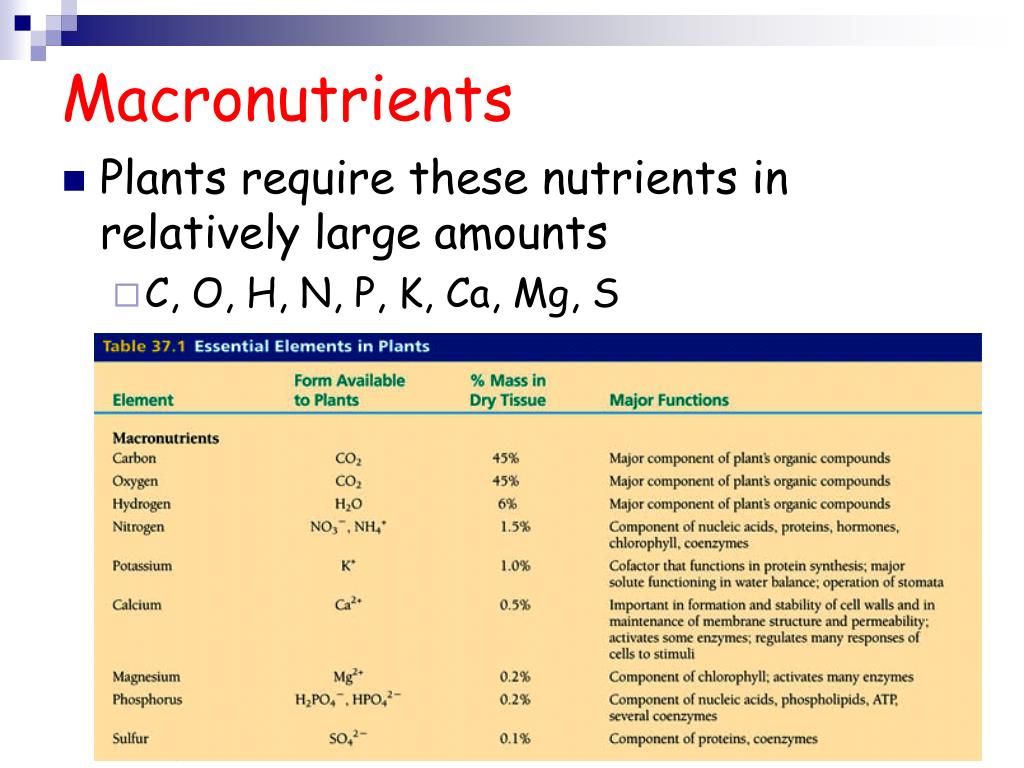
Macronutrients are easy to find.
- Nitrogen – helps foliage grow strong, affects the plant’s leaf development. ...
- Phosphorous – assists with the growth of roots and flowers. ...
- Potassium – strengthens plants, helps contribute to early growth and assists the plants in retaining water. ...
- Magnesium – contributes to the green coloration of the plants.
- Sulfur – resists disease and helps form and grow seeds. ...
What are the three most important nutrients for plants?
- Structural nutrients: C, H, O
- Primary nutrients: N, P, K
- Secondary nutrients: Ca, Mg, S
What are primary secondary and micronutrients in plants?
Plants obtain the three most abundant nutrients – carbon, hydrogen and oxygen – from water and the air. The other 13 elements are divided into three categories: primary, secondary and micronutrients. Nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P) and potassium (K) are primary nutrients which are needed in fairly large quantities compared to the other nutrients.
What are macronutrients and why are they important?
What Are Macronutrients and Why Are They Important? The human body requires a variety of nutrients in order to function at optimal levels. The three main nutrients, also called macronutrients, are carbohydrates, fat and protein. Macronutrients help us grow, develop, repair, give us energy, and make us feel good.
What are the five macronutrients?
Macronutrients: A Simple Guide to Macros
- Carbohydrates. All carbohydrates are eventually broken down into glucose, which is the main energy source for your body.
- Protein. Protein allows your body to grow, build and repair tissues, and protect lean body mass (your muscle mass).
- Fat. ...
What is the role of macronutrients?
Macronutrients are the nutrients that your body needs in large amounts, which include fat, carbohydrates, and protein. They're the nutrients that give you energy and are often called "macros". Macronutrients contain the components of food that your body needs to maintain its systems and structures.
Why do plants need macronutrients and micronutrients?
Macronutrients are elements which plants require in relatively large amounts where micronutrients are those which plants require in much smaller amounts. A combination of macronutrients and micronutrients give the soil its optimum health. The essential macronutrients needed by the soil are: Nitrogen.
