
How do you assess cranial nerves in nursing?
- Test sensory function. Ask the patient to close their eyes, and then use a wisp from a cotton ball to lightly touch their face, forehead, and chin.
- Test motor function. Ask the patient to clench their teeth tightly while bilaterally palpating the temporalis and masseter muscles for strength.
How can therapists evaluate cranial nerves?
Therapists can evaluate cranial nerves at an initial consultation which provides the therapist a window into the patient’s neurological status and the location of the insult. It makes reading the neurologist’s consult clear and the therapist’s objectives more to the point.
Which cranial nerves are usually evaluated during the examination of the eyes?
During a complete neurological exam, most of these nerves are evaluated to help determine the functioning of the brain: Cranial nerve I (olfactory nerve). This is the nerve of smell. The patient may be asked to identify different smells with his or her eyes closed. Cranial nerve II (optic nerve).
What are the ten cranial nerves?
Cranial nerves; CN 0 – Terminal; CN I – Olfactory; CN II – Optic; CN III – Oculomotor; CN IV – ...
How to conduct a cranial nerve examination?
To assess the corneal reflex:
- Clearly explain what the procedure will involve to the patient and gain consent to proceed.
- Gently touch the edge of the cornea using a wisp of cotton wool.
- In healthy individuals, you should observe both direct and consensual blinking. The absence of a blinking response suggests pathology involving either the trigeminal or facial nerve.
How do you assess cranial nerve exam?
Cranial Nerve V – TrigeminalTest sensory function. Ask the patient to close their eyes, and then use a wisp from a cotton ball to lightly touch their face, forehead, and chin. ... Test motor function. Ask the patient to clench their teeth tightly while bilaterally palpating the temporalis and masseter muscles for strength.
How do you assess cranial nerve number?
1st Cranial nerve The patient is asked to identify odors (eg, soap, coffee, cloves) presented to each nostril while the other nostril is occluded.
How would you describe a normal cranial nerve assessment?
Documentation of a basic, normal neuro exam should look something along the lines of the following: The patient is alert and oriented to person, place, and time with normal speech. No motor deficits are noted, with muscle strength 5/5 bilaterally. Sensation is intact bilaterally.
Which tests can be used to assess cranial nerve V?
2:594:02Trigeminal Nerve | Cranial Nerve V Assessment - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipOkay so we're going to go in at the side and touch the cornea. You should blink now we're going toMoreOkay so we're going to go in at the side and touch the cornea. You should blink now we're going to test motor. Function. And what I want you to do is I want you to bite down for me okay. And what you
Why do we assess cranial nerves?
Anatomically, the cranial nerves travel through distinct locations in the brain, and because of this assessing them can sometimes give us early and detailed information about brain injury.
Why do nurses check cranial nerves?
Check out this cranial nerves chart for assessment in nursing! Assessment of the cranial nerves provides insightful and vital information about the patient's nervous system.
What are the 5 steps in the neurological assessment?
It should be assessed first in all patients. Mental status testing can be divided into five parts: level of alertness; focal cortical functioning; cognition; mood and affect; and thought content.
How do you check cranial nerve 9 and 10?
Cranial Nerves 9 & 10 - Sensory and Motor: Gag Reflex The gag reflex tests both the sensory and motor components of CN 9 & 10. This involuntary reflex is obtained by touching the back of the pharynx with the tongue depressor and watching the elevation of the palate.
How does the nurse assess cranial nerve VII?
Cranial nerve VII controls facial movements and expression. Assess the patient for facial symmetry. Have him wrinkle his forehead, close his eyes, smile, pucker his lips, show his teeth, and puff out his cheeks. Both sides of the face should move the same way.
How does the nurse assess cranial nerve 6?
Cranial nerve VI (abducens) Assessment and findings: To assess CN VI, ask the patient to follow your finger as you move it from midline toward the patient's ear on one side and then the other. The affected eye won't cross midline when following the finger to the ear. Impairment can result in diplopia and nystagmus.
How do you test a cranial nerve number 8?
0:001:11Cranial Nerve 8 -- Auditory Acuity, Weber & Rinne Tests - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipViii we know the acoustic nerve has two divisions the one that we're going to test today is the 8th.MoreViii we know the acoustic nerve has two divisions the one that we're going to test today is the 8th. Or the cochlear division and we'll then to first test auditory acuity do you hear that and what is
How many cranial nerves are there?
