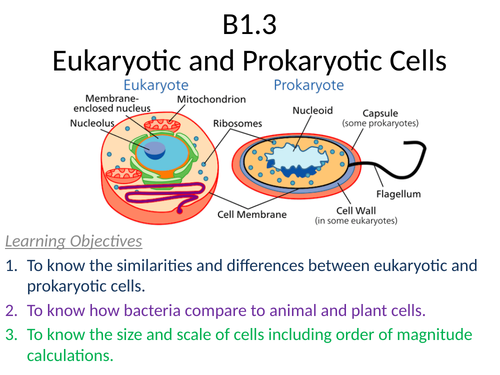
The prokaryotes and eukaryotes difference can be highlighted by the following pointers:
- Prokaryotic cells are unicellular. Eukaryotic cells are multicellular.
- Prokaryotic cells can perform photosynthesis whereas eukaryotic cells can’t.
- Prokaryotic cells can perform locomotion whereas eukaryotic cells can’t.
What is the comparison between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
Well, to summarise, prokaryotic cells are unicellular micro-organisms, whereas eukaryotic cells are multi-cellular organisms. The nucleus is present in eukaryotic cells, while there is no nuclei present in prokaryotic cells.
Why do prokaryotic cells have no nucleus?
They have no nucleus; instead their genetic material is free-floating within the cell. They also lack the many membrane-bound organelles found in eukaryotic cells. Thus, prokaryotes have no mitochondria. How do prokaryotic cells survive in the absence of important organelles like mitochondria and nucleus?
What is a prokaryote vs eukaryote?
The main difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is that eukaryotes contain membrane-bound organelles, and prokaryotes do not. This means that prokaryotes do not have a nucleus; instead, they keep their DNA in a cell region called the nucleoid.
What is an example of a prokaryote cell?
With the prokaryotic cells lacking almost many organelles, some of the examples of prokaryotic cell are the bacteria, mycoplasma and the blue green algae. Among these, bacteria are the most common ones.
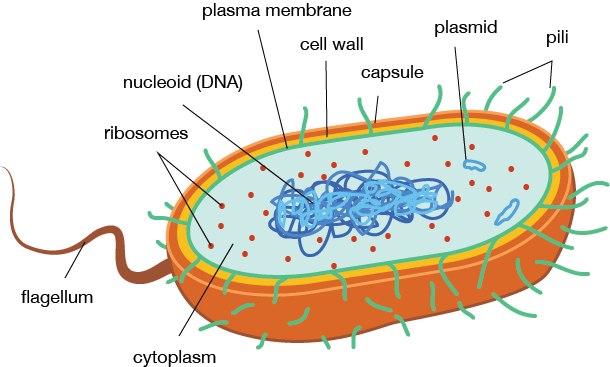
What are 5 differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Thus, two types of cells are found in the organisms: eukaryotic and prokaryotic depending on whether cells contain membrane-bound organelles or not....What is the difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells?Prokaryotic CellEukaryotic cellMitochondria absentMitochondria presentCytoskeleton absentCytoskeleton presentRibosomes smallerRibosomes larger20 more rows•May 20, 2022
What are 3 main differences between a eukaryotic cell and a prokaryotic cell?
Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles, such as the nucleus, while prokaryotic cells do not. Differences in cellular structure of prokaryotes and eukaryotes include the presence of mitochondria and chloroplasts, the cell wall, and the structure of chromosomal DNA.
What are 4 differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
Prokaryotes are exclusively unicellular organisms while eukaryotes consists of unicellular as well as multicellular organisms. Prokaryotes have circular DNA while eukaryotes have linear DNA. Eukaryotes have a true nucleus while prokaryotes do not. Eukaryotes have membrane bound organelles while prokaryotes lack these.
What are the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells quizlet?
Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles, such as the nucleus, while prokaryotic cells do not. Differences in cellular structure of prokaryotes and eukaryotes include the presence of mitochondria and chloroplasts, the cell wall, and the structure of chromosomal DNA.
What are the 3 main differences between animal and plant cells?
Plant cellAnimal cell1. Have a cellulose cell wall outside the cell membrane.1. Have no cell wall.2. Have a cell membrane.2. Have no chloroplasts.3. Have cytoplasm.3. Have only small vacuoles.4. Have a nucleus.4. Often irregular in shape.3 more rows
What are 4 similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Some of the structural similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are cell membrane, cytoplasm, genetic material made up of DNA and ribosomes.
