What influence do pressure groups have on parliamentary law making?
Describe pressure groups as an influence of Parliamentary law making. Pressure groups are a body of people with a shared interest in getting Parliament to change an area of law to benefit a cause or section of society. They do this by lobbying MPs, creating petitions and working with the media to gain as much publicity as possible.
How do press pressure groups work?
Pressure groups work by raising public awareness to gain popular support, through petitions, early day motions and media coverage. These campaigns put pressure on law makers at all stages and successful public campaigns have lead to changes in the law.
What are the three influences on lawmaking?
We have room in this section to consider a limited number of influences on lawmaking: interest groups, public opinion, and the social sciences. The interest-group thesis contends that laws are created because of the special interests of certain groups in the population (Mahood, 2000).
What is an example of a pressure group?
Examples are: GreenPeace, Fathers 4 Justice, Camp Bling, NSPCC, RSPCA and WWF. Only need 1 member in a pressure group. The methods they use are: lobbying MPs, meeting MPs, sit-in, strikes, boycott, petition, and stunts.
What is pressure group?
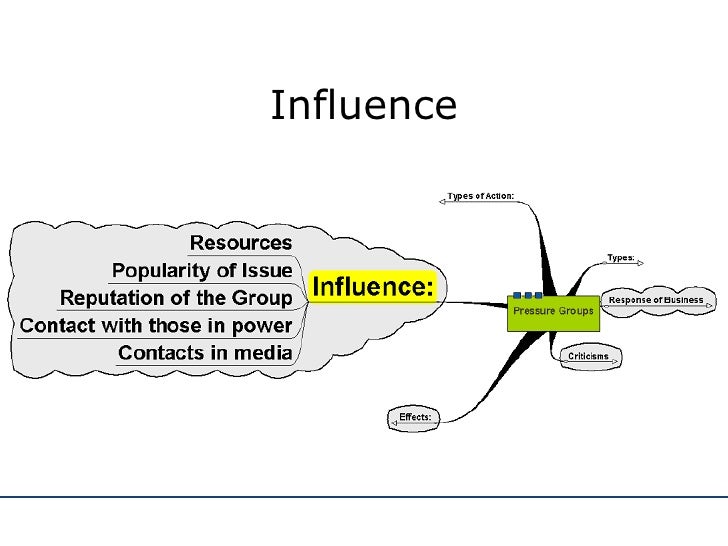
What is the purpose of the membership, aims, methods, resources and effectiveness?

How does pressure group influence the government?
Pressure groups function for Government as a responsible source of criticism, for the political system as a conduit of communication between citizens and the Government, and for group members as a democratic means of expressing their opinions.
What methods can pressure groups use to influence policies and decisions?
Groups use varied methods to try to achieve their aims including lobbying, media campaigns, publicity stunts, polls, research, and policy briefings.
Who can influence the creation of law?
The most important influence on new law creation is the government you vote for. During the next general election you will no doubt hear many promises being made by the various political parties. These promises are usually contained in a party's manifesto, which is their plan for new laws if they are elected.
What impact can a pressure group have on a business?
Pressure groups , also called interest groups , are groups of people who share a common interest and try to influence the decisions made by businesses, organisations or governments. Many pressure groups try to influence businesses to behave more ethically or to act in a more environmentally friendly way.
What are the advantages of pressure groups?
pressure groups help to improve the economic, religious, and social well-being of the members. Pressure groups help to enlighten the citizens particularly the members about government policies and programmes. Pressure groups help to ensure good governance by constructively criticising the government.
What is the aim of pressure groups?
Pressure groups generally promote opportunities for political participation for citizens, without the need to join a political party. Moreover, they allow for the democratic rights of freedom of speech, assembly and association to be upheld. 1.
How can laws be changed?
Laws must be enacted and implemented consistently with the U.S. Constitution. Laws can be changed or amended only when Congress enacts, and the President signs, a later law. When a law is passed by Congress and signed by the President, it is given a Public Law number, formatted as PL-XXX.
What are the factors that limit the rule of law?
In practice, it is usually difficult to apply the principle of rule of law because of some limitations....Limitations of rule of lawCorruption: Corruption is one of the major limitations of the doctrine of rule of law. ... Illiteracy: ... Bad leadership: ... Immunity of some government officials: ... Lack of patriotism:
Why are laws created?
Laws protect our general safety, and ensure our rights as citizens against abuses by other people, by organizations, and by the government itself. We have laws to help provide for our general safety. These exist at the local, state and national levels, and include things like: Laws about food safety.
What are pressure groups explain with examples?
A pressure group is an organisation which attempts to influence government policies through protests and demonstrations. Pressure groups are formed when people with similar opinions get together for similar objectives. Examples of pressure groups are FEDECOR and BAMCEF.
What are pressure groups in business examples?
Examples include: The increasing practice of environmental audits by businesses. The movement to the use of synthetic fur in the fashion industry. The compulsory use of seat belts The decrease in the use of CFCs.
What is the meaning of pressure group in business?
any group of individuals who work together to exert an influence upon the decision-making of a company to achieve some specific outcome.