How do plants absorb micronutrients?
Plants take up essential elements from the soil through their roots and from the air through their leaves. Nutrient uptake in the soil is achieved by cation exchange, wherein root hairs pump hydrogen ions (H+) into the soil through proton pumps.
Why do plants need macronutrients?
Macronutrients in Plants Plants are living organisms and they also require nutrients like us in order to survive, grow, reproduce, and develop. Macronutrients in plants are nutrients that provide energy to the plants and are required in larger amounts to maintain their development and growth.
How much macronutrients do plants need?
Approximately 20 macronutrients and micronutrients are deemed essential nutrients to support all the biochemical needs of plants.
What process do plants use to take in nutrients?
absorptionPlants typically take in nutrients through their roots. The roots absorb water and minerals from the soil and transport them to the rest of the plant. The roots can also absorb nutrients from the air and water. The process of roots taking in nutrients is called absorption.
What is macronutrient in plants?
Macronutrients, as the name suggests, are the nutrients required by the plants in large amounts. These include carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, calcium and potassium. Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen are obtained from air and water while the others are obtained from the soil.
How does a plant absorb nutrients?
Most nutrients are absorbed through root hairs near the very tip of the roots. Root hairs are ultra-fine roots that have a large surface area, allowing them to absorb even more water. The majority of plants also partner with different fungi to absorb even more nutrients from the water in the soil.
What is the role of micro and micronutrients in plants?
Most micronutrients are part of the enzyme systems of plants. Micronutrients play important roles in photosynthesis. Micronutrients are important in reactions such as N fixation, Protein synthesis. It is Complex to identify all roles.
What is macronutrients and micronutrients in plants?
Macronutrients include carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorous, potassium, calcium, sulfur, and magnesium. Micronutrients are boron, chlorine, manganese, iron, zinc, copper, and molybdenum. A plant uses these nutrients to support its growth, life cycle, and biological functions.
How do micronutrients affect plant growth?
Micronutrients are essential plant nutrients that are found in trace amounts in tissue, but play an imperative role in plant growth and development. Without these nutrients, plant nutrition would be compromised leading to potential declines in plant productivity.
What are micronutrients vs macronutrients?
In basic terms, macronutrients are the nutrients that the body requires in large amounts, while micronutrients are those required in smaller amounts. To break this down even further, macronutrients make up your total caloric intake, and include carbohydrates, proteins and fats.
What is the macronutrient for plants?
Another of the macronutrients for plants is sulphur. Sulphur is absorbed as SO 4- - ions. Most of the absorbed sulphate is translocated as such to the shoot where it is incorporated into organic compounds like sulphur containing amino acids. Since sulphur is a constituent of some amino acids, it has indirect role in protein synthesis.
What macronutrients are needed for plant growth?
Phosphorus. Potassium, another macronutrients for plants, does not form a stable structural part of any molecule inside plant cells, yet large amounts of this element are required for proper growth and development of the plant. It acts as a coenzyme or activator for many enzymes. It helps in influential anion-cation balance, ...
What is the most important element in plants?
Nitrogen is taken by plants usually in the form of NO 2 and NO 3 from the soil. Most soils are deficient in nitrogen since this element is easily lost through leaching of nitrate ions or conversion of nitrate ions to volatile N 2 by micro-organisms. Nitrogen is essential to plants because it is a part of several organic compounds like amino acids, proteins, coenzymes, nucleic acids, vitamins, alkaloids and chlorophyll. . It plays an important role in protein synthesis, photosynthesis, respiration, growth and other metabolic processes. So nitrogen is the important Macronutrients for Plants.
Why is nitrogen important for plants?
Nitrogen is essential to plants because it is a part of several organic compounds like amino acids, proteins, coenzymes, nucleic acids, vitamins, alkaloids and chlorophyll. . It plays an important role in protein synthesis, photosynthesis, respiration, growth and other metabolic processes. So nitrogen is the important Macronutrients for Plants.
Why are my tomato leaves green?
Young leaves remain green longer because of soluble forms of nitrogen are transported to them from the older leaves. Some plants like tomato show a purplish coloration on stems, petioles and the lower surface of leaves due to accumulation of anthocyanin pigments.
What is magnesium essential for?
It is an essential part of chlorophyll molecule. Roots and micro-organisms which lack chlorophyll require magnesium for the activation of many essential enzymes. Those enzymes which are known to utilize energy in ATP are activated by magnesium.
