How are lipids synthesized in the body?
Our bodies synthesize lipids by Lipogenesis. For example, Acetyl CoA is used to create lipids (fat), and this process takes place in the cytoplasm of adipocytes (fat cells) and hepatocytes (liver cells). So, when you eat more glucose or carbohydrates than your body needs, acetyl CoA turns excess into fat. Triglycerides.
Where are lipids found in the body?
They are everywhere in our bodies, including the membranes that line our cells, and they also make up bile, which helps break down fat for absorption. Lipids include fatty acids and glycolipids (a type of lipid). The fatty acid chain comprises an even number of carbon atoms, where one end has the ― COOH group and the other end has hydrogen.
Which lipids are utilized for energy in the body?
The common lipids utilized for energy are fats. This fat is usually stored in the adipose (fat) tissue cells. Carbohydrates and proteins can be converted into fats by enzymes and then get stored in these cells. When the body's energy decreases due to starvation or intense work, the body metabolizes/breaks down the stored fat to produce energy.
Why are lipids important to our body?
The essential lipids, linolenic acid and linoleic acid, are vital to your health; they cannot be made in your body and must come from your diet. They are used in the production of cell membranes and hormones, as well for maintaining vision and supporting the immune system.

How does the body obtain lipids?
Lipids are available to the body from three sources. They can be ingested in the diet, stored in the adipose tissue of the body, or synthesized in the liver. Fats ingested in the diet are digested in the small intestine.
Where do you find lipids in the human body?
Lipids (eg cholesterol, cholesteryl esters and triglycerides) are stored in your body primarily in specialized fat cells called adipocytes, which comprise a specialized fatty tissue called adipose tissue. Stored lipids can be derived from the lipids in your diet or from lipids that your body synthesizes.
What are 3 ways lipids are used in your body?
Lipids perform three primary biological functions within the body: they serve as structural components of cell membranes, function as energy storehouses, and function as important signaling molecules. The three main types of lipids are triacylglycerols (also called triglycerides), phospholipids, and sterols.
What foods cause high lipids?
Foods With LipidsBeef Fat. Beef fat, also known as beef tallow, is almost entirely made of saturated fats. ... Poultry Skin. Chicken and turkey are generally quite healthy. ... Heavy Cream. When fresh milk is processed, a lot of the fat is removed and combined into heavy cream. ... Butter. ... Soft Cheese. ... Bacon.
What will happen to your body if we don't have lipids?
Lack of dietary lipids may cause problems with cell formation and function. The body uses certain parts of lipid molecules to build the membranes that enclose and protect your cells. Fatty acids, also contained in lipid molecules, regulate cell function by transmitting information between cells.
Where is most of a healthy person's fat stored?
Answer and Explanation: In a healthy person, most of their fat is stored in adipose tissue, which is tissue made up of cells that store fat. The majority of this tissue is under the skin and around organs.
Why lipids is important in our body?
Lipids play diverse roles in the normal functioning of the body: they serve as the structural building material of all membranes of cells and organelles. they provide energy for living organisms - providing more than twice the energy content compared with carbohydrates and proteins on a weight basis.
Is cholesterol a lipid?
The term "lipids" includes cholesterol and triglycerides, although there are other types of lipids, too. Standard lipid blood tests include a measurement of total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, and triglycerides.
What are lipids in the body?
Lipids contribute to some of the body's most vital processes. Lipids are fatty, waxy, or oily compounds that are soluble in organic solvents and insoluble in polar solvents such as water. Lipids include: Fats and oils (triglycerides)
Where are proteins found in the body?
Protein is found throughout the body—in muscle, bone, skin, hair, and virtually every other body part or tissue. It makes up the enzymes that power many chemical reactions and the hemoglobin that carries oxygen in your blood.
What are four examples of lipids?
The four main groups of lipids include:Fatty acids (saturated and unsaturated)Glycerides (glycerol-containing lipids)Nonglyceride lipids (sphingolipids, steroids, waxes)Complex lipids (lipoproteins, glycolipids)
What lipid is most abundant in foods and in the body?
Triglycerides. The major lipids in food and stored in the body as fat are the triglycerides, which consist of three fatty acids attached to a backbone of glycerol (an alcohol).
Which is a main function of lipids?
The main function of lipids is energy storage. Lipids, mostly fats, are stored in the adipose tissue cells. Metabolism of the stored fats yields mu...
Why are lipids important to life?
Lipids are important to life since they play a significant role in various bodily functions. For instance, they are structural components of cell m...