Which is the important method used by pressure groups to influence the government Mcq?
The pressure groups influence the policy-making in the government through legal and legitimate methods like lobbying, correspondence, publicity, propagandising, petitioning, public debating, legislations, etc.
What are the techniques used in lobbying and advocacy?
While letters or personal visits are the most effective methods of lobbying, telephone calls can also get results. Telephone calls can be especially important for time sensitive lobbying efforts. You can also make a follow-up call to check if your letter or e-mail has been received and registered.
What are the influences on Parliament?
The influences on parliament can be many; here are some of the influences;Government Policy. The government of the day will have had a party manifesto. ... European Union Law. ... Individual MPs. ... Other Influence. ... Pressure Groups. ... Media. ... Reform Bodies and Commissions. ... Law Reform Committee.More items...•
What do you mean by lobbying?
“Lobbying” means influencing or attempting to influence legislative action or nonaction through oral or written communication or an attempt to obtain the goodwill of a member or employee of the Legislature.
Examples of Pressure Groups – A Level Politics AQA Revision – Study ...
Examples of Pressure Groups Examples of Pressure Groups. 38 Degrees: 38 Degrees is an example of a wide, ‘umbrella’ group that uses social media and other tactics to attempt to effect change. The group was set up in 2009 and has around 2.5 million members. The success in stopping the privatisation of England’s forests was a notable success for the group.
Pressure Groups. - Revision Notes in A Level and IB Law
See all Law resources » See all Parliamentary law making resources » Related discussions on The Student Room. Law unit 1 exam 22 may » Representation and Democracy in Britain 1830-1931 » OCR AS Government and Politics Exam 2016 »
Examples Of Pressure Groups That Have Changed The Law - PaperAp.com
It was set up in 1965 with its main task to be codification. In 1965 it was announced that it would begin codifying family law, contract, landlord and tenant and evidence.
Pressure Groups / Protest Movements - A-Level Politics Revision
A pressure group is a body which seeks to influence government policy without seeking office itself, usually focused on a single issue or narrow group of ideas.. Differs from a political party as they just seek to influence policy. Political parties will seek to appeal to a variety of different pressure groups in order to achieve victory.
Pressure Groups & Other Influences – A Level Politics Edexcel ...
Pressure Groups & Other Influences Definitions. A pressure group is an organised group of people that aims to influence the policies or actions of government.. Pressure groups have three key features: They seek to exert influence from outside, meaning they don’t try to win political power in the same way as a party
List of pressure groups in the United Kingdom - Wikipedia
N.B.: Trade unions may be invariably described as pressure groups; these organisations should be mentioned at the list of trade unions in the United Kingdom article, not here. There are many pressure groups around the world. This is a list of pressure groups in the United Kingdom.Based on their relationship with United Kingdom policy makers, they can be divided into insider groups, who have ...
What is pressure group?
Pressure groups are a body of people with a shared interest in getting Parliament to change an area of law to benefit a cause or section of society. They do this by lobbying MPs, creating petitions and working with the media to gain as much publicity as possible.
What are the two types of pressure groups?
There are two types of pressure group: sectional and promotional. The success of a pressure groups tend to depend on governmental links. The larger the group, the wealthier it tends to be and the more likely it is to have access to MPs as they will represent a larger sections of society. This is why sectional groups tend to be more influential.
Which is more successful, the Labour or the Trade Unions?
Their success can depend on the Government. Trade Unions tend to be more successful under a Labour Government as they provide 90% of their income, whereas business groups like NFU and CBI are more influential under Conservative Governments.
What is a promotion group?
Promotional groups are groups which promote a certain cause. Successful, large groups like Greenpeace and Friends of the Earth have been successful in getting Parliament to consider the environment when making law as they are well-organised and have huge publicity.
Pressure Groups
A pressure group is a group of people who campaign for a change in the law. Examples are: GreenPeace, Fathers 4 Justice, Camp Bling, NSPCC, RSPCA and WWF.
Disadvantages of Pressure Groups
1) Some causes are inappropriate of trivial - only interest a minority.
How do pressure groups affect the community?
The pressure groups perform a major role in modifying the community as a whole by generating political awareness and making the electorate politically aware. They act as a bridge between the electorate and the government by making the government aware of the needs of the governed. The pressure groups give representation to the minority and make their voices heard. They even act as an advisor to the government as and when needed. The presence of the pressure groups makes a democracy rich and viable.
Why are pressure groups autocratic?
Besides, enhancing the quality of democracy, pressure groups at times are autocratic in nature; they represent the powerful minority who are financially affluent, thereby overshadowing the needs of the vast majority. The methods of resistance used by these groups (strikes, demonstrations, rallies) hinder the movement of the community as a whole. They also pressurize the government at times to implement policies benefitting their own interest, disregarding the interests of the vast majority, this is most commonly observed with regard to the trade unions and the business groups.
What is the method of placing representatives favoring their issues in prominent public offices?
Electioneering: In this method, they place representatives favoring their issues in prominent public offices.
How do pressure groups and movements help preserve public opinion?
