Do sulfonamides inhibit folic acid synthesis?
Ex- periments with a variety of bacterial species have established that sulfonamides inhibit synthesis in vivo of compounds with folic acid activity and that p-aminobenzoate competitively re- verses the inhibition (5-7).
How do sulfa drugs work in the folate biosynthesis pathway?
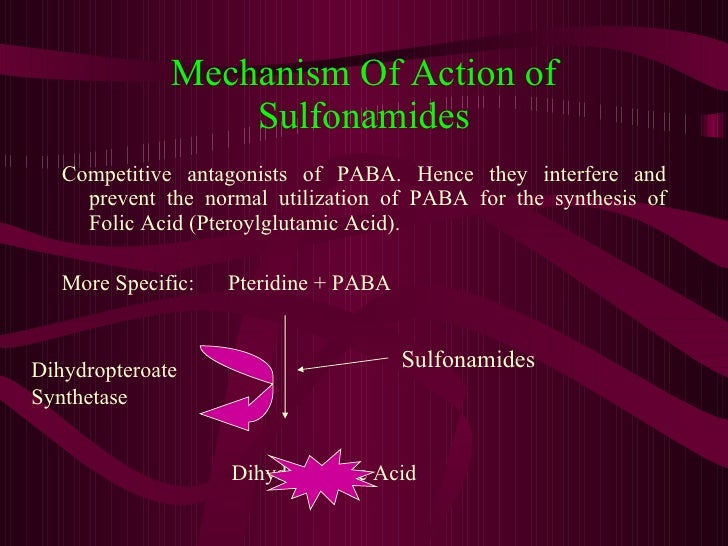
In the folate biosynthetic pathway, sulfa drugs (sulfonamides and sulfones) compete with the natural substrate, para-aminobenzoate (pABA) causing depletion of dihydrofolate (DHF) and subsequent growth inhibition.
How do sulfona-MIDES inhibit the growth of bacteria?
These results, along with other observations that folate-utilizing bacteria are not affected by sulfonamides (7-lo), have led to the conclusion that sulfona- mides inhibit the growth of bacteria by competitively inhibiting the utilization of p-aminobenzoate for the biosynthesis of folic acid.
What class of antibiotics interfere with the synthesis of folic acid?
Folic acids are the enzymes that are necessary for the bacterial protein synthesis and synthesis of amino acids. Trimethoprim and Sulfonamides are the antimicrobial classes that interfere with the synthesis of folic acid at different levels and are bacteriostatic.
How does sulfanilamide interfere with folic acid synthesis?
Sulfonamides, which are derivatives of sulfanilamide, interfere with microbial folic acid synthesis by competitively inhibiting the enzyme dihydropteroate synthase. This enzyme is involved in the step in folic acid synthesis that precedes the step blocked by pyrimethamine and TMP.
How do sulfa drugs inhibit folic acid synthesis?
Sulfa drugs work by binding and inhibiting a specific enzyme called dihydropteroate synthase (DHPS). This enzyme is critical for the synthesis of folate, an essential nutrient. Mammals get folate from their diet, but bacteria must synthesize this vitamin.
How does sulfanilamide act as an inhibitor?
As a sulfonamide antibiotic, sulfanilamide functions by competitively inhibiting (that is, by acting as a substrate analogue) enzymatic reactions involving para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA). Specifically, it competitively inhibits the enzyme dihydropteroate synthase.
Is sulfonamide a folate antagonist?
Sulfonamides and trimethoprim inhibit synthesis of folate at two different sites. The sulfonamides are structurally similar to PABA and block the incorporation of PABA into dihydropteroic acid. Trimethoprim prevents reduction of dihydrofolate to tetrahydrofolate by inhibiting the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase.
Why do sulfonamides act as folic acid antagonists in bacteria but not in humans?
Sulfonamides, such as sulfamethoxazole, are similar in structure to para-aminobenzoic acid, a compound critical for synthesis of folic acid. All cells require folic acid and it can diffuse easily into human cells. But the vitamin cannot enter bacterial cells and thus bacteria must make their own.
How do antibiotics inhibit folate synthesis?
Bacteria need folic acid to synthesize the nucleic acids that make up their DNA. Sulfonamides inhibit folate synthesis by targeting dihydropteroate synthase (DHPS) in the folic acid pathway.
What type of inhibitor is sulfanilamide?
Sulfanilamide is a competitive inhibitor of bacterial enzyme dihydropteroate synthetase. This enzyme normally uses para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) for synthesizing the necessary folic acid.
How do sulfonamides work?
Sulfonamide antibiotics work by interfering with folic acid synthesis in susceptible organisms, due to their structural similarity to para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) in bacterial cells. Folic acid is essential for nucleic acid synthesis.
Which antibacterial agents inhibit the production of folic acid *?
Sulfonamides and trimethoprim act by inhibiting the synthesis of folic acid.
How do folate antagonists work?
A folic acid antagonist, MTX primarily acts via inhibiting dihydrofolate reductase, a key enzyme in the synthetic pathway for producing purines and pyrimidines [72].
What drugs are folate antagonists?