What is the role of a coenzyme in the formation of a cell membrane?
It acts as a coenzyme or activator for many enzymes. It helps in influential anion-cation balance, and turgidity in cells and is concerned in protein synthesis. It is also concerned in the formation of cell membranes and in opening and closing of stomata.
How do macronutrients affect plant growth?
Both macronutrients and micronutrients impact plant growth and function. Particularly with macronutrients, when a plant experiences nutrient deficiency, it can adversely affect plant growth. In general, these deficiencies can also lead to a condition called chlorosis and even cell death.
What Are Macronutrients?
Macronutrients are nutrients that are required in larger amounts by plants and other living organisms. The following elements are categorized as macronutrients: carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorous, potassium, calcium, sulfur, and magnesium. Let's take a look at a few of these macronutrients in further detail.
What are the essential elements of plants?
Macronutrients are essential elements used in large quantities by plants. When essential elements are used in smaller amounts, they are called micronutrients. Macronutrients include carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorous, potassium, calcium, sulfur, and magnesium. Micronutrients are boron, chlorine, manganese, iron, zinc, copper, and molybdenum. A plant uses these nutrients to support its growth, life cycle, and biological functions. Deficiencies in these nutrients can lead to plant cell death, chlorosis, stunted growth, and other disorders.
What are the micronutrients that plants need to survive?
Micronutrients are boron, chlorine, manganese, iron, zinc, copper, and molybdenum. A plant uses these nutrients to support its growth, life cycle, and biological functions. Deficiencies in these nutrients can lead to plant cell death, chlorosis, stunted growth, and other disorders.
Why is chlorine important for plants?
Chlorine is an important micronutrient since it works with potassium to regulate water in the plant. It also plays a role in photosynthesis. When a plant cell needs to form a strong, tough cell wall, it uses elements such as boron. Plant Deficiency Disorders.
Why do plants need water regulators?
Plants need a water regulator to control the amount of water that enters plant cells. They rely on the presence of potassium to help control both the uptake and loss of water in a plant. The last macronutrients we'll cover are nitrogen and magnesium.
What is the role of chlorophyll in photosynthesis?
If you look at chlorophyll, you'll find both these elements in its structure. Chlorophyll is light-absorbing pigment that plays a vital role in supplying plant energy through photosynthesis. You can thank chlorophyll for the green color you see in plants. Nitrogen also plays a role in vitamin and protein synthesis.
What macronutrient is needed for plants to grow?
The following macronutrient up for proper plant nutrition is oxygen . Oxygen is just as essential for plants as it is for animal life. Plants have the luxury of producing their own oxygen as a byproduct of photosynthesis. However, this oxygen only affects the leaves and stems.
How many macronutrients are in plants?
There are 9 macronutrients in plant nutrition and we have tips on recognizing deficiencies. They are carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, phosphorus...
What are the last two macronutrients?
The last of the primary macronutrients is Potassium. Potassium is used in processes that form proteins and carbohydrates. Plants lacking in potassium also show similar symptoms to nitrogen and phosphorus deficiency. Growth is reduced while the leaves of the plant start to turn yellow and purple.
Why is phosphorus important to plants?
The macronutrient phosphorusis extremely important because it is an essential part of DNAand RNA. It is also a primary piece in the structure of the aforementioned ATP. Phosphorus deficiency is very difficult to diagnose in plants due to its similarities with nitrogen deficiency. Rather than the stems becoming purplish, the older leaves become purplish. Its role in plant structure, development, seed production, and energy process makes it as important as nitrogen.
What is the first macronutrient to consider in plant nutrition?
The first macronutrient to consider in plant nutrition is carbon. Plants get the carbon they require from sunlight. Plants utilize sunlight and carbon dioxide in a process called photosynthesis. As a result, this process becomes the primary source of carbon for plants through glucose production. We get back that sweet, sweet oxygen in return (most ...
Why do my plants have yellow leaves?
If unsure your plants get enough sunlight, look for drooping or yellowing leaves in the lower stem, stalk, or trunk areas. Plants often have smaller leaves, poor growth, and do not flower without enough sunlight. Conversely, too much sunlight will cause the plant to dry out due to increased water usage for cooling.
How to know if your plant has low nitrogen?
Plant Nutrition Tips. If you are having problems with nitrogen, it is certainly from a deficiency of ammonium. Signs to look for are purplish stems and slowed or stunted growth. The tried-and-true way to keep nitrogen levels balanced is crop rotation.
What are the nutrients that plants need?