The pressure groups and the movements are essential tools in preserving public opinion in a democracy by ensuring adequate public representation, by acting as an effective check against the arbitrary decision-making of the government.
What is a sectional pressure group?
Sectional: This type of pressure group includes self-interest organisations such as trade unions, business and farming groups.
What is pressure group?
David Truman defined pressure groups as “that on the basis of one or more shared attitudes, makes certain claims upon other groups in the society for the establishment, maintenance, enhancement of forms of behavior that are implied by shared attitude.” Pressure groups and movements are the very essences of modern democracy; they are capable of influencing government decisions by their powerful representation. They can range from very small groups to a nexus of a million people. The pressure groups are not political by nature and they do not contest for political power. Individuals with shared interests come together to change the government’s outlook and alter government decisions.
What is the role of propaganda in a democracy?
Propagandizing: This involves influencing public opinion in their favour and pressurising the government to accept their interests, as, in a democracy, public opinion is regarded as the sovereign.
What are the influences that affect the creation of new laws?
One final influence that affects the creation of new laws is the one you most likely already know about: the media and pressure groups. When you read an article in the newspaper or hear a news story on the TV, you are potentially influencing the laws that may be made in the future.
What is the most important influence on new laws?
The most important influence on new law creation is the government you vote for . During the next general election you will no doubt hear many promises being made by the various political parties. These promises are usually contained in a party’s manifesto, which is their plan for new laws if they are elected.
What is the concept of Parliamentary supremacy?
There is a concept known as Parliamentary supremacy which, as the name suggests, makes laws made by Parliament very near the top in terms of importance.
Why are laws created?
This is because of our membership in the European Union. Examples of new laws (properly called Acts of Parliament) created because of the influence of Europe include laws on sexual discrimination, employment and consumer protection. European law and its influence on English law is a specialist area of study involving the legal theory on the separation of powers. This is beyond what many legal practitioners would deal with in day-to-day practice, and although of interest, it is beyond the scope of this article.
What is European law?
European law and its influence on English law is a specialist area of study involving the legal theory on the separation of powers. This is beyond what many legal practitioners would deal with in day-to-day practice, and although of interest, it is beyond the scope of this article.
What is the law commission?
In a previous Journal article, we wrote about the recent removal of hundreds of obsolete Acts of Parliament. This type of ‘maintenance’ of our laws is usually the function of the Law Commission, established in 1965. The commission is sometimes described as the lawyer’s lawyer, and they keep the law under review.
What are the forces that influence lawmaking?
Lawmaking is a response to many social forces . The forces that influence lawmaking cannot always be precisely determined, measured, or evaluated. At times, several forces operate simultaneously. We have room in this section to consider a limited number of influences on lawmaking: interest groups, public opinion, and the social sciences.
How do interest groups influence lawmakers?
Several specific conditions enhance the potential influence of interest groups on lawmakers (Ripley, 1988). In many instances, there may not be two competing groups on an issue. When only one point of view is presented, the group is likely to get much of what it wants. For example, when banking and other money-lending interests, such as pawnshops, push for a higher ceiling for usury laws in a state, they are more likely to succeed if there is no organized opposition. Similarly, if the groups on one side of a controversy are unified and coordinated on the principal issues they want to push (or if they can minimize their disagreements), they will enhance their chances of success. If certain key members of legislative bodies (such as a subcommittee chairperson) believe in the interest group’s position, the probability of success is also greatly enhanced.
What are the interactions between interest groups and legislative and administrative lawmakers?
Interactions between interest groups and legislative and administrative lawmakers are more overtly political in nature. As Chapter 3 noted, many interest groups maintain Washington and state capital offices staffed with people who keep track of developments in the legislative and administrative branches and attempt to influence their activities. Some groups pay for the services of law firms in dealing with legislators or administrators. These firms provide expertise in such areas as antitrust and tax regulations and use their personal contacts with important lawmakers on behalf of their clients.
How do interest groups help judges?
By instituting test cases, interest groups provide judges with opportunities to make social policy . These groups often submit legal briefs that communicate relevant social science research findings to a particular case. By providing information through amicus curiae briefs, interest groups expand the confines of the judicial process and build coalitions with other groups (McGuire, 1994). Another technique is to publish decisions in legal periodicals. Judges generally read these journals to keep abreast of legal scholarship and sometimes even cite them as authority for their ruling. Publication in these journals gets one’s views before the courts and before the attentive public.
How to bring conflicts to the attention of the courts?
The principal techniques are: to bring conflicts to a courts attention by initiating test cases, to bring added information to the courts through amicus curiae (friend of the court) briefs , and to communicate with judges indirectly by placing information favorable to the group's cause in legal and general periodicals.
What is pressure group?
Pressure groups are an organised group that exists for the purpose of representing particular interests. Different types can be defined as sectional, who exist to further the interests of a particular body of people (Law Society- solicitors) or cause, who further a particular ideal (RSPCA - animal rights).
What is the purpose of the membership, aims, methods, resources and effectiveness?
Clearly, the membership, aims, methods, resources and effectiveness range greatly but they all have a common purpose which is to ultimately influence the legislative process to benefit or better reflect their ideas or needs.