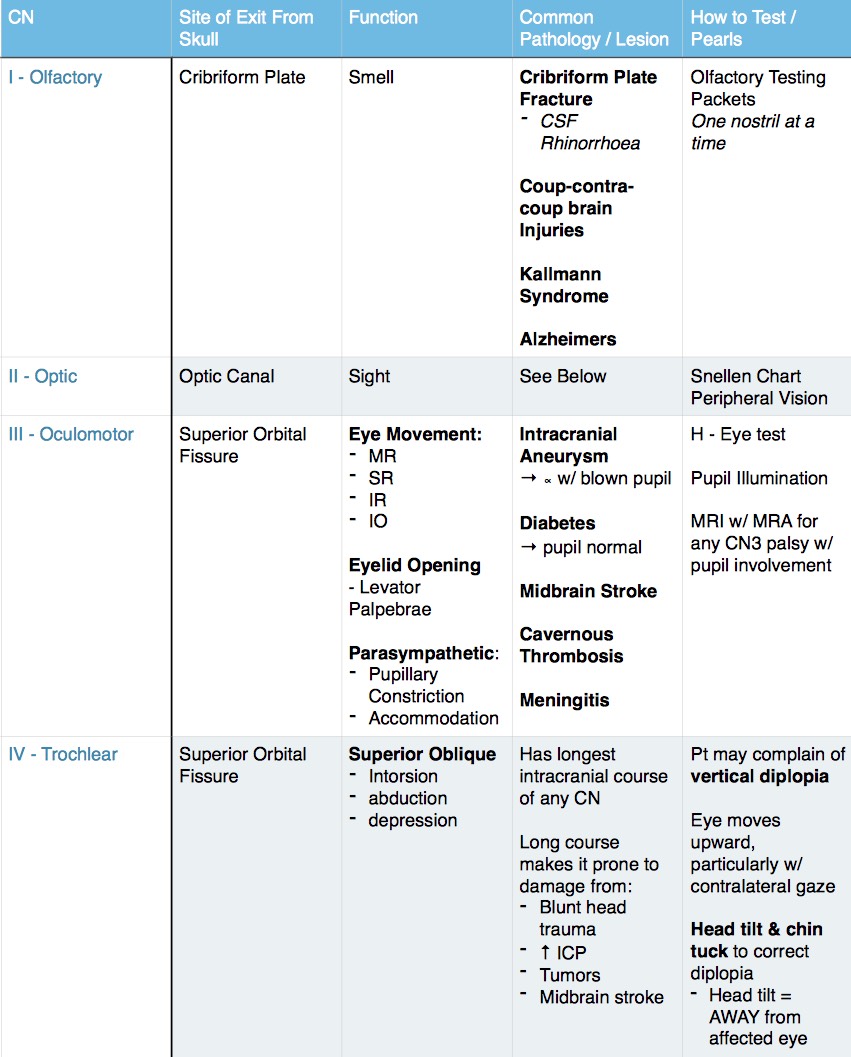
Listed below is a chart of the 12 cranial nerves, the assessment technique used, if the response elicited is normal, and how to document it.
How many cranial nerves are there in the nervous system?
Assessment of the cranial nerves provides insightful and vital information about the patient’s nervous system. There are 12 cranial nerves that are often forgotten by nurses, so with that in mind, here’s a free assessment form that you can use!
How to test light sensation?
(same as above) (same as above) To test deep sensation, use alternating blunt and sharp ends of an object. Determine sensation to warm and cold object by asking client to identify warmth and coldness. (same as above)
What should a client be able to do?
Client should be able to smile, raise eyebrows, and puff out cheeks and close eyes without any difficulty. The client should also be able to distinguish different tastes. Client performed various facial expressions without any difficulty and able to distinguish varied tastes.
How to use a penlight?
Hold a penlight 1 ft. in front of the client’s eyes. Ask the client to follow the movements of the penlight with the eyes only. Move the penlight upward, downward, sideward and diagonally. Client’s eyes should be able to follow the penlight as it moves. Both eyes are able to move as necessary.
What reflex should a client have to respond to light and deep sensation?
While the client looks upward, lightly touch the lateral sclera of eye to elicit blink reflex. Client should have a (+) corneal reflex, able to respond to light and deep sensation and able to differentiate hot from cold. Client was able to elicit corneal reflex, sensitive to pain stimuli and distinguish hot from cold.
Who is Matt Vera?
Matt Vera, BSN, R.N. Matt Vera is a registered nurse with a bachelor of science in nursing since 2009 and is currently working as a full-time writer and editor for Nurseslabs. During his time as a student, he knows how frustrating it is to cram on difficult nursing topics. Finding help online is nearly impossible.
