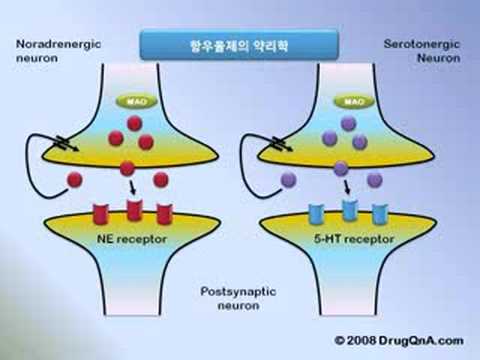
What are tricyclic antidepressants?
You can see a complete list of antidepressants here. Tricyclic drugs work by increasing the brain's supply of norepinephrine and serotonin levels - chemicals that are often abnormally low in depressed patients. Unlike some other antidepressants, tricyclics do not act by stimulating the central nervous system or by blocking monoamine oxidase.
How do cyclic antidepressants work?
Cyclic antidepressants block the absorption (reuptake) of the neurotransmitters serotonin (ser-o-TOE-nin) and norepinephrine (nor-ep-ih-NEF-rin), increasing the levels of these two neurotransmitters in the brain. Cyclic antidepressants also affect other chemical messengers, which can lead to a number of side effects.
How do tricyclic antidepressants interact with other medications or foods?
Tricyclic antidepressants can increase the effects of epinephrine on your heart. This can lead to high blood pressure and problems with your heart rhythm. Cimetidine can increase levels of tricyclic antidepressant in your body, making side effects more likely. Other drugs and substances can also interact with tricyclic antidepressants.
How should I take my tricyclic antidepressant?
Almost all tricyclic antidepressants come in tablet or capsule form. Depending on the medication and dosage you’re prescribed, you may need to take your tricyclic antidepressant one or several times per day. Follow the instructions provided by your healthcare provider and use your medication exactly as prescribed.

What does tricyclic do to the brain?
Tricyclic antidepressants increase levels of norepinephrine and serotonin, two neurotransmitters, and block the action of acetylcholine, another neurotransmitter. Scientists believe that by restoring the balance in these neurotransmitters in the brain that tricyclic antidepressants alleviate depression.
How are tricyclics different from SSRIs?
Tricyclic antidepressants are less selective than SSRIs, meaning they have the potential to affect more body systems. They also have more potential for serious or fatal toxicity when taken in large amounts, compared with SSRIs.
What do tricyclic antidepressants do?
Tricyclic antidepressants, or TCAs, were first used to manage major depression. They are believed to block the reuptake of the monoamine neurotransmitters—including serotonin and norepinephrine.
What receptors do tricyclics work on?
In summary, tricyclic antidepressants can act through NMDA antagonism, opioidergic effects, sodium, potassium and calcium channel blocking, through interfering with the reuptake of serotonin and acting as antagonists to SHAM (serotonin, histamine, alpha, muscarinic) receptors.
Why are tricyclic antidepressants not used anymore?
Due to their adverse effects and lethality in overdose quantities, over time they have been largely replaced by selective serotonin reup-take inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) in depression management.
Are tricyclic antidepressants stronger than SSRI?
Results: There is no overall difference in efficacy between SSRIs and TCAs (effect size -0.03, 95% confidence interval -0.09 to 0.03).
What is the most concerning issue with tricyclic antidepressants?
Some tricyclic antidepressants are more likely to cause side effects that affect safety, such as: Disorientation or confusion, particularly in older people when the dosage is too high. Increased or irregular heart rate. More-frequent seizures in people who have seizures.
Do tricyclics affect dopamine?
Tricyclic antidepressants interfere with the reuptake of norepinephrine, serotonin, and dopamine. The side effects of these drugs are mostly due to their interference with the function of the autonomic nervous system and may include dryness of the mouth, blurred vision, constipation, and difficulty urinating.
What is the safest tricyclic antidepressant?
Among these drugs, amitriptyline and nortriptyline have the largest body of reassuring safety data in pregnancy and lactation.
Why are antidepressants called tricyclics?
First introduced in the 1950s, tricyclic antidepressants are so-named because their molecular structure is composed of three rings of atoms.