What are three major things that lipids do in the body?
Lipids do three major things in the body and a number of other functions. The three major functions include energy storage, insulation, and cushion...
Why are lipids synthesized?from verywellhealth.com
Lipids are synthesized or stored to support the cells and assist in essential processes. Lipids also have many external uses.
What is a lipid?from verywellhealth.com
Tolu Ajiboye. Published on November 12, 2020. A lipid is an organic molecule that can only dissolve in nonpolar solvents and will not dissolve in water. Lipids include hormones, fats, and oils and sometimes refer to fatty acids or derivatives of fatty acids. Lipids play key roles in the function of the body in both health and disease.
What is the difference between HDL and LDL?from verywellhealth.com
There are two types of proteins that carry cholesterol through the bloodstream: high-density lipoprotein (HDL) and low-density lipoprotein (LDL). HDL is considered “good” cholesterol, as it absorbs cholesterol and brings it back to the liver, whereas LDL is “bad” cholesterol that builds up in the body. 3
How many lipids are involved in cell division?from sciencing.com
Lipids also participate in cell division. Dividing cells regulate lipid content depending on the cell cycle. At least 11 lipids are involved in cell cycle activity. Sphingolipids play a role in cytokinesis during interphase. Because cell division results in plasma membrane tension, lipids appear to help with mechanical aspects of division such as membrane stiffness.
What are sphingolipids made of?from sciencing.com
Sphingolipids make up structural and signaling lipids found in the skin. Sphingomyelins, made from ceramides, are prevalent in the nervous system and help motor neurons survive. Lipids also play a role in cell signaling.
What is the role of phospholipids in the cell membrane?from sciencing.com
Phospholipids form the foundation for lipid bilayers, with their amphipathic nature, that make up cell membranes. The outer layer interacts with water while the inner layer exists as a flexible oily substance. The liquid nature of cell membranes aids in their function.
How do phospholipids help plants?from sciencing.com
Phospholipids in plants also work in response to environmental stressors on the plants as well as in response to pathogen infections. In animals, lipids also serve as insulation from the environment and as protection for vital organs. Lipids provide buoyancy and waterproofing as well.
What is Lipid?
Lipids are important fats that serve different roles in the human body. The three main types of lipids are triacylglycerols (also known as triglycerides), phospholipids, and sterols.
Why are phospholipids important?
Phospholipids are crucial for building the protective barrier, or membrane, around your body’s cells. In fact, phospholipids are synthesized in the body to form cell and organelle membranes. In blood and body fluids, phospholipids form structures in which fat is enclosed and transported throughout the bloodstream.
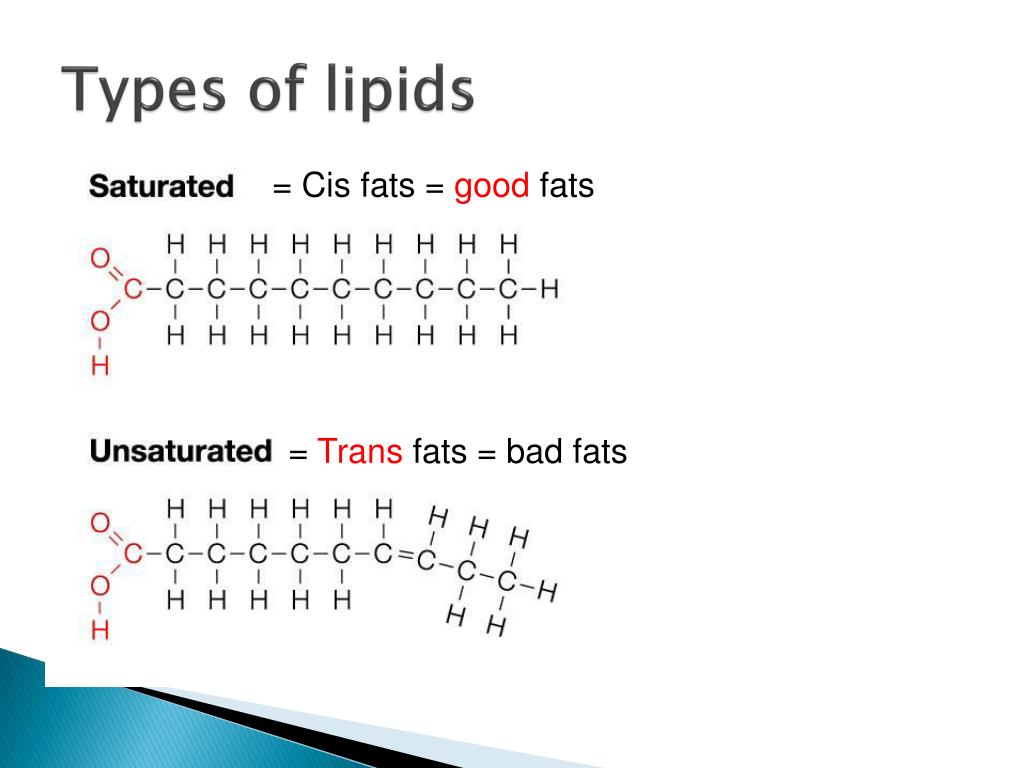
What are the different types of saturated fats?