A number of drugs such as aminopterin, methotrexate (amethopterin), pyrimethamine, trimethoprim and triamterene act as folate antagonists and produce folate deficiency by inhibiting this enzyme.
Which of the following is folate antagonist?
The folic acid antagonist methotrexate (MTX) displays a variety of antiinflammatory effects and has been shown effective in the treatment of a number of autoimmune diseases, including RA, psoriasis, and SLE.
How do sulfa drugs inhibit microbial growth?
Sulfa drugs are bacteriostatic; i.e., they inhibit the growth and multiplication of bacteria but do not kill them. They act by interfering with the synthesis of folic acid (folate), a member of the vitamin B complex present in all living cells.
Which method does sulfa drugs used to inhibit bacterial growth?
Pharmacology. Sulfonamides have a bacteriostatic effect by inhibiting bacterial folic acid synthesis.
Which antibiotic blocks the synthesis of folic acid?
5.2 Trimethoprim. TMP is a synthetic antibiotic that binds with the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) inhibiting the folic acid synthesis pathway (Brogden et al., 1982).
How can a competitive inhibitor stop the synthesis of folic acid in bacteria?
Note: These drugs act as competitive inhibitors in the folic acid in bacteria, there it gets attached to the active site of the enzyme and starts to inhibit the formation of folic acid and thus, it inhibits the growth and multiplication of the bacteria.
What enzyme is used to synthesize folic acid?
Bacteria resistant to sulfa drugs often have mutations in the DHPS enzyme. These mutations occur on 2 floppy loops that sit near the enzyme's active site.
How does sulfa work?
Sulfa drugs work by binding and inhibiting a specific enzyme called dihydropteroate synthase (DHPS). This enzyme is critical for the synthesis of folate, an essential nutrient. Mammals get folate from their diet, but bacteria must synthesize this vitamin.
How do sulfa antibiotics work?
Sulfa antibiotics work because they fit into the DHPS active site and take PABA's place. By embedding sulfa antibiotics into the enzyme crystals, the scientists found that the sulfa drugs are held in place by the floppy loop structures. However, a small portion of the drug sticks out of the binding pocket. The researchers discovered that DHPS ...
What is sulfa used for?
While antibiotic resistance remains a problem for this class of antibiotics, sulfa drugs are still commonly used to treat a variety of bacterial infections. Sulfa drugs work by binding ...
What is the DHPS enzyme?
The scientists isolated the DHPS enzyme from 2 bacterial species: Bacillus anthracis, which causes anthrax, and Yersinia pestis, which causes plague.
What is the role of sulfa antibiotics in the metabolism of bacteria?
Sulfa antibiotics inhibit the pathway that bacteria use to synthesize folic acid, which is an important metabolite, or substance formed by metabolism for all cells. Folic acid is a vitamin that is needed in order to make nucleotides and many amino acids.
Why are folic acid metabolites bacteriostatic?
Drugs that inhibit folic acid synthesis are bacteriostatic because the bacteria can't reproduce if they don't have enough folic acid to make new DNA, RNA and proteins.
What is sulfa used for?
They are often used to treat bladder infections because they reach high concentrations in the urine. Sulfa antibiotics inhibit the pathway that bacteria use to synthesize folic acid, which is an important metabolite, or substance formed by metabolism for all cells.
How do sulfa and trimethoprim work?
Sulfa drugs and trimethoprim are usually used in combination.
Which antibiotics inhibit bacterial metabolism?
In this lesson, we'll learn about two antibiotics that inhibit bacterial metabolism: the sulfa drugs and trimethoprim.
When a sulfa drug is present, it is called synergism?
It's like a one-two punch. When two drugs work significantly better in combination than when given alone, it is called synergism. Sulfa drugs and trimethoprim are a great example of drug synergism.
Why do women take folic acid?
For example, women who are pregnant or who are hoping to become pregnant take folic acid to prevent birth defects in their new babies. Pathway of folic acid synthesis in bacteria. But, bacteria have to make folic acid on their own. Above is the pathway that leads to folic acid synthesis in bacteria.
Which drugs inhibit the synthesis of folate?
Sulfonamides and trimethoprim inhibit synthesis of folate at two different sites.
Is sulfasalazine used for inflammatory bowel disease?
There are other sulfonamides ; please check your textbook. Note that sulfasalazine is also used to treat inflammatory bowel disease (see Chapter 42 ).
Can bacteria absorb folic acid?
To understand the mechanism of action of this class of drugs, we need to first review the synthesis of folic acid ( Figure 28–1 ). Bacteria cannot absorb folic acid, but must make it from PABA (para-aminobenzoic acid), pteridine, and glutamate. For humans, folic acid is a vitamin. We cannot synthesize it. This makes this metabolic pathway a nice, selective target for antimicrobial agents.
Is trimethoprim a human enzyme?
This enzyme is present in humans, but trimethoprim has a lower affinity for the human enzyme. There are other examples of folate reductase inhibitors that we will consider later (pyrimethamine and methotrexate). + +. The combination of sulfonamides and trimetho prim is synergistic, and they are rarely used alone.