Who should not take tricyclic antidepressants?
Warnings and PrecautionsAre under age 25 or over age 65.Have diabetes, heart problems, or a thyroid disorder.Have any conditions affecting your urinary tract or an enlarged prostate.Have glaucoma.Have a liver disease.Have a history of seizures.Take medications to help manage your mood.
Why do you take amitriptyline at night?
It's best to take your amitriptyline in the evening or before you go to bed. This is because it can make you feel sleepy. You may start to feel better after 1 or 2 weeks, but it can take 6 weeks for amitriptyline to work as a painkiller. Amitriptyline can cause extra side effects if you stop taking it suddenly.
What is the difference between SSRI and antidepressants?
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are the most commonly prescribed antidepressants. They can ease symptoms of moderate to severe depression, are relatively safe and typically cause fewer side effects than other types of antidepressants do.
Which is an advantage of taking SSRIs over TCAs?
Whilst their clinical efficacy is equivalent to that of the tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), the SSRIs have a greatly reduced risk of toxicity in overdose and have been shown to be significantly better tolerated.
Are tricyclic antidepressants more effective?
For instance, severe depression promoted selection of TCAs by psychiatrists in line with several studies suggesting that TCAs are more effective than SSRIs in treatment of severe melancholic depression [35,36,37].
Why are antidepressants called tricyclics?
First introduced in the 1950s, tricyclic antidepressants are so-named because their molecular structure is composed of three rings of atoms.
How Cyclic Antidepressants Work
Cyclic antidepressants ease depression by impacting chemical messengers (neurotransmitters) used to communicate between brain cells. Like most anti...
Cyclic Antidepressants Approved to Treat Depression
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved these cyclic antidepressants to treat depression:Tricyclic antidepressants: 1. Amitriptyline 2. Amo...
Possible Side Effects and Cautions
Because of the different ways cyclic antidepressants work, side effects vary somewhat from medication to medication. Some side effects may go away...
Suicide Risk and Antidepressants
Most antidepressants are generally safe, but the FDA requires that all antidepressants carry black box warnings, the strictest warnings for prescri...
Stopping Treatment With Cyclic Antidepressants
Cyclic antidepressants aren't considered addictive. However, stopping antidepressant treatment abruptly or missing several doses can cause withdraw...
Finding The Right Antidepressant
People may react differently to the same antidepressant. For example, a particular drug may work better — or not as well — for you than for another...
How do cyclic antidepressants work?
Like most antidepressants, cyclic antidepressants work by ultimately effecting changes in brain chemistry and communication in brain nerve cell circuitry known to regulate mood, to help relieve depression. Cyclic antidepressants block the reabsorption (reuptake) of the neurotransmitters serotonin (ser-o-TOE-nin) and norepinephrine ...
What is the name of the tetracyclic antidepressant?
In certain cases, they relieve depression when other treatments have failed. Cyclic antidepressants are designated as tricyclic or tetracyclic, depending on the number of rings in their chemical structure — three (tri) or four (tetra).
What is the chemical structure of cyclic antidepressants?
Cyclic antidepressants are designated as tricyclic or tetracyclic, depending on the number of rings in their chemical structure — three (tri) or four (tetra).
What neurotransmitter is blocked by cyclic antidepressants?
Cyclic antidepressants block the reabsorption (reuptake) of the neurotransmitters serotonin (ser-o-TOE-nin) and norepinephrine (nor-ep-ih-NEF-rin), increasing the levels of these two neurotransmitters in the brain. Cyclic antidepressants also affect other chemical messengers, which can lead to a number of side effects.
Can you take cyclic antidepressants while pregnant?
Talk to your doctor about the risks and benefits of using specific antidepressants. Some antidepressants may harm your baby if you take them during pregnancy or while you're breast-feeding.
Can cyclic antidepressants cause health problems?
Overdose of cyclic antidepressants can be dangerous. Chronic health conditions. Cyclic antidepressants can cause problems in people with certain health conditions.
Can you react differently to the same antidepressant?
People may react differently to the same antidepressant. For example, a particular drug may work better — or not as well — for you than for another person. Or you may have more, or fewer, side effects from taking a specific antidepressant than someone else does.
What is the difference between cyclic and tricyclic antidepressants?
