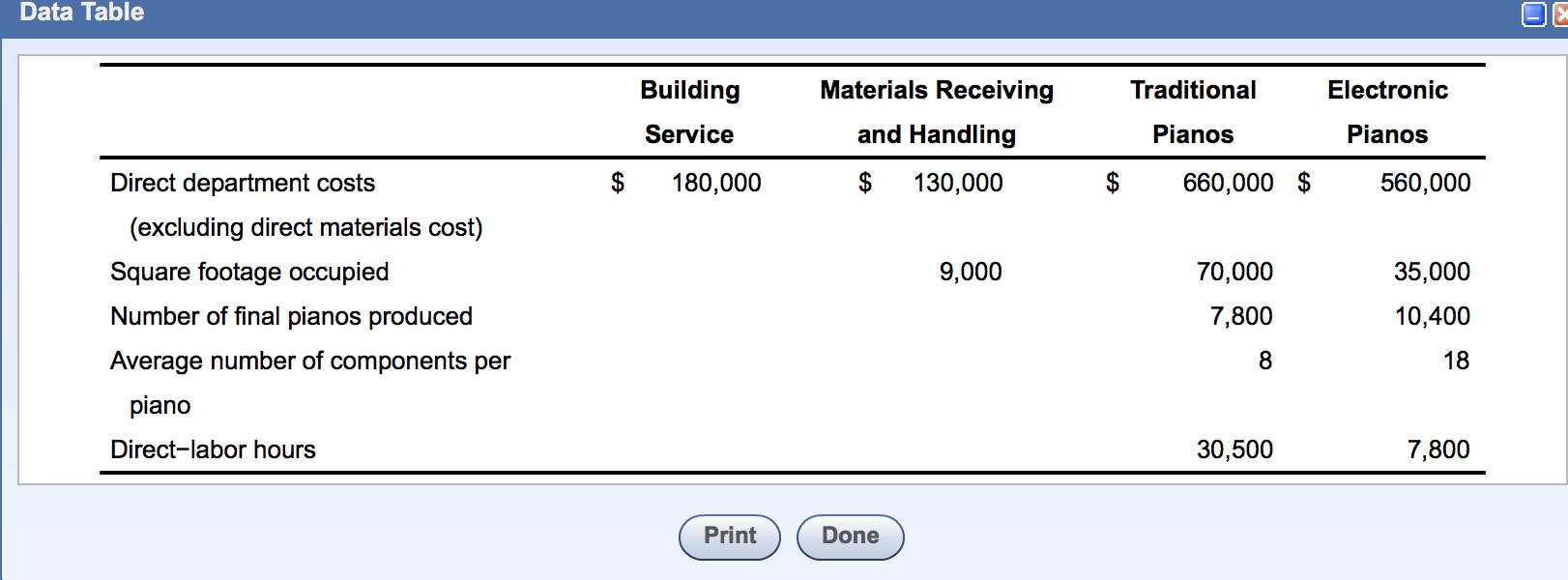
There are three methods commonly used to allocate support costs: (1) the direct method; (2) the sequential (or step) method; and (3) the reciprocal method. What are the four cost allocation methods? When allocating costs, there are four allocation methods to choose from. Direct labor.
What are the most common ways to allocate costs?
This is a practical method for expenses that “follow the people.” The most common allocation methods are: FTE or staff time, square footage, number of clients, “units” of services, and percentage of total direct costs.
How do you allocate fundraising expenses?
Similarly, the cost of fundraising is valuable to programs and the final step is to allocate fundraising expenses to each. The most common basis for allocating fundraising costs is based on percentage of total support received by each program.
What is the direct approach to cost allocation?
The direct approach assigns the expenses of all the support departments to every other manufacturing unit calculated based on the rates of each operational department rates. Services that other support departments receive are not considered in this method of cost allocation.
What are the best allocation methods?
The best allocation methods are reasonable and justifiable while also being simple enough to calculate and maintain over time. An example would be the cost of office supplies that are used by all of our programs and by fundraising and administration.
What are the methods used to allocate support costs?
