How are trade winds formed?
The trade winds begin as warm, moist air from the equator rises in the atmosphere and cooler air closer to the poles sinks. The trade winds are created by a cycle of warm, moist air rising near the equator. The air eventually cools and sinks a bit further north in the tropics. This phenomenon is called the Hadley cell.
How do trade winds affect the movement of hurricanes?
In the Atlantic Ocean, some of these storms become hurricanes, and the trade winds can steer hurricanes west toward the United States. NOAA’s GOES-East satellite keeps an eye on how trade winds impact the movement of hurricanes and tropical storms toward the southeastern United States.
How are trade winds used by sailors?
These winds are formed when the hot air rises and hits the equator where it is pulled towards the poles making them chilled. These winds are used by the sailors. Christopher Columbus discovered America with the help of trade winds.
Where do the trade winds of both hemispheres meet?
The trade winds of both hemispheres meet at the doldrums. As they blow across tropical regions, air masses heat up over lower latitudes due to more direct sunlight. Those that develop over land (continental) are drier and hotter than those that develop over oceans (maritime), and travel northward on the western periphery of the subtropical ridge.

How do the trade winds flow?
The Short Answer: The trade winds are winds that reliably blow east to west just north and south of the equator. The winds help ships travel west, and they can also steer storms such as hurricanes, too.
What direction do trade winds come from?
What Are Trade Winds? Trade winds can be defined as the wind that flows towards the equator from the north-east in the Northern Hemisphere or from the south-east in the Southern Hemisphere. These are also known as tropical easterlies and are known for their consistency in force and direction.
Do trade winds move air masses?
Trade Winds The bulk of air mass movement and transfer of solar heat energy occurs in the Hadley circulation cells located directly north and south of the equator. The sun warms the tropical ocean and causes evaporation of seawater into water vapor in the air.
How fast are the trade winds?
Its average speed is about 5 to 6 metres per second (11 to 13 miles per hour) but can increase to speeds of 13 metres per second (30 miles per hour) or more. The trade winds were named by the crews of sailing ships that depended on the winds during westward ocean crossings.
Why are trade winds stronger in winter?
Trade winds originate more from the direction of the poles (northeast in the Northern Hemisphere, southeast in the Southern Hemisphere) during the cold season, and are stronger in the winter than the summer.
Are the trade winds constant?
The trade winds blow steadily for days and are among the most consistent on earth. When trade winds move over warm tropical waters, they pick up moisture and bring heavy rainfall to the windward-facing slopes of mountainous areas, contrasting with the downward motion of dry air that creates desert areas on land.
Why does wind stop at night?
At night, there is no surface heating and therefore less turbulence and the surface wind tends to resume its normal direction and speed. It backs and decreases.
Do storms move north to south?
The prevailing wind direction here across the U.S. is from west to east, which explains why most storm systems move in that direction. However, depending on certain factors, such as jet stream placement and positioning, some storm systems can move from south to north, and even east-to-west!
Why do trade winds weaken?
The strengthening and weakening of the trade winds is a function of changes in the pressure gradient of the atmosphere over the tropical Pacific. Ironically, the warming of the sea surface works to decrease the atmospheric pressure above it by transfering more heat to the atmosphere and making it more buoyant.
Why do trade winds exist?
Trade winds are caused by the strong warming and evaporation within the atmosphere around the equator. (1) Around the equator, the warm air rises rapidly, carrying a lot of moisture.
What are the three types of trade winds?
On earth, winds are broadly classified into three categories:Primary Wind.Secondary Wind.Tertiary Wind.
Why are tradewinds called that?
Trade Winds, so named because if you had a ship full of goods to sell or trade and no way to get it to the place you wanted to sell or trade it other than your sailing vessel, a reliable and predictable wind that always blew in the same places in the same direction would be pretty nifty.
What is the direction of trade winds in the Northern Hemisphere?
In the northern hemisphere the Trade Winds generally blow from the north east while in the southern hemisphere they blow from the south east.