In lower doses, cyclic antidepressants are used to prevent migraines and to treat chronic pain. They are also sometimes used to help people with panic disorder. Tricyclic antidepressants treat depression, but they have other effects on your body as well.
Why do doctors prescribe tricyclic antidepressants?
Tricyclic antidepressants help keep more serotonin and norepinephrine available to your brain. These chemicals are made naturally by your body and are thought to affect your mood.
Can you drink alcohol with tricyclic antidepressants?
People who drink alcohol frequently should avoid tricyclic antidepressants. Alcohol lessens the antidepressant action of these drugs. It also increases their sedating effects. Tricyclic antidepressants can cause harmful side effects if you take them with certain medications, including epinephrine (Epi-Pen) and cimetidine (Tagamet).
Can tricyclic antidepressants cause constipation?
Tricyclic antidepressants are more likely to cause constipation, weight gain, and sedation than other antidepressants. However, different drugs have different effects. If you have a troublesome side effect on one tricyclic antidepressant, tell your doctor. Switching to another cyclic antidepressant may help.
Is cyclic antidepressant effective?
They were one of the first antidepressants, and they’re still considered effective for treating depression. These drugs are a good choice for some people whose depression is resistant to other drugs. Although cyclic antidepressants can be effective, some people find their side effects difficult to tolerate. That’s why these drugs are not often used ...
Do tricyclic antidepressants affect blood sugar?
Tricyclic antidepressants also affect blood sugar levels, so people with diabetes who take these drugs may need to check their blood sugar level more frequently.
Can tricyclic antidepressants interact with other drugs?
Other drugs and substances can also interact with tricyclic antidepressants. It’s important for you to tell your doctor about all drugs and substances you use. Your doctor can help you avoid any interactions.
How do tricyclic antidepressants work?
Tricyclic antidepressants work by preventing the reabsorption of neurotransmitters called serotonin and norepinephrine. The body needs both of these to function normally. If there is too much of either, you may end up experiencing anxiety. If there is not enough, depression may ensue.
How long does it take for tricyclic medication to work?
Approved Medications. With tricyclic antidepressants, like other antidepressants, it will usually take between six to eight weeks before you feel any substantial improvement in your depression symptoms. 3 Some of the more commonly prescribed TCAs include: Anafranil (clomipramine) Ascendin (amoxapine)
Why are TCAs so named?
First introduced in the 1950s, tricyclic antidepressants are so-named because their molecular structure is composed of three rings of atoms.
What are the conditions that are treated with tricyclic antidepressants?
Conditions Treated. Tricyclic antidepressants are used primarily to treat mood disorders but also have their place in the treatment of anxiety disorders, personality disorders, and neurological disorders. 2 They are often used when other drugs are unable to provide relief. Mood disorders often treated with TCAs include: Bipolar disorder.
Why do TCAs help with depression?
If you have depression, the restoration of the serotonin and norepinephrine levels can lead to an improvement in your symptoms. 1 .
Can TCAs cause drug dependence?
While not strictly addictive per se, the long-term use of TCAs may lead to drug dependence.
Do TCAs have the same mechanism of action?
While different TCAs have slightly different mechanisms of action, they share similar side effects. Many of these are associated with the effect the drugs have on the smooth muscles of the internal organs. Common side effects include:
How long does it take for tricyclics to work?
Typically, tricyclic antidepressants take several weeks to produce a noticeable improvement in your mood and general quality of life. It may take several weeks or longer before you begin to experience the full effects of any tricyclic antidepressant.
Why are tricyclic antidepressants prescribed?
They’re often prescribed to treat depression when newer medications aren’t completely effective.
How long does it take for tricyclic antidepressants to work?
Like other antidepressants, tricyclic antidepressants can take several weeks to start treating depression. It’s important to continue using your medication as prescribed during the first few weeks, even if you don’t notice any immediate improvements.
How much weight gain is a tricyclic antidepressant?
In a 1984 study, people prescribed low to modest doses of several tricyclic antidepressants had a mean monthly weight gain of 1.3 to 2.9 lbs and an average weight gain of three to 16 lbs over the course of treatment.
What is a tricyclic antidepressant?