Saturated and Unsaturated Fats 1 Monounsaturated fat – This type of fat is found in plant oils. Common sources are nuts (almonds, cashews, pecans, peanuts, and walnuts) and nut products, avocados, extra virgin olive oil, sesame oil, high oleic safflower oil, sunflower oil, and canola oil. 2 Polyunsaturated fat – This type of fat is found mainly in plant-based foods, oils, and fish. Common sources are nuts (walnuts, hazelnuts, pecans, almonds, and peanuts), soybean oil, corn oil, safflower oil, flaxseed oil, canola oil, and fish (trout, herring, and salmon). 3 Saturated fat – This fat is found in animal products, dairy products, palm and coconut oils, and cocoa butter. Limit these products to less than 10 percent of your overall dietary fat consumption. Saturated fat, which is found in meat, dairy products, and some plant oils, is associated with increased bloodstream cholesterol. High cholesterol levels indicate that a person is at a major risk for disease, such as heart attack. Avoid saturated fat, or at least consume in moderation.
What is the fat that protects the body?
3) Insulate and Protect – Our bodies are padded with fat, protecting us from everyday friction. The average body fat for a man is 18 to 24 percent and for a woman is 25 to 31 percent 1. Still, adipose tissue can comprise a much larger percentage of bodyweight depending on the degree of obesity of the individual. Some of this fat is stored within the abdominal cavity, called visceral fat, and some are stored just underneath the skin, called subcutaneous fat. Visceral fat protects vital organs—such as the heart, kidneys, and liver. The blanket layer of subcutaneous fat insulates the body from extreme temperatures and helps keep the internal climate under control. It pads our hands and buttocks and prevents friction, as these areas frequently come in contact with hard surfaces. It also gives the body the extra padding required when engaging in physically demanding activities such as ice skating, horseback riding, or snowboarding. There are two types of fat stored as adipose tissue: subcutaneous fat and visceral fat.
What are the functions of fat in the body?
In the body, fat functions as an important depot for energy storage offers insulation and protection and plays important roles in regulating and signaling. Large amounts of dietary fat are not required to meet these functions ...
Where are triacylglycerols found?
Naturally occurring triacylglycerols are found in many foods, including avocados, olives, corn, and nuts. We commonly call the triglycerides in our food “fats” and “oils.”. Fats are lipids that are solid at room temperature, whereas oils are liquid. 2) Phospholipids make up only about 2 percent of dietary lipids.
How does fat pack together?
Fats pack together tightly without water and store far greater amounts of energy in a reduced space. A fat gram is densely concentrated with energy, containing more than double the amount of energy as a gram of carbohydrate.
Why do we need lipids?
Lipids allow us to have healthy hair and nails because it forms structures called keratin, which helps make up these structures.
What are Lipids?
Lipids are a group of molecules in the body made up of fats, cholesterol, and animal waxes. They are everywhere in our bodies, including the membranes that line our cells, and they also make up bile, which helps break down fat for absorption. Lipids include fatty acids and glycolipids (a type of lipid).
How do lipids help with blood pressure?
Lipids also play a role in maintaining healthy blood pressure levels by helping to store certain proteins within the lipid bilayers of cells that can help promote vascular relaxation, which will reduce your blood pressure.
Why are lipids needed in the plasma membrane?
A lipid bilayer is required around the plasma membrane to maintain cell integrity and keep out unwanted substances. Lipids are also involved in cell signaling processes when certain receptors embedded within the lipid bilayers bind with specific signaling molecules.
What is a triglyceride?
Triglycerides. Triglycerides are fats that can be solid or semisolid at room temperature. If the three fatty acids in a triglyceride are identical, it is called simple triglyceride. Mixed Triglycerides have different fat content, and their melting point depends on how many of each type there are and what types they consist of. ( Trusted Source 1*)
How do lipids help us see?
