
- Abdominal ultrasound. This is the most common test to diagnose abdominal aortic aneurysms. ...
- Abdominal CT scan. This painless test uses X-rays to create cross-sectional images of the structures inside the belly area. ...
- Abdominal MRI .
What are the signs and symptoms of a stomach aneurysm?
- back or flank pain,
- severe or worsening abdominal pain,
- a pulsating abdominal mass, or
- feeling a pulse near the bellybutton.
What are the symptoms of a ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm?
- Abdominal or back pain, which is sudden, sharp and severe.
- Hypotension (low blood pressure).
- Pulsatile mass in the abdomen.
What are the symptoms of abdominal aorta?
Though rare, an abdominal aortic aneurysm that has not ruptured could trigger persistent back pain; deep, constant abdominal pain; or a pulsating feeling near the belly button. Symptoms of a ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm include sudden back pain, abdominal pain or fainting.
How to diagnosis aortic aneurysm?
Thoracic aortic aneurysm
- Diagnosis. Thoracic aortic aneurysms are often found during routine medical tests, such as a chest X-ray, CT scan or ultrasound of the heart, sometimes ordered for a different reason.
- Treatment. ...
- Clinical trials. ...
- Lifestyle and home remedies. ...
- Coping and support. ...
- Preparing for your appointment. ...
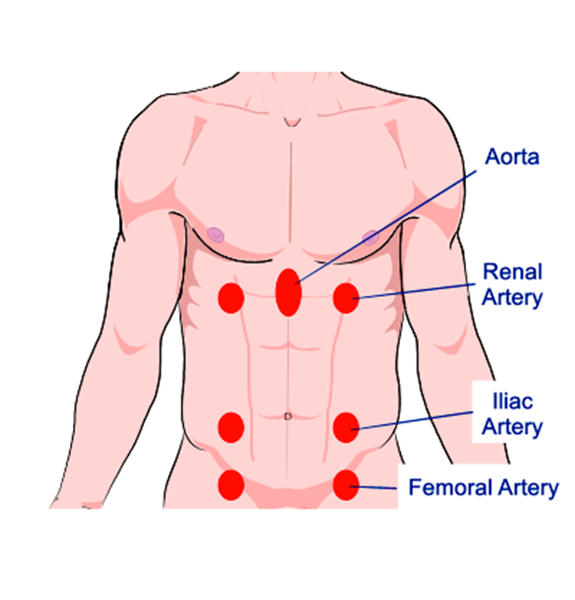
Can you palpate an abdominal aortic aneurysm?
The proper technique for detecting an AAA with abdominal palpation begins with placing the patient in a supine position with the knees raised and the abdominal muscles relaxed. The aortic pulse can be palpated just above and to the left of the umbilicus.
What is the most common symptom in a client with abdominal aortic aneurysm?
Pain is the most common symptom of an abdominal aortic aneurysm. The pain associated with an abdominal aortic aneurysm may be located in the abdomen, chest, lower back, or groin area. The pain may be severe or dull. Sudden, severe pain in the back or abdomen may mean the aneurysm is about to rupture.
How do you assess an aneurysm?
Magnetic resonance angiography (an MRI scan) is usually used to look for aneurysms in the brain that haven't ruptured. This type of scan uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of your brain.
What are the symptoms of an aortic aneurysm in the abdomen?
What are the symptoms of an abdominal aortic aneurysm?Clammy, sweaty skin.Dizziness.Fainting.Fast heartbeat.Nausea and vomiting.Shortness of breath.Sudden, severe pain in your belly, lower back or legs.
What is the gold standard for diagnosing abdominal aortic aneurysm?
Abdominal ultrasound. This is the most common test to diagnose abdominal aortic aneurysms. An abdominal ultrasound is a painless test that uses sound waves to show how blood flows through the structures in the belly area, including the aorta.
When should you suspect an abdominal aortic aneurysm?
The most common symptom of a ruptured aortic aneurysm is sudden and severe pain in the abdomen. If you suspect that you or someone else has had a ruptured aneurysm, call 999 immediately and ask for an ambulance.