Why do winds come in from the northeast in winter?
The coriolis effect, an offshoot of the Earth's rotation, makes moving air masses curve, so that the winds converging on the Equator come from the northeast in the Northern Hemisphere and the southeast in the Southern Hemisphere.
Why wind blows from west to east?
However, air moving toward the poles retains its eastward momentum while the earth's rotational velocity decreases beneath it. The result is the wind moves faster than the earth rotates so it moves from west to east (relative to us at the surface).
Do storms move north to south?
The prevailing wind direction here across the U.S. is from west to east, which explains why most storm systems move in that direction. However, depending on certain factors, such as jet stream placement and positioning, some storm systems can move from south to north, and even east-to-west!
What is wind?
The flow of gases or air on a large scale from the high-pressure area to low-pressure area is known as wind.
What are the factors on which the wind is classified?
Factors on which the wind is classified are: Spatial scale Speed Types of forces Regions in which they occur
What are trade winds?
Trade winds are mainly caused due to the Coriolis effect and Ferrel’s law. Trade winds blow as north-eastern trades in the Northern Hemisphere and...
What are planetary winds?
Planetary winds are caused due to the difference in air pressure from one latitude to another latitude.
When does the trade wind move?
During mid-summer in the Northern Hemisphere (Ju ly), the westward-moving trade winds south of the northward-moving subtropical ridge expand northwestward from the Caribbean sea into southeastern North America (Florida and Gulf Coast).
What are the trade winds in the Northern Hemisphere?
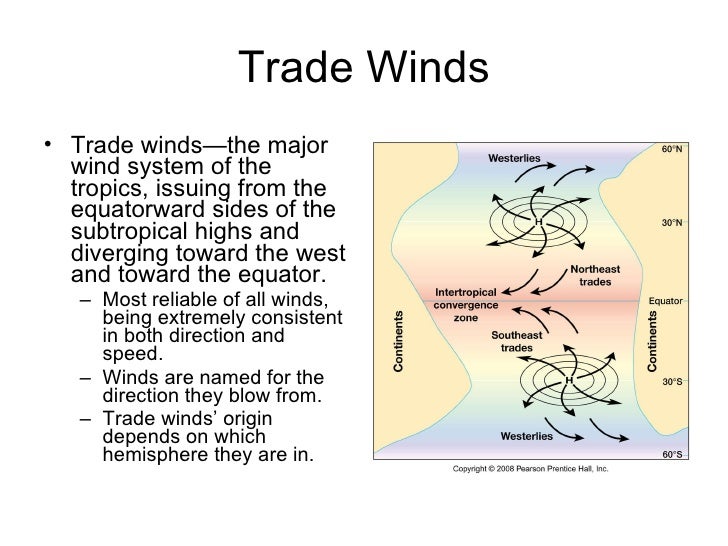
Because winds are named for the direction from which the wind is blowing, these winds are called the northeasterly trade winds in the Northern Hemisphere and the southeasterly trade winds in the Southern Hemisphere. The trade winds of both hemispheres meet at the Doldrums.
What are the prevailing winds that flow in the equatorial region?
Permanent east-to-west prevailing winds that flow in the Earth's equatorial region. The westerlies (blue arrows) and trade winds (yellow and brown arrows) The trade winds or easterlies are the permanent east-to-west prevailing winds that flow in the Earth's equatorial region. The trade winds blow mainly from the northeast in ...
What did the Portuguese do to the trade winds?
The Portuguese recognized the importance of the trade winds (then the Volta do mar, meaning in Portuguese "turn of the sea" but also "return from the sea") in navigation in both the north and south Atlantic ocean as early as the 15th century. From West Africa, the Portuguese had to sail away from continental Africa, that is, to west and northwest.
How tall are trade wind clouds?
Clouds which form above regions within trade wind regimes are typically composed of cumulus which extend no more than 4 kilometres (13,000 ft) in height, and are capped from being taller by the trade wind inversion.
Why do air masses heat up?