Tricyclic antidepressants, or TCAs, are a type of antidepressant. Developed in the middle of the 20th century, tricyclic antidepressants were some of the first prescription medications prescribed to treat depression and related conditions.
When was the first tricyclic antidepressant developed?
The first tricyclic antidepressants were developed in the 1950s. Imipramine, an early TCA, was developed in 1950s and approved in 1959 by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Amitriptyline, a TCA marketed under the brand name Elavil, was developed and approved in the ‘60s by the FDA
How much weight can I gain with Nortriptyline?
A study published in 2011 found that patients prescribed nortriptyline, a tricyclic antidepressant, gained an average of 2.64 lbs over 12 weeks -- more than those who were prescribed the SSRI escitalopram.
What are the chemicals in antidepressants?
These chemicals include serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine. In various ways, different antidepressants seem to affect how these neurotransmitters behave. Here's a rundown of the main types of antidepressants.
How long does it take for antidepressants to work?
But that's just not how antidepressants work. No one knows exactly why, but they can take weeks or months before they gain their full effect. When you're taking an antidepressant, it's important to adjust your expectations and to try to be patient. Share on Facebook Share on Twitter Share on Pinterest Email Print.
What is the name of the antidepressant that blocks the reuptake of serotonin and no?
Serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) are among the newer types of antidepressant. As the name implies, they block the reuptake of both serotonin and norepinephrine. They include duloxetine ( Cymbalta ), venlafaxine ( Effexor ), desvenlafaxine ER ( Khedezla ), levomilnacipran ( Fetzima ), and desvenlafaxine ( Pristiq ).
What is the name of the drug that prevents neurotransmitters from being reabsorbed?
A reuptake inhibitor prevents this from happening. Instead of getting reabsorbed, the neurotransmitter stays -- at least temporarily -- in the gap between the nerves, called the synapse.
How do antidepressants affect the brain?
That said, many researchers believe that the benefits of antidepressants stem from how they affect certain brain circuits and the chemicals (called neurotransmitters) that pass along signals from one nerve cell to another in the brain. These chemicals include serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine. In various ways, different antidepressants seem to affect how these neurotransmitters behave. Here's a rundown of the main types of antidepressants.
What is depression a chemical imbalance?
If you've read up on antidepressants -- in newspapers and magazines, or on the Web -- you might see depression explained simply as a "chemical imbalance" or a "serotonin deficiency." Unfortunately, it's not that simple. We really don't know what causes depression or how it affects the brain. We don't exactly know how antidepressants improve the symptoms.
Why is tricyclic antidepressant receptor affinity important?
Using tricyclic antidepressant receptor affinity to select an optimal medication that accounts for an individual patient’s comorbidities allows for anticipation and avoidance of unnecessary side effects and improved patient efficacy and safety. Application of these concepts is generally unique to pharmacy practice and serves to improve pharmacists’ clinical utility and generate trust among their fellow health care professionals.
When were tricyclic antidepressants introduced?
Tricyclic antidepressants were introduced in painful diabetic neuropathy in the 1970s, based on findings from empiric observations. However, the drugs’ potential analgesic properties were noted long before in a study published in 1960. 8. Although tricyclic antidepressants remained the mainstay of pharmacological treatment for neuropathic pain ...
Which metabolite of amitriptyline is better tolerated?
Amitriptyline (Ki=18) and clomipramine (Ki=25) have the strongest affinity at this receptor, so they are not as well tolerated. Nortriptyline (Ki=37), the active metabolite of amitriptyline, retains some potency as a muscarinic receptor antagonist, but it is better tolerated than its parent drug.
Is tricyclic pain medication effective?
Though newer medication classes have more appealing side effect profiles, there is still a place for tricyclic antidepressants in neuropathic pain treatment. These drugs are not only effective, but also inexpensive, making them attractive to patients without insurance coverage or with limited budgets.
Is tricyclic antidepressant effective for neuropathic pain?
Effective Tricyclic Antidepressant Dosing for Neuropathic Pain. When prescribing any tricyclic antidepressant for the treatment of neuropathic pain, it is important to realize that these drugs are effective at much lower doses in this setting than in depression. For example, amitriptyline and desipramine have been proven effective in neuropathic ...
