Are All Stars made out of the same materials?
You might not be surprised to know that stars are made of the same stuff as the rest of the Universe: 73% hydrogen, 25% helium, and the last 2% is all the other elements. That’s it. Except for a few differences here and there, stars are made of pretty much the same stuff.
Are We really all made of stars?
We are made of stars As unbelievable as this may sound, this is in fact true. We are in fact made up of the very same material that stars are made of. The reason for this is that very light particles, such as hydrogen and helium, where formed and scattered after the Big Bang.
What are stars and how are they formed?
Stars form when clouds of interstellar dust and gas collapse in on themselves and heat up, eventually leading to the nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium. Several stars typically form out of a single cloud, making star clusters extremely common. According to NASA, stars are formed when clouds of gas and other material either gain sufficient mass to begin a gravitation collapse or are acted on by an outside source.
What are stars mainly made up with?
What Are Stars Made From? Stars are mostly made up of hydrogen and helium, with only trace amounts of heavier elements. A star is a massive incandescent ball of plasma held together by its own gravity. The principle process that occurs within a star is the conversion of hydrogen into helium.

How do we know stars are made of hydrogen and helium?
Using powerful telescopes, scientists have made extensive spectroscopic surveys of distant stars and galaxies. The data indicates that hydrogen and helium make up nearly all of the nuclear matter in the universe.
How do we know stars are made of the same material?
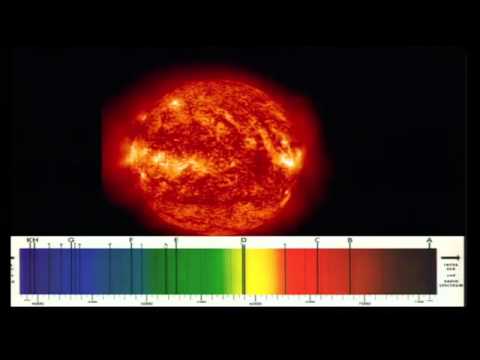
Because each element has its own unique rainbow, called an 'emission spectrum', we can tell what the star is made of based on what we can see in the rainbow, and what's missing. For example, if we point a spectrometer at something and get this emission spectrum... ... we know it's made of hydrogen.
How do we know what stars like our sun are made of?
Surprisingly, no one knows the stars' exact chemical composition: how many carbon, nitrogen and oxygen atoms they have relative to hydrogen, the most common element. These numbers are crucial, because they affect how stars live and die, what types of planets form and even how readily life might arise on other worlds.
How do we know what is inside stars?
When they reach the star's surface, they create pulses, similar to earthquakes on Earth's surface. Astronomers can detect these pulsation patterns as changes in the brightness of stars, and from there determine the star's age, temperature, composition and internal structure.
Are stars living things?
How do stars die? Even though stars are not living things, they have “life cycles” and at some point they are said to “die.” How a star lives and dies depends on how large it is. The smallest stars, brown dwarf stars, are too large to be considered planets, but too small to be considered stars.
Why do astronomers think that we are made of star stuff?
Then, later on, when new stars and new planets are forming, some of that new matter ends up in them. So, a lot of the matter that's inside of our Sun and inside of our planet and even inside of us was made within stars long, long ago. That means that you are made of star stuff!
When did man realize the sun was a star?
around 450 BCThe first person we know of to suggest that the Sun is a star up close (or, conversely, that stars are Suns far away) was Anaxagoras, around 450 BC.
Do we have 2 Suns?
Our Sun is a solitary star, all on its ownsome, which makes it something of an oddball. But there's evidence to suggest that it did have a binary twin, once upon a time.
Is the Sun fire?
The Sun does not "burn", like we think of logs in a fire or paper burning. The Sun glows because it is a very big ball of gas, and a process called nuclear fusion is taking place in its core.
How old are the stars we see?
Stars are like your very own sparkly, astronomical time machine, taking you back thousands of years. All of the stars you can see with the unaided eye lie within about 4,000 light-years of us. So, at most, you are seeing stars as they appeared 4,000 years ago.
Are the stars Suns?
Namely, every Sun is a star, but not every star is a Sun. The Sun is larger and as such a lot brighter than most stars. There are billions of Suns in our galaxy alone and as mentioned, many of the stars we see are also Suns. But many celestial objects you see when looking up are not stars.