What is accessory nerve?
The accessory nerve is a mixed nerve but mostly the motor nerve of the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles. During this assessment, you will check the strength and movement of the patient’s sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscle.
What nerve is the main nerve of the face?
Cranial Nerve V – Trigeminal Nerve. The trigeminal nerve is the main nerve of the face. You will be testing the sensory function of the nerve. You will be looking for a loss of sensation, pain or any fine rapid muscle movements called fasciculations.
What nerve supplies the motor fibers used for facial expressions?
The facial nerve is a motor nerve. This nerve supplies the motor fibers used for facial expressions and, also the salivary and lacrimal glands.
What nerve is responsible for smell?
The olfactory nerve is the sensory nerve of smell. Before beginning, have some type of aromatic substance available such as coffee, toothpaste, peppermint or soap to use as part of the assessment.
Which nerve is responsible for transmitting information about balance and hearing from the inner ear to the brain?
Cranial Nerve VIII – Vestibulocochlear Nerve. The vestibulocochlear nerve is a sensory nerve and is responsible for transmitting information about balance and hearing from the inner ear to the brain. Assess the vestibulocochlear nerv e using the Rinne test, the Weber test, and the Romberg test.
How many pairs of cranial nerves are there?
The nervous system is comprised of the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS). There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves and 12 pairs of cranial nerves. Below are the procedures for performing an ...
How to test near vision?
You may test a patient’s near vision by asking the patient to read from a magazine or a newspaper.
How to test cranial nerves II and III?
The pupillary light reflex tests both cranial nerves II and III. First, inspect both pupils and make sure they are equal in size and shape. Then dim the lights if possible and shine a penlight directly into the right eye. Both pupils should constrict and maintain symmetry. Note if they are brisk or sluggish and if they are symmetric. Remove the light source and watch both eyes dilate equally as well. Do the same for the left eye.
Why is cranial nerve assessment important?
The cranial nerve assessment is an important part of the neurologic exam, as cranial nerves can often correlate with serious neurologic pathology. This is important for nurses, nurse practitioners, and other medical professionals to know how to test cranial nerves and what cranial nerve assessment abnormalities may indicate.
What is the NIH scale for stroke?
When evaluating a stroke, The NIH scale is a method to evaluate the severity of a stroke. This scale walks you through evaluating many of the cranial nerves, but not all of them. If you want to feel confident when you chart “Cranial nerves II-XII grossly intact”, then keep reading!
Why is my cranial nerve compressed?
This nerve is often the first nerve compressed when there is any increased intracranial pressure (ICP). However, more common causes include vascular disease (diabetes, hypertension, atherosclerosis) or trauma.
What nerve is responsible for the sense of smell?
The olfactory nerve is responsible for the sense of smell. Although rarely tested in practice, alterations in smell can be caused by serious intracranial pathology (brain tumors, strokes, TBI), neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, or MS, or benign and transient causes such as the common cold.
Which nerve innervates the lateral rectus muscle?
The sixth cranial nerve, the abducents nerve innervates the lateral rectus muscle of the eye. This means its responsible for outward movement of the eyes. Patients with dysfunction of this nerve will be unable to outwardly move their eyes. This causes horizontal diplopia, where the double images are side-by-side, which is worse at far distances.
Which cranial nerve is responsible for facial sensation?
The Trigeminal nerve is the 5 th cranial nerve and responsible for facial sensation, as well as moving the muscles involved with biting and chewing. This has three branches including the ophthalmic V1, maxillary V2, and Mandibular V3. Compression of this nerve root can cause trigeminal neuralgia – a rare but painful condition.
What nerve is used to test for uvula?
To test cranial nerve IX (glossopharyngeal) and X (vagus) have patient say “ah”…the uvula will move up ( cranial nerve IX intact) and if the patient can swallow with ease and has no hoarseness when talking, cranial nerve X is intact.
What nerve causes blurry vision?
Therefore, you can assess this nerve (cranial nerve II) for any type of abnormalities.
What chart do you use for visual acuity?
Visual Acuity: use a Snellen chart and have patient wear glasses or contact lenses if they normally wear them
Why do we assess cranial nerves?
Why do we assess cranial nerves? In short, to see if the neuron/nerve works!
Which nerve is responsible for mastication?
Cranial Nerve V. To test Cranial Nerve V…..trigeminal nerve: This nerve is responsible for many functions and mastication is one of them. Have the patient bite down and feel the masseter muscle and temporal muscle. Then have the patient try to open the mouth against resistance.