What is the difference between eukaryotes and prokaryotes class 8?
The defining characteristic feature that distinguishes between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell is the nucleus. In prokaryotic cells, the true nucleus is absent, moreover, membrane-bound organelles are present only in eukaryotic cells.
What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell wall?
Eukaryotes have a nucleus with a membrane, larger ribosomal subunits, usually reproduce sexually, and may not have a cell wall. Prokaryotes have no membrane around the nucleus, smaller ribosomal subunits, reproduce asexually, and do have cell walls.
What is a Prokaryotic cell?
A prokaryotic cell is a primitive type of cell that is characterized by the absence of a nucleus. Furthermore, prokaryotes do not possess membrane-...
What is a Eukaryotic cell?
Eukaryotic cells are cells that possess a true nucleus along with membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotes can either be unicellular or multicellular.
What is the difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells?
The defining characteristic feature that distinguishes between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell is the nucleus. In prokaryotic cells, the true nucle...
Define Cell?
The cell is the basic functional and structural unit of life. Cell plays a vital role in all biological activities and include membrane-bound organ...
What is Ribosome?
The ribosome is a multi-component cell organelle consisting of RNA and protein. Therefore, it is called the site of protein synthesis. Ribosomes ar...
List out the unique features of Animal and Plant Cells.
Both animal and plant cells have several unique features. Listed below are some important features: In structure, both animal and plant cells are q...
List out the functions of Chloroplasts.
Chloroplasts are the plastids found in all plant cells. These cell organelles comprise the photosynthetic pigment called chlorophyll and are involv...
Who discovered Cell and Cell Theory?
The cell was first discovered in the year 1665 by an English natural philosopher Robert Hooke. The Cell Theory was explained by Theodor Schwann and...
What is the difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
There are several differences between the two, but the biggest distinction between them is that eukaryotic cells have a distinct nucleus containing the cell's genetic material, while prokaryotic cells don't have a nucleus and have free-floating genetic material instead.
What are prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
These organisms are made of prokaryotic cells — the smallest, simplest and most ancient cells.
What are the ribosomes in prokaryotic cells?
In prokaryotic cells, the ribosomes are scattered and floating freely throughout the cytoplasm. The ribosomes in prokaryotic cells also have smaller subunits. All ribosomes (in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells) are made of two subunits — one larger and one smaller. In eukaryotes, these pieces are identified by scientists as ...
What are the characteristics of prokaryotic cells?
Although prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have many differences, they share some common features, including the following: 1 DNA: Genetic coding that determines all the characteristics of living things. 2 Cell (or plasma) membrane: Outer layer that separates the cell from the surrounding environment and acts as a selective barrier for incoming and outgoing materials. 3 Cytoplasm: Jelly-like fluid within a cell that is composed primarily of water, salts and proteins. 4 Ribosomes: Organelles that make proteins.
How long ago did eukaryotes develop?
Both are eukaryotes and share similar cell structure to all other eukaryotes. Eukaryotes developed at least 2.7 billion years ago, following 1 to 1.5 billion years of prokaryotic evolution, according to the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
Which bacterium has two circular chromosomes?
For example, Vibrio cholerae, the bacterium that causes cholera, has two circular chromosomes. Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells: Eukaryotic cells have several other membrane-bound organelles not found in prokaryotic cells.
Which cell type is most likely to have a cell wall?
Conjugation can occur in bacteria, protozoans and some algae and fungi. Cell Walls: Most prokaryotic cells have a rigid cell wall that surrounds the plasma membrane and gives shape to the organism. In eukaryotes, vertebrates don't have a cell wall but plants do.
What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Differences in Organization. Prokaryotic cells engage in reproduction through a process of cell division called binary fission. Eukaryotic cells use a different process of cell division called mitosis, which involves a constant cycle of cell growth and development.
Why are prokaryotic cells different from eukaryotic cells?
The reason for the difference in cell sizes between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells belongs to the different structure and organization between the two types of cells. The lack of membrane-bound organelles in prokaryotes might be the most noticeable difference. While eukaryotic cells contain organelles enclosed in membranes – two examples ...
What are the two main categories of cells?
All of these cells, whether they operate as a solitary bacterial cell or as part of a complex system such as the human body, can be sorted into two main categories: eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells .
How do eukaryotes reproduce?