These include carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, calcium and potassium. Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen are obtained from air and water while the others are obtained from the soil. Micronutrients are the ones required in very small amounts by the plants. These include iron, zinc, boron etc. In addition to these, some elements like silicon, cobalt, selenium, and sodium are present which are required by higher plants. The elements referred to as macronutrients and micronutrients can be further divided into the following categories:
What are the two types of nutrients that plants need to produce food?
Role Of Macronutrients And Micronutrients. Plants are able to produce their own food through a process called photosynthesis. They absorb nutrients through their roots from the soil and is transported through the stem to the different parts that are above ground level. They require two types of nutrients- macronutrients and micronutrients .
What is the role of chlorine in a cell?
Chlorine: Chlorine helps in determining the solute concentration and the anion-cation balance of the cells. Stay tuned with BYJU’S to learn more about the macronutrients and micronutrients or any other related topics @ BYJU’S Biology. Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs.
What are the elements that are required for plants to grow?
These include iron, zinc, boron etc. In addition to these, some elements like silicon, cobalt, selenium, and sodium are present which are required by higher plants. The elements referred to as macronutrients and micronutrients can be further divided into the following categories: Elements as components of biomolecules and hence are structural ...
Why is manganese important?
Manganese: Enzymes involved in photosynthesis, respiration etc are activated by this. It helps in the splitting of water during photosynthesis.
What are macro nutrients?
Macros are Proteins, Carbohydrates and Fats but not carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, calcium and potassium.
What are the functions of nitrogen?
Functions of some important elements are as follows: Nitrogen: It is required by plants in large amounts. It is taken in the form of ions from the soil. It is required for the division of cells. It is the major constituent of proteins, vitamins, hormones etc.
Which macronutrient is essential for plant growth?
Other, more secondary macronutrients that are essential to plant growth are Calcium (Ca), Magnesium (Mg), and Sulfur (S).
Why are micronutrients important for plants?
Micronutrients. Micronutrients in plants are used in smaller amounts, but they are just as vital to the overall health of plants and microbial life. Plants’ root systems absorb these micronutrients from the soil just like they do macronutrients, the absence of any of which can cause nutrient deficiencies.
What is the difference between macronutrients and micronutrients?
The terms macronutrients and micronutrients refer to the quantity of each nutrient that the plants in your garden need. Macronutrients are used and necessary in larger quantities than micronutrients and are more prominently displayed on fertilizer packages.
What are the elements that plants need in large quantities?
Macronutrients are the elements that plants require in large quantities, while micronutrients are the elements plants need in much smaller amounts. Amending your soil with organic fertilizers, organic soil amendments, and feeding soil with rich organic matter can help you on your journey to healthy soil that is infused with macronutrients ...
How to keep soil alive?
Here are some easy ways to keep soil thriving: Fertilize with a quality organic fertilizer, which will trace elements and micronutrients in addition to the main macronutrients (N-P-K).
What are the macronutrients in fertilizer?
The primary macronutrients are Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), and Potassium (K), and you may be familiar with the term N-P-K on the fertilizer packaging. Nitrogen encourages foliage growth, and potassium is essential for overall flower and fruit development. Phosphorous promotes healthy root development and bolsters flower and fruit formation.
What nutrient is needed for high yielding plants?
Amending your soil bonemeal, limestone, gypsum, or rock phosphate can help increase the content of this key nutrient in your soil. Magnesium is an essential nutrient for many high-yielding plants because it helps encourage new fruit-setting flowers and increases the plants’ ability to uptake other key soil nutrients.
Role of Nutrients in Plant Growth
Macronutrients
- [Click Here for Previous Questions] Macronutrients are elements that are found in enormous levels in plant tissues. They exceed 10 moles per kilogram of dry materials. The macronutrients are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulphur, potassium, calcium, and magnesium. The element is essential for average growth and reproduction to take place. Plants …
Deficiency Symptoms of Essential Elements
- [Click Here for Sample Questions] 1. The critical concentration of an essential element is the level below which plant growth is slowed. 2. When the element is present below the critical concentration, it is said to be deficient. 3. Plants exhibit distinct morphological changes in the absence of a specific element, known as deficiency symptoms and are diagnostic of particular e…
Things to Remember
- [Click Here for Previous Questions] 1. Plants are made up of 60 chemical elements, among which 16 elements are essential. 2. Micronutrients include iron, manganese, copper, molybdenum, zinc, copper, boron, chlorine, and nickel. 3. The macronutrients are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulphur, potassium, calcium, and magnesium. 4. M...