As they blow across tropical regions, air masses heat up over lower latitudes due to more direct sunlight. Those that develop over land (continental) are drier and hotter than those that develop over oceans (maritime), and travel northward on the western periphery of the subtropical ridge. Maritime tropical air masses are sometimes referred to as trade air masses. All tropical oceans except the northern Indian Ocean have extensive areas of trade winds.
When is the windy season in South America?
As an example, the windy season in the Guianas, which lie at low latitudes in South America, occurs between January and April. When the phase of the Arctic oscillation (AO) is warm, trade winds are stronger within the tropics. The cold phase of the AO leads to weaker trade winds.
What was the trade wind?
Early commerce to the Americas relied on the trade winds—the prevailing easterly winds that circle the Earth near the equator.
How did the trade winds help sailors?
Known to sailors around the world, the trade winds and associated ocean currents helped early sailing ships from European and African ports make their journeys to the Americas. Likewise, the trade winds also drive sailing vessels from the Americas toward Asia.
What causes the doldrums to warm up?
Intense solar heat in the doldrums warms and moistens the trade winds, thrusting air upwards into the atmosphere like a hot air balloon. As the air rises, it cools, causing persistent bands of showers and storms in the tropics and rainforests. The rising air masses move toward the poles, then sink back toward Earth's surface near the horse latitudes. The sinking air triggers the calm trade winds and little precipitation, completing the cycle.
What is the direction of the Earth's rotation?
Between about 30 degrees north and 30 degrees south of the equator, in a region called the horse latitudes, the Earth's rotation causes air to slant toward the equator in a southwesterly direction in the northern hemisphere and in a northwesterly direction in the southern hemisphere. This is called the Coriolis Effect.
What is the Coriolis effect?
This is called the Coriolis Effect. The Coriolis Effect, in combination with an area of high pressure, causes the prevailing winds—the trade winds—to move from east to west on both sides of the equator across this 60-degree "belt.".
What happens when air masses rise?
The rising air masses move toward the poles, then sink back toward Earth's surface near the horse latitudes. The sinking air triggers the calm trade winds and little precipitation, completing the cycle .
What is the belt around the Earth's midsection called?
This 10-degree belt around Earth's midsection is called the Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone, more commonly known as the doldrums .
How are trade winds formed?
These winds are formed when the hot air rises and hits the equator where it is pulled towards the poles making them chilled. These winds are used by the sailors. Christopher Columbus discovered America with the help of trade winds.
What causes trade winds?
Trade winds are mainly caused due to the Coriolis effect and Ferrel’s law. Trade winds blow as north-eastern trades in the Northern Hemisphere and as south-eastern trades in the Southern Hemisphere.
What is the Coriolis effect?
The Coriolis effect is defined as the inertial or fictitious force responsible for the deflection of winds towards the right in the Northern Hemisphere and towards the left in the Southern Hemisphere. Coriolis effect is used for deriving Ferrel’s law. 1,51,787.
What are the different types of wind?
Based on the above parameters, wind can be classified into different types: 1 Planetary winds: These winds are also known as prevailing winds and are caused due to the difference in air pressure from one latitude to another latitude. 2 Trade winds: These winds are mainly caused due to the Coriolis effect and Ferrel’s law. They blow as north-eastern trades in Northern Hemisphere and as south-eastern trades in Southern Hemisphere. 3 The westerlies: These winds are developed between 40° and 65°S latitudes and these latitudes are known as the Roaring Forties, Furious Fifties and Shrieking Sixties. 4 Periodic winds: These winds are dependent on seasons and change their direction accordingly like monsoons. 5 Local winds: These are caused due to local differences in temperature and pressure and classified as hot, cold, conventional and slope.
What is trade wind?
Trade winds can be defined as the wind that flows towards the equator from the north-east in the Northern Hemisphere or from the south-east in the Southern Hemisphere. These are also known as tropical easterlies and are known for their consistency in force and direction. These winds are formed when the hot air rises and hits ...
What hemisphere do westerlies blow?