What are the 3 most common causes of abdominal aneurysms?
Several things can play a role in the development of an abdominal aortic aneurysm, including:Hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis). Atherosclerosis occurs when fat and other substances build up on the lining of a blood vessel.High blood pressure. ... Blood vessel diseases. ... Infection in the aorta. ... Trauma.
What is the most common cause of abdominal aortic aneurysm?
Smoking is the most common cause of an abdominal aortic aneurysm as well as many other health problems. Exercising daily can also be beneficial, as can lifestyle changes that help lower your blood pressure.
What are the signs of an oncoming aneurysm?
SymptomsNausea and vomiting.Stiff neck.Blurred or double vision.Sensitivity to light.Seizure.A drooping eyelid.Loss of consciousness.Confusion.
Are there warning signs before an aortic aneurysm?
5 warning signs and symptoms that aortic aneurysm might be suspected include: 1) Chest tenderness or chest pain, dizziness or light-headedness, back pain, coughing up blood (hemoptysis) and loss of consciousness due to the ruptures.
What is a common finding with an aortic aneurysm?
Signs and symptoms of thoracic aortic aneurysm can include the following: Sharp, sudden pain in the chest or upper back. Shortness of breath. Trouble breathing or swallowing.
What is the most common location of an abdominal aortic aneurysm?
The most common location of arterial aneurysm formation is the abdominal aorta, specifically, the segment of the abdominal aorta below the kidneys. An abdominal aneurysm located below the kidneys is called an infrarenal aneurysm.
What is a common finding with an aortic aneurysm?
Signs and symptoms of thoracic aortic aneurysm can include the following: Sharp, sudden pain in the chest or upper back. Shortness of breath. Trouble breathing or swallowing.
What is the most common type of abdominal aortic aneurysm?
Infrarenal abdominal aortic aneurysms are the most common aneurysms of the aorta. Screening ultrasound has helped detect AAA and allows for surveillance in asymptomatic patients with a diameter < 5 cm. In females, the repair should be considered at 5 cm and in males at 5.5 cm.
What is significant of an abdominal aortic aneurysm?
An abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) is a bulge or swelling in the aorta, the main blood vessel that runs from the heart down through the chest and tummy. An AAA can be dangerous if it is not spotted early on. It can get bigger over time and could burst (rupture), causing life-threatening bleeding.
What is an abdominal aortic aneurysm quizlet?
Abdominal aortics aneurysm. - is an abdominal ballooning of the abdominal portion of the aorta, which is the major artery from the heart; aneurysm greater than 5 cm in diameter has a higher risk of rupture.
Physical exam
During a physical exam, your provider may do a few basic steps to look for an aortic aneurysm.
Screening and diagnostic tests
Screening for aortic aneurysm is usually done using ultrasound. This test shows if the diameter of your aorta is bigger than it should be. If it is larger than normal, your provider may recommend another screening later to check for growth.
Who should be screened for a thoracic aortic aneurysm?
Certain groups of people may be screened for a thoracic aortic aneurysm. They include:
Who should be screened for an abdominal aortic aneurysm?
There are certain groups of people who may be screened for abdominal aortic aneurysm:
How are aneurysms diagnosed?
Your doctor will do a complete medical history and physical exam. Other possible tests include:
How to tell if an aortic aneurysm is ruptured?
Symptoms, when they do occur, include pain in the back or near the naval. An extremely sharp and severe pain may indicate rupture, requiring emergency medical treatment. Smaller, slow-growing aortic aneurysms may be treated with watchful waiting, lifestyle changes and medication.
What is an abdominal aortic aneurysm?
It delivers oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body. An aortic aneurysm is a bulging, weakened area in the wall of the aorta. Over time, the blood vessel balloons and is at risk for bursting (rupture) or separating (dissection). This can cause life threatening bleeding and potentially death.
What is aortic dissection?
