
How do vertebrates respire? ALL VERTEBRATES (animals with a spinal cord, including humans) on land breathe with LUNGS. They breathe with GILLS, flaps of skin on both sides of their heads or in their mouths.
How do vertebrates breathe?
- Answers How do vertebrates breathe? Mammals, birds and reptiles all have lungs. The particulars differ just a bit by group, but the essentials remain common to all. A diaphragm expands the cavity in which the lungs are situated, and the reduced pressure inside causes outside pressure to force air into the lungs.
How do insects respire?
Like all living things, insects respire by absorbing oxygen and excreting carbon dioxide. They have an air-based respiration, as gas exchanges are carried out with gases in the air. Unlike most of the air-breathing vertebrates , the insects (invertebrate animals) do not breather using lungs.
What are the respiratory organs in vertebrates?
In vertebrates the skin may be respiratory (e.g., anurans), while in some fishes and aquatic turtles, the vascular rectum or cloaca is respiratory. But there are two main types of respiratory organs- gills for aquatic respiration and lungs for aerial respiration.
How does the respiratory system work in animals?
The particulars differ just a bit by group, but the essentials remain common to all. A diaphragm expands the cavity in which the lungs are situated, and the reduced pressure inside causes outside pressure to force air into the lungs. The lung cavity (or chest cavity in some animals) gets smaller when the diaphragm relaxes, and air is forced out.
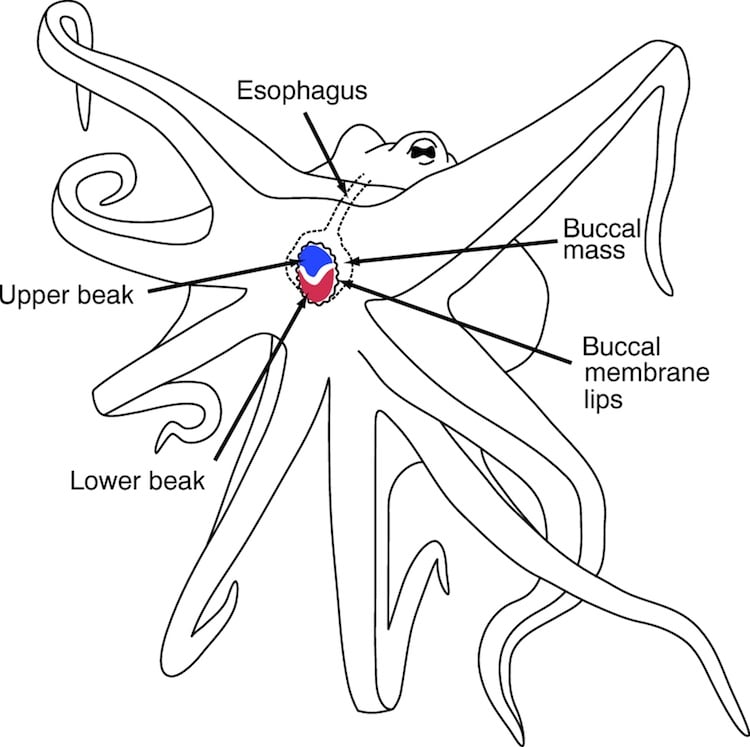
How do animals respire?
The Four Respiratory Systems in Animals: Lung breathing: Mammals, birds, reptiles and some amphibians. Gill breathing: Fish and crabs. Tracheal breathing: nsects, centipedes and spiders. Skin respiration: Amphibians, z.
How do different vertebrates obtain oxygen?
Obtaining oxygen entirely from air, instead of from water, involved drastic changes in the circulatory system. Land vertebrates use their lungs to exchange carbon dioxide for oxygen from the air.
How do vertebrate lungs work?
Vertebrate lungs evolved as supplementary air-breathing organs in primary fishes, being ventilated by buccal pumping. In most recent fishes the lungs are transformed into the hydrostatic swimbladder. This basic type of unicameral lungs and their buccal pumping ventilation are also found in recent amphibians.
Do all vertebrates need oxygen?
All vertebrates need oxygen for aerobic energy supply. Lungs and gills are the organs specialized for O2 and CO2 exchange between air or water and blood;in some animals, the skin serves this task, partly or exclusively.
Which vertebrate can do the respiration without lungs?
Frogs have lungs, cockroaches have trachea, while fishes have gills for respiration. Earthworms don't have special organs for respiration, instead, they breathe through their skin. This type of respiration is known as cutaneous respiration.
Which vertebrates use lungs to breathe?
All vertebrate animals that live on land have lungs. When we breathe in, the muscle below the rib cage (called the diaphragm) is pulled down, and air gets sucked into the rib cage, filling the lungs.
Why are lungs important for vertebrates?
Terrestrial vertebrates (amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals) use a pair of lungs to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide between their tissues and the air.
Did gills turn into lungs?
Darwin believed that lungs evolved from gas bladders, but the fact that fish with lungs are the oldest type of bony fish, plus molecular and developmental evidence, points to the reverse – that lungs evolved before swim bladders.
How do monkeys breathe?
3:434:53Breathing in animals | Respiration in Mammals | Inspiration | ExpirationYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThey use fire cells for breathing. Spirals are connected to air tubes called the trachea trachea isMoreThey use fire cells for breathing. Spirals are connected to air tubes called the trachea trachea is in turn connected to the smaller tubes. The smaller tubes are in turn connected with the body cell.
What are the 4 types of respiration?
Key Takeaways: Types of Respiration External respiration is the breathing process. It involves inhalation and exhalation of gases. Internal respiration involves gas exchange between the blood and body cells. Cellular respiration involves the conversion of food to energy.
What are the 4 types of respiration in animals?
Respiration in AnimalsThrough Plasma Membrane. In unicellular animals, such as amoeba, exchange of gases takes place through cell surface. ... Through Body Wall or Skin. Tapeworms, earthworms, and leeches use their skin for the exchange of gases. ... Through Tracheal System. ... Through Gills. ... Through lungs.
Why can't lungs breathe water?
Humans cannot breathe underwater because our lungs do not have enough surface area to absorb enough oxygen from water, and the lining in our lungs is adapted to handle air rather than water.
Why do different animals have different respiratory systems?
Along the evolutionary tree, different organisms have devised different means of obtaining oxygen from the surrounding atmosphere. The environment in which the animal lives greatly determines how an animal respires. The complexity of the respiratory system is correlated with the size of the organism.
What are the adaptations seen in different types of vertebrates?
Adaptations in VertebrateAble to obtain space, air, and warmth.Secure water, food, and nutrients.Able to reproduce and rear offspring.Cope with harsh physical conditions like- high or low temperature, light, and heat.Protect themselves from their enemies.Better react to the environmental changes taking around them.
What are the 5 types of vertebrates?
The phylum chordata (animals with backbones) is divided into five common classes: fish, amphibians, reptiles, mammals and birds.
What type of circulatory system do vertebrates have?
closed circulatory systemMost vertebrates and some invertebrates, like this annelid earthworm, have a closed circulatory system. In (b) open circulatory systems, a fluid called hemolymph is pumped through a blood vessel that empties into the body cavity.