There are three methods commonly used to allocate support costs: (1) the direct method; (2) the sequential (or step) method; and (3) the reciprocal method.
How do you allocate costs?
Basic Steps of Cost AllocationIdentify shared facilities or support services.Identify the costs to be allocated.Determine the allocation factors/methodology to distribute the costs equitably.Allocate the costs.Update and monitor the data and methodology to ensure the allocation remains fair and equitable over time.
What are the four cost allocation methods?
When allocating costs, there are four allocation methods to choose from.Direct labor.Machine time used.Square footage.Units produced.
What are cost allocation methods in healthcare?
Cost allocation is a method to calculate overhead cost for a patient-services department. The full costs can be determined by adding the direct costs and indirect (overhead) costs of a service.
What are the three bases of cost allocation?
There are three types of allocation bases in Cost accounting: Predefined dimension member allocation bases. Hierarchy allocation bases. Formula allocation bases.
What is the process of allocation?
An allocation is the process of shifting overhead costs to cost objects, using a rational basis of allotment. Allocations are most commonly used to assign costs to produced goods, which then appear in the financial statements of a business in either the cost of goods sold or the inventory asset.
Why do we allocate costs?
Allocating costs serves three main purposes. These are to: 1) make decisions, 2) reduce waste, and 3) determine pricing.
What are the types of allocation?
There are three types of allocation: contiguous allocation. linked allocation. indexed allocation.
What cost allocation method is the most accurate?
The reciprocal method of support department cost allocation is the most precise method and therefore is used most often.
How do you allocate overhead costs?
To allocate the overhead costs, you first need to calculate the overhead allocation rate. This is done by dividing total overhead by the number of direct labor hours. This means for every hour needed to make a product, you need to allocate $3.33 worth of overhead to that product.
Why do we allocate costs?
Allocating costs serves three main purposes. These are to: 1) make decisions, 2) reduce waste, and 3) determine pricing.
What is the direct method of cost allocation?
What is the Direct Allocation Method? The direct allocation method is a technique for charging the cost of service departments to other parts of a business. This concept is used to fully load operating departments with those overhead costs for which they are responsible.
How to allocate costs?
The three main methods of allocating the costs are used by companies depending on the nature of the business and resources available. There are benefits and limitations of all the methods that are faced by the companies using them. The direct and sequential methods are the easiest and the most convenient ways of allocating the costs. On the other hand, the reciprocal method of allocating the costs is the most difficult and is rarely used by companies. There is no rule as to which method is best for a specific company. Each organization uses the method of cost allocation depending on the resources and time that can be given. When all expenses are transferred from the service departments to the manufacturing department, it is possible to compute the overhead rates of every manufacturing department individually.
Why is cost allocation important?
The goal of cost allocations in the services team should be to have correct prices on products, services, and customer interactions. The choice of an allocation technique is essential in tracking expenses for many organizations, particularly those where the number of service departments and the prices and services supplied is growing rapidly. The most significant advantage of the reciprocal approach is that it fully includes the cross-departmental service. Consequently, it is a far more precise technique of distributing department expenses when compared to the other two approaches.
What is the step technique of distributing service department expenses?
The step technique of distributing service department expenses is the second way of allocating costs. As part of a sequential process, service expenses are allocated to operational departments and other service departments by using this approach. The following are the critical phases in the allocation process:
What is direct allocation technique?
The direct allocation technique is very straightforward to implement, but it is ideal for writing off all indirect expenses as department expenditures rather than distributing them to cost components. Although indirect allocation can produce more accurate results, it is more time-consuming than the direct allocation technique regarding the accounting effort involved. The direct method is intended to remind production management that services such as information technology and repair are not “free of cost” but are included in the cost of the goods and services provided.
Why are service department expenses important?
There are numerous advantages to having a precise and clear grasp of service department expenses. Primarily, service department expenses are taken into consideration when determining the total cost of a certain product. Moreover, they are useful for limiting the demands for internal services—if zero cost is asked for a facility, for instance, it is possible that the operational departments would overconsume the service. It is also feasible to evaluate the efficiency and productivity of the department because of their use. A service department may be evaluated for removal of the internal cost of providing a service that is more than the offered price by an external provider for the same service.