Eukaryotes reproduce sexually through meiosis, which allows for genetic variance. Prokaryotic cells reproduce asexually, copying themselves. Despite this, gene transfer processes still allow for genetic variance. One of these is transduction in which viruses move DNA from one bacterium to another.
Which is larger, prokaryotes or eukaryotes?
Most prokaryotes are unicellular and are either archaea or bacteria. Their cells are smaller than eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes include larger, more complex organisms such as plants and animals. Only eukaryotes have membrane-bound organelles and a nucleus. Prokaryotes divide via using binary fission, while eukaryotic cells divide via mitosis.
Which domain has eukaryotic cells?
Eukarya. The organisms in Archaea and Bacteria are prokaryotes, while the organisms in Eukarya have eukaryotic cells. The Archaea domain has subcategories, but scientific sources differ on whether these categories are phyla or kingdoms. They are:
Where does DNA store in a prokaryote?
Instead, most of their DNA is in one chromosome-like structure that sits in an area of the cytoplasm called the nucleoid. This nucleoid does not have a membrane of its own.
What is a Prokaryotic Cell?
A prokaryotic cell is one in which both membrane-bound cell organelles and a well-defined nucleus are absent.
What is a Eukaryotic cell?
A cell that has a well-defined nucleus and a membrane to bind it is called a eukaryotic cell.
Prokaryotic Pros and Cons
These cells add essential nutrients to the soil by decomposing dead organic matter.
Eukaryotes Pros and Cons
The lack of a cell wall helps in the efficient and fast exchange of nutrient absorption.
Considering the Similarities Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells conduct necessary living functions.
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells FAQs
Yes, ribosomes are found freely floating throughout the cytoplasm in a prokaryotic cell.
The Final Words
When we compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, we see that both help in conducting necessary living functions but they have many different characteristics. Prokaryotic cells do not have membrane-bound organelles while eukaryotic cells do have a membrane to bind the nucleus.
What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
The main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is that the latter has a membrane-bound nucleus while the former does not. All genetic information of the eukaryotes is stored in this nucleus.
What is a prokaryotic cell?
A prokaryotic cell is a unicellular organism that has a single chromosome. The plasma membrane acts as a protective coating around the cell. There is also a rigid cell wall that provides additional support and protection.
How did the nucleus of a prokaryote start?
Well, according to endosymbiotic theory, it all started about 2 billion years ago, when some large prokaryote managed to create a nucleus by folding its cell membrane in on itself. "Over time, a smaller prokaryotic cell was engulfed by this larger cell," says Shanle.
What are the two types of organisms?
But what if I were to tell you that there are just two kinds of organisms? According to scientists, the world is split into two kinds of organisms — prokaryotes and eukaryotes — which have two different types of cells. An organism can be made up of either one type or the other. Some organisms consist of only one measly cell, but even so, ...
Which cell type lacks the nucleus and membrane bound organelles?
Prokaryotic cells are simpler and lack the eukaryote's membrane-bound organelles and nucleus, which encapsulate the cell's DNA. Though more primitive than eukaryotes, prokaryotic bacteria are the most diverse and abundant group of organisms on Earth — we humans are literally covered in prokaryotes, inside and out.
Where is DNA stored in a cell?
For example, DNA is stored, replicated, and processed in the eukaryotic cell's nucleus, which is itself surrounded by a selectively permeable membrane. This protects the DNA and allows the cell to fine-tune the production of proteins necessary to do its job and keep the cell alive.
Do prokaryotic cells have separate rooms?
Prokaryotic cells have to do a lot of this same stuff, but they just don't have separate rooms to do it in. They're more of a two-bit operation in this sense. "Many eukaryotic organisms are made up of multiple cell types, each containing the same set of DNA blueprints, but which perform different functions," says Shanle.

What Is A Prokaryotic cell?
Prokaryotic Pros and Cons
Eukaryotes Pros and Cons
Prokaryotic Cells vs. Eukaryotic Cells Examples
Considering The Similarities Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells FAQs
The Final Words
- When we compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, we see that both help in conducting necessary living functions but they have many different characteristics. Prokaryotic cells do not have membrane-bound organelles while eukaryotic cells do have a membrane to bind the nucleus. Considering cytoplasm prokaryotic or eukaryotic, a prokaryotic cell has ...
References
to Organelle Or Not to organelle?
Prokaryotic Efficiency Apartment vs. Eukaryotic Mansion
The Evolution of Eukaryotes