An aortic dissection starts with a tear in the inner layer of the aortic wall of the thoracic aorta. The aortic wall is made up of 3 layers of tissue. When a tear occurs in the innermost layer of the aortic wall, blood is then channeled into the wall of the aorta separating the layers of tissues. This generates a weakening in the aortic wall with a potential for rupture. Aortic dissection can be a life-threatening emergency. The most commonly reported symptom of an aortic dissection is sudden, severe, constant chest or upper back pain, sometimes described as "ripping" or "tearing." The pain may move from one place to another.
How to repair an aneurysm in the groin?
Using X-ray guidance and specially-designed instruments, the surgeon can repair the aneurysm by inserting the stent or graft inside the aorta. The graft material may cover the stent. The stent helps hold the graft open and in place.
What is an aneurysm in the aorta?
An aneurysm is a weak section of an artery wall. Pressure from inside the artery causes the weakened area to bulge out beyond the normal width of the blood vessel. An abdominal aortic aneurysm is an aneurysm in the lower part of the aorta, the large artery that runs through the torso.
What is the most common shape of an abdominal aneurysm?
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Shapes. The more common shape is fusiform, which balloons out on all sides of the aorta.
How to diagnose an aortic aneurysm?from mayoclinic.org
To diagnose an abdominal aortic aneurysm, doctors will review your medical and family history and do a physical exam. If your doctor suspects that you have an aortic aneurysm, specialized tests, such as the following, can confirm it. Abdominal ultrasound. This test is most commonly used to diagnose abdominal aortic aneurysms.
What is the best test for abdominal aneurysms?from mayoclinic.org
Abdominal ultrasound. This test is most commonly used to diagnose abdominal aortic aneurysms. You lie on a table while a technician moves a wand (transducer) around your abdomen. Ultrasound uses sound waves to send images to a computer screen. CT scan.
What is an abdominal aortic aneurysm?from hopkinsmedicine.org
It delivers oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body. An aortic aneurysm is a bulging, weakened area in the wall of the aorta. Over time, the blood vessel balloons and is at risk for bursting (rupture) or separating (dissection). This can cause life threatening bleeding and potentially death.
What is aortic dissection?from hopkinsmedicine.org
An aortic dissection starts with a tear in the inner layer of the aortic wall of the thoracic aorta. The aortic wall is made up of 3 layers of tissue. When a tear occurs in the innermost layer of the aortic wall, blood is then channeled into the wall of the aorta separating the layers of tissues. This generates a weakening in the aortic wall with a potential for rupture. Aortic dissection can be a life-threatening emergency. The most commonly reported symptom of an aortic dissection is sudden, severe, constant chest or upper back pain, sometimes described as "ripping" or "tearing." The pain may move from one place to another.
How are aneurysms diagnosed?from hopkinsmedicine.org
Your doctor will do a complete medical history and physical exam. Other possible tests include:
How is an aneurysm repaired?from hopkinsmedicine.org
Using X-ray guidance, a stent graft is inserted into the femoral artery and sent to the site of the aneurysm. A stent is a thin metal mesh framework shaped into a long tube, while the graft, a fabric covering the mesh, is made of a polyester fabric called PTFE. The stent holds the graft open and in place. EVAR is used only for an infrarenal (below the kidneys) AAA. It may be more easily tolerated by high-risk patients. However, the graft can sometimes slip out of place and may later need to be fixed.
How to tell if you have an AAA?from bmj.com
The classic sign of an AAA is a pulsatile mass on abdominal palpation, which suggests aneurysmal dilation of the abdominal aorta. However, the reported sensitivity of palpation for detecting aneurysms varies greatly, particularly in obese patients. w12 w14 One small prospective study found that the sensivitity of abdominal palpation by a doctor was 0.57 for detection of aneurysms less than 4 cm diameter and 0.98 for those over 5 cm. The specificity for excluding an AAA was 0.64. w15
What is an Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm?
An aneurysm ("AN-yuh-rizm") is a bulge in a weakened blood vessel. An aneurysm can lead to serious problems.
Who should be screened?
Men between the age of 65 and 75, who have EVER smoked cigarettes, should be screened. Other people do not benefit as much from screening.
How to determine if a bulge is in the aorta?