What is cross departmental service?
In the service sector, cross-departmental services are services offered by two or even more service departments to one another. Take the following scenario: service department 1 gives service to service department 2, and department 2, in turn, offers service to service department 1.
What is direct cost allocation?
The direct technique is the easiest in terms of cost allocation, even though it has several shortcomings. Nevertheless, because of its simplicity of using it, it became one of the most widely applied cost allocation techniques in recent years. In a nutshell, it assumes that service departments do not give facilities or services to each other, and it merely distributes the service departments’ costs in the company’s manufacturing departments.
What are the most common allocation methods?
The most common allocation methods are: FTE or staff time, square footage, number of clients, “units” of services, and percentage of total direct costs. Other methods may also be appropriate and useful if there is a reasonable connection between the method and the actual use of the resources or expense.
How to develop accurate program budgets?
Developing accurate program budgets and allocation formulas requires a number of data sources. Assemble as much as you can in advance, though it’s likely that more questions will come up once the process is underway. Some of the information will be specific to your organization, but as a first step you’ll need: a list of income and expense categories, detailed budgets, a list of staff, their compensation, and records or estimates of their activities, and information about major expense items, such as facility and program expenses.
What is indirect cost?
The cost of administration, categorized as indirect costs, adds value to every program at a nonprofit. Programs are more effective, better managed, and more responsive to the community when an organization has good accounting and technology, high quality leadership, planning, and governance.
Why is understanding the true cost of programs important?
One of the most valuable results of understanding the true cost of programs is the ability to make wise choices about how to support mission critical work. For most nonprofits, some programs may be financially self-sustaining or even generate a surplus.
Do nonprofits return profits to shareholders?
While the long-term goal for nonprofits is not to return profits to shareholders, we all know that nonprofits are business entities that need to maintain financial health and stability in order to achieve their mission. Understanding the true, full cost of delivering various programs and services in the community is a critical piece ...
Does fundraising have direct costs?
Fundraising may also have direct costs or receive an allocated portion of a direct cost, as will be explained later. Sometimes direct costs will be allocated to all program areas and cost centers, including fundraising and administration.
How does cost allocation work?
Allocation works best in specific cases where the cost is mostly variable and related to internal or external customer demand, so that managers receiving the expense on their P&L can see a clear relationship between their organization’s activities and behaviors and the expense. For example, usage of an IT service desk or a customer call center varies according to factors such as the quality of training the business unit is providing its employees or the level of service it is providing to customers. In these sorts of situations, costs can be allocated to the appropriate P&L owners. With standard pricing, such as a charge per call to the IT service desk, managers have a clear incentive: reduce the number of calls made.
What are the problems with allocation practices?
A global consumer-services company illustrates one of the basic problems with allocation practices: they often result in business units paying for costs they can’t control. In this case, the charges billed to individual units included line items for corporate HR and tax support, which the units could do nothing to reduce. If company leaders thought that corporate HR costs were rising too quickly, the more direct approach would have been to create incentives for the leaders of the function to contain costs, rather than put an added administrative burden on leaders of units whose behavior had little effect on the function’s activities.
What is the one allocation activity that a majority of respondents considered “highly effective.”.?
That insight leads to several implications. 1. Allocate as needed for compliance. Compliance with tax, accounting, and similar regulatory requirements was the one allocation activity that a majority of respondents considered “highly effective.”. These allocations are usually unavoidable.
What is the problem with functional support?
A recent McKinsey survey confirms that deciding who pays what for functional support is a significant source of dissatisfaction for senior executives and the organizations they help lead.
How have organizations revolutionized how they manage their support functions?
Throughout the world, organizations in virtually every sector have revolutionized how they manage their support functions. New technologies, partnerships, and sources of talent are turning areas once viewed only as cost centers into new generators of competitive advantage.
Is traditional allocation of support function costs working well?
Traditional allocation of support-function costs isn’t working well , executives say. They need a better way to foster value-conscious decisions without creating too much complexity.