Lipids have an important role in vision. By forming lipid rafts, they help transmit light signals from the retina to the central nervous system, which we can have sight.
What is lipid in food?
Lipids are a type of fat that your body can’t produce on its own. They’re found in many foods, including meat and dairy products.
How is bread broken down in the digestive system?
Bread is rich in complex carbohydrates, particularly starch which is predominantly digested in the small intestine where it is broken down to its constituent glucose monosaccharide units.
What is the chemical breakdown of food called?
As food travels from your mouth into your digestive system, it’s broken down by digestive enzymes that turn it into smaller nutrients that your body can easily absorb. This breakdown is known as chemical digestion.
Where is most fat digested?
The majority of fat digestion happens once it reaches the small intestine. This is also where the majority of nutrients are absorbed. Your pancreas produces enzymes that break down fats, carbohydrates, and proteins. Your liver produces bile that helps you digest fats and certain vitamins.
What are the end products of lipid digestion?
The major products of lipid digestion – fatty acids and 2-monoglycerides – enter the enterocyte by simple diffusion across the plasma membrane. A considerable fraction of the fatty acids also enter the enterocyte via a specific fatty acid transporter protein in the membrane.
What is the role of phospholipase in lipid digestion?
Phospholipases are enzymes that hydrolyze specific portions of phospholipid molecules. Their role in the digestion of exogenous phospholipids and as the active principle in snake and bee venoms has long been appreciated.
What two secretions are needed for lipid digestion?
The two key secretions enabling this process are bile and pancreatic juices. These secretions enable the lipids to form micelles for absorption. Bile supplies bile salts and pancreatic juice and enzymes.
What is the enzyme that breaks down protein?
Once a protein source reaches your stomach, hydrochloric acid and enzymes called proteases break it down into smaller chains of amino acids. Amino acids are joined together by peptides, which are broken by proteases.
What are the functions of fats?
Fats also play important functional roles in sustaining nerve impulse transmission, memory storage, and tissue structure. More specifically in the brain, lipids are focal to brain activity in structure and in function. They help form nerve cell membranes, insulate neurons, and facilitate the signaling of electrical impulses throughout the brain.
What is the main source of energy for the human body?
Most of the energy required by the human body is provided by carbohydrates and lipids. As discussed in the Carbohydrates chapter, glucose is stored in the body as glycogen. While glycogen provides a ready source of energy, lipids primarily function as an energy reserve.
What are fat soluble nutrients?
Fat-soluble nutrients are especially important for good health and exhibit a variety of functions. Vitamins A, D, E, and K —the fat-soluble vitamins—are mainly found in foods containing fat. Some fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamin A) are also found in naturally fat-free foods such as green leafy vegetables, carrots, and broccoli.
What percentage of body fat is made up of fat?
Did you know that up to 30 percent of body weight is comprised of fat tissue? Some of this is made up of visceral fat or adipose tissue surrounding delicate organs. Vital organs such as the heart, kidneys, and liver are protected by visceral fat. The composition of the brain is outstandingly 60 percent fat, demonstrating the major structural role that fat serves within the body. You may be most familiar with subcutaneous fat, or fat underneath the skin. This blanket layer of tissue insulates the body from extreme temperatures and helps keep the internal climate under control. It pads our hands and buttocks and prevents friction, as these areas frequently come in contact with hard surfaces. It also gives the body the extra padding required when engaging in physically demanding activities such as ice- or roller skating, horseback riding, or snowboarding.
How does fat help digestion?
Aiding Digestion and Increasing Bioavailability. The dietary fats in the foods we eat break down in our digestive systems and begin the transport of precious micronutrients. By carrying fat-soluble nutrients through the digestive process, intestinal absorption is improved.
What does tricyceride do to the body?
Regulating and Signaling. Triglycerides control the body’s internal climate, maintaining constant temperature. Those who don’t have enough fat in their bodies tend to feel cold sooner, are often fatigued, and have pressure sores on their skin from fatty acid deficiency.
What is subcutaneous fat?
You may be most familiar with subcutaneous fat, or fat underneath the skin. This blanket layer of tissue insulates the body from extreme temperatures and helps keep the internal climate under control. It pads our hands and buttocks and prevents friction, as these areas frequently come in contact with hard surfaces.
What are lipids? What are some examples?
Keep reading to find examples of the different types of lipids. Lipids from butter, milk, cheese, and eggs.
What are the lipids found in the cell membrane?