An ultrasound is used to create a picture of your abdominal aorta using sound waves. The width of your abdominal aorta is then measured to determine whether there is a bulge.
Does smoking cause aneurysms?
Smoking increases your risk of having an aneurysm. If you are smoking now, the most important step you can take is to STOP smoking.
What is an aortic aneurysm?
An abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) is a permanent outpouching of an artery's wall. Often asymptomatic, AAAs are usually found during routine physical exams or accidentally while evaluating other health concerns. Assessment of an AAA includes bruits, abdominal or lower back pain, and a pulsating sensation in the abdomen. An X-ray is required for diagnosis and surgery is necessary to prevent rupture resulting in shock. Early detection and intervention are critical for prevent aneurysm rupture leading to death.
Where does AAA pain feel?
During an AAA rupture, tearing pain is felt in the lower abdomen and back. If the AAA is leaking, the patient will feel a severe and unrelenting pain felt mainly in the lower back.
Can an aortic aneurysm cause pain in the lower back?
Abdominal aortic aneurysms may compress nearby nerves and cause abdominal or lower back pain. The patient may feel epigastric discomfort or have alterations in bowel movements. Rupture of AAA will also cause pain in the abdomen or back.
Can an aortic aneurysm rupture?
Small aneurysms measuring less than 5 cm in diameter rarely rupture. However, abdominal aortic aneurysms that do rupture cause hypovolemic shock. During ruptures in the retroperitoneal space, surrounding organs help compress the aneurysms and control the level of bleeding to prevent death. However, the majority of AAA ruptures in the thoracic cavity will experience massive hemorrhage leading to death.
What is the procedure for an aortic aneurysm?
Open repair. For this surgery, your doctor makes a large incision in the abdomen to expose the aorta. Once he or she has opened the abdomen, a graft can be used to repair the aneurysm. Open repair remains the standard procedure for an abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. Endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR).
What is an abdominal aortic aneurysm repair?
Your doctor may recommend abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) repair to treat an aneurysm. An aneurysm is a bulging, weak spot in the aorta that may be at risk for rupturing. In this case, the aneurysm is in part of the aorta that is in the abdomen. Repair of an AAA may be done in one of two ways:
What are the risks of AAA repair?
As with any surgical procedure, complications can occur. Some possible complications may include:
How to repair an aneurysm without a large incision?
This means it is done without a large incision. Instead, the doctor makes a small incision in the groin. He or she will insert special instruments through a catheter in an artery in the groin and thread them up to the aneurysm. At the aneurysm, your doctor will place the stent and graft to support the aneurysm.
What is regional anesthesia?
Regional anesthesia is medicine delivered through an epidural (in the back) to numb the area to be operated on. You will receive medicine to help you relax and analgesic medicine for pain relief.
How big is an aneurysm?
Size of aneurysm greater than 5 centimeters in diameter (about 2 inches) Growth rate of aneurysm of more than 0.5 centimeter (about 0.2 inch) over 1 year. When risk of rupture outweighs the risk of surgery. Emergency life-threatening bleeding. There may be other reasons for your doctor to advise an AAA repair.
What do anesthesiologists do during surgery?
The anesthesiologist will monitor your heart rate, blood pressure, breathing, and oxygen level during the surgery. Once you are sedated, your doctor will insert a breathing tube through your throat into your lungs and connect you to a ventilator. This will breathe for you during the surgery.
Summary of Recommendations
The USPSTF recommends 1-time screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) with ultrasonography in men aged 65 to 75 years who have ever smoked ( Table 1). B recommendation.
Importance
An AAA is typically defined as aortic enlargement with a diameter of 3.0 cm or larger. The prevalence of AAA has declined over the past 2 decades among screened men 65 years or older in various countries such as the United Kingdom, New Zealand, Sweden, and Denmark.
USPSTF Assessment of Magnitude of Net Benefit
The USPSTF concludes with moderate certainty that screening for AAA in men aged 65 to 75 years who have ever smoked is of moderate net benefit ( Table 1 and Table 2).