Can you switch to imipramine or nortriptyline?
Amitriptyline and imipramine are often attempted first, but it is common to switch to nortriptyline or desi pramine if the patient is unable to tolerate the drug, or it lacks efficacy. This can be predicted by assessing Ki values.
Is clomipramine a tricyclic antidepressant?
For example, clomipramine, a tricyclic antidepressant developed in the 1960s, is used much like an SSRI in the treatment of major depressive disorder, but it generally isn’t used in treatment of neuropathic pain. This is expected when comparing clomipramine’s affinity for the serotonin reuptake receptor (Ki= 0.14) to the affinity of the SSRI sertraline (Ki= 0.26).
What is tricyclic antidepressant?
Tricyclic antidepressants are a class of medications used in the management and treatment of major depressive disorder. This activity reviews the indications, actions, and contraindications for tricyclic antidepressants as a valuable agent in the treatment of major depressive disorder. This activity will highlight the mechanism of action, adverse event profile, monitoring, relevant interactions, off-label uses, and other key elements of tricyclic antidepressant therapy pertinent for members of the interprofessional team in the management of patients with major depressive disorder and related conditions.
What are the effects of TCA?
TCAs have varying degrees of receptor affinities, leading to several adverse effects. The most common adverse effects include constipation, dizziness, and xerostomia [28]. Due to its blockade of cholinergic receptors, it can lead to blurred vision, constipation, xerostomia, confusion, urinary retention, and tachycardia.[29] Due to the blockade of alpha-1 adrenergic receptors, it can cause orthostatic hypotension and dizziness. [28][29] TCA-induced histamine blockade (H1) may lead to sedation, increased appetite, weight gain, and confusion. [30][28]
What are the conditions that are considered pre-existing for TCA?
All patients starting a TCA need screening for pre-existing cardiac conditions, including prolonged QTc intervals, heart disease, and a family history of arrhythmias. Patients who test positive for pre-existing heart conditions may need additional evaluation by a cardiologist before initiating treatment. Additionally, these patients require regular monitoring for the presence of new cardiac symptoms. Patients with low potassium blood concentrations should have periodical monitoring to reduce the risk of arrhythmias.[31] In patients over the age of 50, obtaining an ECG is recommended.
What is the chemical structure of TCA?
The chemical structure of a TCA consists of a three-ringed structure with an attached secondary or tertiary amine. Secondary amines include desipramine, nortriptyline, and protriptyline, while tertiary amines consist of amitryptiline, clomipramine, doxepin, imipramine, and trimipramine. Tertiary amines tend to have greater blockage of serotonin reuptake, while secondary amines have greater blockage of norepinephrine uptake.[23] The combination of different amine structures and variations in chemical composition contribute to the multitude of adverse effects seen with TCA usage as these factors affect TCA-receptor affinity and binding. [24]
Is TCA narrow or broad?
Overall, the therapeutic index of TCAs is narrow, and the therapeutic range for each specific TCA is dependent on the drug prescribed. Because of the narrow therapeutic index of TCAs, patients should be monitored closely for symptoms of toxicity, i.e., QRS-widening on electrocardiogram (ECG), tremors, confusion, muscle rigidity, and coma. [23]
Is TCA a PO?
However, oral administration (PO) remains the usual route of administration for TCAs. [26] The exact dosages for each of the different TCA tablets vary, however, because TCAs have a high risk of adverse effects, initial dosing is low and is gradually increased based on the level of response.[27] If patients are unresponsive at a low dose, then they may respond at higher doses, especially since TCAs have shown increased efficacy at higher dosages when compared with high dose SSRIs.[27] Blood monitoring of TCA concentrations is available; however, there is mixed evidence on its effect on treatment outcomes.[7] In general, patients are given an oral dose of a TCA once a day due to the long half-life and sedative effects of the drug class. [24]
Should TCA be monitored?
All patients starting a TCA or presently taking a TCA should be monitored for worsening depressive symptoms or new-onset suicidal thoughts or behaviors. It may be helpful to monitor the blood concentrations of TCAs in non-adherent patients, have decreased tolerability, or little response to the drug. However, there is mixed evidence on the effectiveness of blood concentration monitoring on clinical outcomes. [7]