Phospholipids. The last category of lipids are phospholipids. These lipids are found in most cell membranes and make up a protective layer between the cell and its outer membrane. Some foods that contain phospholipids include: Type of Phospholipid. Function in the Body. Vitamin-Rich Foods. Phosphatidylcholine.
What are the similarities between lipids and carbohydrates?
Similarities between lipid structures include: They are made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen (same as carbohydrates, but more hydrogen than oxygen molecules). Lipids are hydrophobic and are not water soluble. Most lipids are made up of long hydrocarbon chains.
Why is it important to have a balance of lipids?
It’s important to have a balance of these types of lipids to keep the body functioning. People with low amounts or imbalanced vitamins can take supplements to help their bodily functions. Some examples of fat-soluble vitamins include: Type of Vitamin. Function in the Body.
What determines a lipid's chemical makeup?
The chemical makeup and structure of a lipid determines whether it’s a fat, steroid, wax, or phospholipid. It allows them to pass through a body easily, insulate nerve cells and block surfaces from water. Similarities between lipid structures include:
Do lipids form naturally?
Many types of lipids are part of your everyday diet. Other types of lipids form naturally in your body. No matter how they get there, lipids are an important part of our lives and our health. Here are some lipid examples that you might discover in your body – and where you can find them in a healthy diet.
Should we cut lipids out of our diet?
It’s easy to think that we should cut lipids out of our diet to stay healthy. However, human bodies require many lipids to properly function. If you’d like some tips on avoiding saturated and trans fats, check out an article that features several examples of monounsaturated fats and where to find them.
Why are HDL particles considered good cholesterol?
High-density lipoprotein (HDL) particles are called "good" cholesterol because some of them remove cholesterol from circulation and from artery walls and return it to the liver for excretion. – By Julie Corliss. Executive Editor, Harvard Heart Letter.
What is the name of the protein that moves cholesterol and other fats throughout the body?
These tiny particles, called lipoproteins (lipid plus protein), move cholesterol and other fats throughout the body. Cholesterol and other lipids circulate in the bloodstream in several different forms. Of these, the one that gets the most attention is low-density lipoprotein— better known as LDL, or "bad" cholesterol.
Why is LDL considered bad?
LDL is known as "bad" cholesterol because it delivers cholesterol to tissues and is strongly associated with the buildup of artery-clogging plaque.
What are the different types of cholesterol?
Cholesterol and other lipids circulate in the bloodstream in several different forms. Of these, the one that gets the most attention is low-density lipoprotein— better known as LDL, or "bad" cholesterol. But lipoproteins come in a range of shapes and sizes, and each type has its own tasks. They also morph from one form into another. These are the five main types: 1 Chylomicrons are very large particles that mainly carry triglycerides (fatty acids from your food). They are made in the digestive system and so are influenced by what you eat. 2 Very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) particles also carry triglycerides to tissues. But they are made by the liver. As the body's cells extract fatty acids from VLDLs, the particles turn into intermediate density lipoproteins, and, with further extraction, into LDL particles. 3 Intermediate-density lipoprotein (IDL) particles form as VLDLs give up their fatty acids. Some are removed rapidly by the liver, and some are changed into low-density lipoproteins. 4 Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) particles are even richer in pure cholesterol, since most of the triglycerides they carried are gone. LDL is known as "bad" cholesterol because it delivers cholesterol to tissues and is strongly associated with the buildup of artery-clogging plaque. 5 High-density lipoprotein (HDL) particles are called "good" cholesterol because some of them remove cholesterol from circulation and from artery walls and return it to the liver for excretion.
How much cholesterol does the liver produce?
In fact, cholesterol production is so important that your liver and intestines make about 80% of the cholesterol you need to stay healthy. Only about 20% comes from the foods you eat. (See illustration.) If you eat only 200 to 300 milligrams (mg) of cholesterol a day (one egg yolk has about 200 mg), your liver will produce an additional 800 ...
Where are LDLs made?
But they are made by the liver. As the body's cells extract fatty acids from VLDLs, the particles turn into intermediate density lipoproteins, and, with further extraction, into LDL particles. Intermediate-density lipoprotein (IDL) particles form as VLDLs give up their fatty acids.
What is the purpose of cholesterol?
The Harvard Special Health Report Managing Your Cholesterol explains cholesterol as a waxy, whitish-yellow fat and a crucial building block in cell membranes. Cholesterol also is needed to make vitamin D, hormones (including testosterone and estrogen), and fat-dissolving bile acids.