What is the closest star to Earth?
Distance Information Proxima Centauri, the closest star to our own, is still 40,208,000,000,000 km away. (Or about 268,770 AU.) When we talk about the distances to the stars, we no longer use the AU, or Astronomical Unit; commonly, the light year is used.
How do we know what distant stars are made of quizlet?
Solution. Astronomers are able to tell which elements are present in distant stars by analyzing the line spectra of the light emitted. This spectra is then compared to the known spectra of the elements to determine the identity of these elements.
What is redshift used to determine?
Astronomers use redshifts to measure how the universe is expanding, and thus to determine the distance to our universe's most distant (and therefore oldest) objects.
What are some differences between stars?
Difference between Stars and PlanetsThey are objects that produce their own light and do not rely on an external source for the production of lightPlanets are incapable of producing their own light.Stars have a unique effect of twinkling in the sky.Planets do not exhibit the twinkling effect unlike stars4 more rows
What do scientist think is the reason that irregular galaxies may not have consistent shapes?
What is the reason for irregular galaxies not having a consistent shape? Some irregular galaxies contain in stellar matter. Others have large amounts of it and contain mostly young, hot, blue stars. How many galaxies do scientists think exist?
How do students do science and engineering?
Students do science and engineering through the science and engineering practices. Engaging in these practices necessitates students be part of a learning community to be able to share ideas, evaluate competing ideas, give and receive critique, and reach consensus. Whether this community of learners is made up of classmates or family members, ...
Can students make spectroscopes at home?
Below are some examples of spectroscopes that students can easily and inexpensively make at home or in the classroom. Links are provided to materials that students or teachers might not have readily available.
What happens when a star light is collected, magnified and allowed to pass through the prism?
But while doing so the scientists in the past have noted that when a star light is collected, magnified and allowed to pass through the prism, the output spectrum contained a few dark lines embedded on it (Pic)
Which element has different atomic structure?
All the elements like Hydrogen, Oxygen, Helium, Iron etc have different atomic structure having different number of electrons and different energy levels. So the frequency or wavelength of the absorbed/emitted photon will never be same for two different element, meaning the absorption/emission lines on the spectra of two different elements will be totally different. See the pic.
What does every dark line on absorption spectra mean?
So the conclusion is that every dark line on absorption spectra signifies that the atom of the medium from which the light is generated has absorbed the photon of that particular frequency (wavelength), while reverse is the case for the emission spectra.
How many colors are in a prism?
Now we all know that a prism disperses a light ray into 7 color waves in VIBGYOR Pattern (pic), which basically means that a light (light from stars, galaxies or any object) is made up of 7 different waves of different colors and hence different frequencies. Each color (photon) signify a particular frequency (wavelength). Red light (Red Photon) has the frequency of 400 Tera Hertz (620 nano meters), while the Violet light (Violet Photon) signifies a frequency of 789 Tera Hertz (450 nano meters). Higher the frequency lower is the wavelength and vice versa.
Can light be a continuous spectra?
OK so we have understood that any light (from any source) must contain a continuous spectra (Colors). If we capture a light from a star and allow it to pass through a prism, it should again dissect the star light into 7 Different colors, isn’t it? Yes 100%
Does it matter which spectra we get?
So it really does not matter which spectra we get
What is the Sun made of?
What she found was that the Sun is mostly hydrogen and helium. The rest of the elements are basically the same as those that make up the Earth and in the same relative proportions.
When certain substances were heated, they glowed with a different color?
As early as the 1750s it was noticed that when certain substances were heated they glowed with a different color. When this light was analyzed by separating it into a spectrum it was seen that each element has a distinctive set of colors of light that it emits. Here's the pattern produced by the elements hydrogen and helium when heated enough to make them glow.
How can we learn about objects from afar?
We can also observe objects from afar and learn a lot about them by just studying the light that they give off, or that they reflect.
Do we have pieces of the moon?
The simplest way is to get a piece of the planet and look at it, but in reality this doesn't happen very often. We sent astronauts to the moon and they picked up rocks and brought them back, so we have pieces of the moon to study. We also have a few pieces of mars and the asteroid belt that have falled to the earth as meteorites. But what about the rest of the universe?