They blow as north-eastern trades in Northern Hemisphere and as south -eastern trades in Southern Hemisphere. The westerlies: These winds are developed between 40° and 65°S latitudes and these latitudes are known as the Roaring Forties, Furious Fifties and Shrieking Sixties.
What are the two main causes of the prevailing winds?
Trade winds: These winds are mainly caused due to the Coriolis effect and Ferrel’s law.
Which direction does wind shear push an anticyclone?
Wind shear pushes the anticyclone at storm top off to one side. The low level cyclone and the upper level anticyclone then push each other in one direction, in this case, toward the north.
How do hurricanes move?
The movement of a hurricane from one location to another is known as hurricane propagation. In general, hurricanes are steered by global winds. The prevailing winds that surround a hurricane, also known as the environmental wind field, are what guide a hurricane along its path. The hurricane propagates in the direction of this wind field, which also factors into the system’s propagation speed. While each storm makes its own path, the movement of every hurricane is affected by a combination of factors, as described below.
How does wind shear affect hurricanes?
By displacing the cyclonic (counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere) circulation in the lower troposphere downstream from the anticyclonic (clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere) circulation in the upper troposphere, the vertical wind shear may allow the lower circulation to push the upper one and the upper circulation to push the lower one, having a combined effect of changing the track of the entire hurricane.
What is the name of the wind that steers a hurricane towards the west?
In the tropics, where hurricanes form, easterly winds called the trade winds steer a hurricane towards the west.
What are the main wind fields that affect hurricanes?
The persistent easterly trade winds in the tropics (~0 to 30°N and ~0 to 30°S) and the Westerlies in the mid-latitudes are the Earth’s major wind fields that impact hurricane movement. Image provided by the National Snow and Ice Data Center.
What is the clockwise rotation of the wind?
Embedded within the global winds are large-scale high and low-pressure systems. The clockwise rotation (in the Northern Hemisphere) of air associated with high-pressure systems often cause hurricanes to stray from their initially east-to-west movement and curve northward.
Why do hurricanes drift northwestward?
In addition to the steering flow by the environmental wind, a hurricane drifts northwestward (in the Northern Hemisphere) due to a process called beta drift, which arises because the strength of the Coriolis force increases with latitude for a given wind speed.
How does the Coriolis effect affect wind?
Outside storm systems, the impact of the Coriolis effect helps define regular wind patterns around the globe. As warm air rises near the Equator, for instance, it flows toward the poles. In the Northern Hemisphere, these warm air currents are deflected to the right (east) as they move northward.
Which way do hurricanes rotate?
As air masses are pulled into cyclones from all directions, they are deflected, and the storm system—a hurricane —seems to rotate counter-clockwise. In the Southern Hemisphere, currents are deflected to the left. As a result, storm systems seem to rotate clockwise. Outside storm systems, the impact of the Coriolis effect helps define regular wind ...
What invisible force appears to deflect the wind?
The invisible force that appears to deflect the wind is the Coriolis force. The Coriolis force applies to movement on rotating objects. It is determined by the mass of the object and the object's rate of rotation. The Coriolis force is perpendicular to the object's axis. The Earth spins on its axis from west to east.
What is the Coriolis effect?
The Coriolis effect describes the pattern of deflection taken by objects not firmly connected to the ground as they travel long distances around Earth. The Coriolis effect is responsible for many large-scale weather patterns.
Why does the Earth rotate so slowly?
The slow rotation of Earth means the Coriolis effect is not strong enough to be seen at slow speeds over short distances, such as the draining of water in a bathtub.
How to observe the Coriolis effect?
You could observe the Coriolis effect if you and some friends sat on a rotating merry-go-round and threw or rolled a ball back and forth. When the merry-go-round is not rotating, rolling the ball back-and-forth is simple and straightforward.
Where is the Coriolis force strongest?
The Coriolis force is strongest near the poles, and absent at the Equator. Cyclones need the Coriolis force in order to circulate. For this reasons, hurricanes almost never occur in equatorial regions, and never cross the Equator itself.