How far can a patient see with normal vision?
This means the patient can see at 20 feet what a person with normal vision can see at 30 feet.
Which eye do you cover?
Cover your left eye, while the patient covers their right eye.
What is the role of the cranial nerve 5?
What is the role of cranial nerve 5? The trigeminal nerve allows us to feel sensation in our face, and it has motor functions that allow us to chew food and clench down.
What is abnormal findings?
Result: Abnormal findings would be a loss or decrease in sensation or sensation that is unequal in various segments.
Which muscle should feel like a small ball?
Palpate the masseter and temporal muscle. Each muscle should feel like a small ball and be equal on both sides.
Can you remove eye contacts from a test?
Have the patient remove any eye contacts, if they wear them. This will alter the test if worn.
How many efferent limbs are there in the pupillary reflex?
Each afferent limb of the pupillary reflex has two efferent limbs, one ipsilateral and one contralateral. The afferent limb functions as follows: Sensory input (e.g. light being shone into the eye) is transmitted from the retina, along the optic nerve to the ipsilateral pretectal nucleus in the midbrain.
Why do you move a pen torch between pupils?
Move the pen torch rapidly between the two pupils to check for a relative afferent pupillary defect (see more details below).
What does strabismus mean in a patient?
Strabismus: may indicate oculomotor, trochlear or abducens nerve palsy. Limbs: pay attention to the patient’s arms and legs as they enter the room and take a seat noting any abnormalities (e.g. spasticity, weakness, wasting, tremor, fasciculation) which may suggest the presence of a neurological syndrome).
Why dim lights in assessment room?
With the patient seated, dim the lights in the assessment room to allow you to assess pupillary reflexes effectively.
What does it mean when a pupil is pronounced in bright light?
If the pupil is more pronounced in bright light this would suggest that the larger pupil is the abnormal pupil, if more pronounced in dark this would suggest the smaller pupil is abnormal. Examples of asymmetry include a large pupil in oculomotor nerve palsy and a small and reactive pupil in Horner’s syndrome.
What causes anosmia in the nose?
There are many potential causes of anosmia including: Mucous blockage of the nose: preventing odours from reaching the olfactory nerve receptors. Head trauma: can result in shearing of the olfactory nerve fibres leading to anosmia. Genetics: some individuals have congenital anosmia.
Where does motor output come from?
Motor output is transmitted from the pretectal nucleus to the Edinger-Westphal nuclei on both sides of the brain (ipsilateral and contralateral). Each Edinger-Westphal nucleus gives rise to efferent nerve fibres which travel in the oculomotor nerve to innervate the ciliary sphincter and enable pupillary constriction.

Use Mnemonics to Aid Remembering and Identifying Abnormal findings.
- Takeaways 1. Many nurses find remembering the cranial nerves and their functions to be challenging. 2. Neurologic assessments occur in all healthcare settings. 3. Understanding normal and abnormal cranial nerve assessments can aid early diagnosis and treatment. Acute and chronic neurologic presentations exist in all healthcare settings. Abnormal fi...
Cranial Nerves
- The 12 pairs of cranial nerves are referred to by Roman numerals (CN I through XII) or by name. The cranial nerves control most of the sensory and motor function in the head and neck in addition to peripheral nerves that exit from the midbrain or the brainstem. Each cranial nerve has either a sensory, motor, or a combined function. Cranial nerve assessments help you determine …
Mnemonics
- Several mnemonics have been created to help nurses remember the name and function of the 12 cranial nerves. However, the most important component of a cranial nerve assessment is knowing normal vs. abnormal. Other creative tools for aiding cranial nerve recall include a University of Texas Southwestern Neurology YouTube video and a visual developed by Bolek. Remembering a…
Prevent Complications
- Cranial nerves control essential sensory and motor functions, including protective reflexes. Understanding these functions can help you identify abnormalities and intervene to prevent potential complications. Melissa Moreda is a diabetes clinical nurse specialist at the Duke Health System in Raleigh, North Carolina. Michelle Hill is the comprehensive stroke program coordinato…
References
- Bader MK, Littlejohns LR, Olson DM, eds. AANN Core Curriculum for Neuroscience Nursing. 6th ed. Chicago, IL: American Association of Neuroscience Nurses; 2016. Bolek B. Facing cranial nerve assessment. Am Nurse Today. 2006;1(2):21-2. Hickey JV. Comprehensive neurological examination. In Hickey JV, ed. The Clinical Practice of Neurological and Neurosurgical Nursing. …