
What is the difference between SLE and Aro and ale?
The focus is more on single loss expectancy (SLE), annualized rate of occurrence (ARO), annualized loss expectancy (ALE). The SLE is the cost of any single loss. The ARO indicates how many times you can expect the loss in a year. The ALE is calculated as SLE x ARO.
What is the value of ale with an ARO of 3?
For an ARO of 3, the equation is: ALE = 3 * $25,000. Therefore: ALE = $75,000 ^ "Annualized Loss Expectancy".
How do you calculate annual loss expectancy from ARO?
ALE = ARO * SLE For an annual rate of occurrence of 1, the annualized loss expectancy is 1 * $25,000, or $25,000. For an ARO of 3, the equation is: ALE = 3 * $25,000. Therefore: ALE = $75,000
What is an ale formula and how is it used?
What Is an ALE Formula? (And How To Use It) An annualized loss expectancy, or ALE formula, is used to calculate your organization's annualized loss expectancy for a specific asset to determine its quantitative risk.
What is SLE and ARO?
The annualized loss expectancy (ALE) is the product of the annual rate of occurrence (ARO) and the single loss expectancy (SLE). It is mathematically expressed as: Suppose that an asset is valued at $100,000, and the Exposure Factor (EF) for this asset is 25%.
What is meant by annual rate of occurrence Aro?
Annual rate of occurrence (ARO) – expected number of an incident's occurrences during a calendar year. For rare incidents, it is equivalent to a probability of one or more incidents during a year; for frequent incidents, it is equivalent to the expected number of incidents per year.
What is Aro in computing?
Annual Rate of Occurrence (ARO), which is simply the likelihood of a risk being compromised and is calculated by dividing the estimated number of incidents by the time frame.
How is ale calculated?
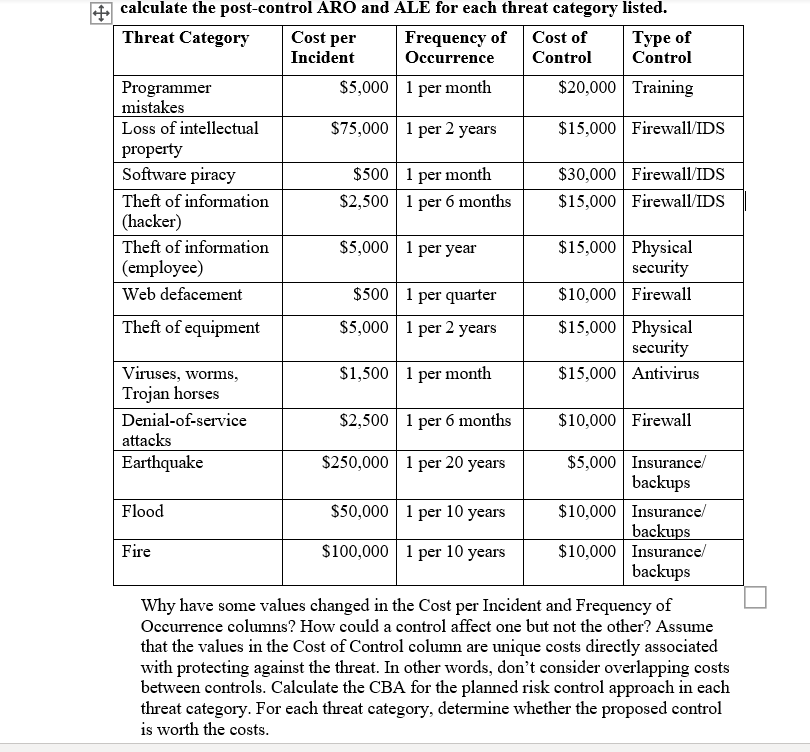
The ALE represents the yearly average loss over many years for a given threat to a particular asset, and is computed as follows: ALE = SLE x ARO. Some risk assessment professionals add another factor: uncertainty.
How do you calculate annual risk?
A commonly used method to annualize risk measures based on monthly returns is to multiply the outcome by 12 or 12, depending on the type of measure. This way, the measure should be expressed in the same unit as the annual return.
What is the formula for computing risk assessment?
It is calculated as follows: SLE = AV x EF, where EF is exposure factor. Exposure factor describes the loss that will happen to the asset as a result of the threat (expressed as percentage value).
What are the basic formulas used in quantitative risk assessment?
Quantitative Risk Analysis Formula The industry-standard formula for quantitative risk analysis is: (ALE = SLE × ARO). That is, Annualized Loss Expectancy (ALE) = Single Loss Exposure (SLE) × Annualized Rate of Occurrence (ARO). SLE is calculated as asset value x exposure factor.
What is the correct formula to calculate single loss expectancy?
It can be defined as the monetary value expected from the occurrence of a risk on an asset. It is mathematically expressed as follows: Single Loss Expectancy (SLE) = Asset Value (AV) * Exposure Factor (EF) where the Exposure Factor is represented in the impact of the risk over the asset, or percentage of asset lost.
What is the Annualised rate of occurrence?
Annual rate of occurrence — This is the number of times you expect a specific incident to occur in one year. If you expect your server to crash five times per year, your ARO would be 5.
How is annual loss expectancy calculated?
The annualized loss expectancy (ALE) is computed as the product of the asset value (AV) times the exposure factor (EF) times the annualized rate of occurrence (ARO). This is the longer form of the formula ALE = SLE x ARO.
What is a risk register and why is it used?
A risk register is a document that is used as a risk management tool to identify potential setbacks within a project. This process aims to collectively identify, analyze, and solve risks before they become problems.
Which factor is defined as the amount of exposure to a hazard?
Exposure factor (EF) is the subjective, potential percentage of loss to a specific asset if a specific threat is realized. The exposure factor is a subjective value that the person assessing risk must define. The exposure factor is represented in the impact of the risk over the asset, or percentage of asset lost.
Risk Is a Constant
We may not always know it, but we constantly evaluate risk in our everyday life. It could be something as simple as avoiding a pothole in the road so you don't get a flat tire or something significant that involves many risks, like buying a new house.
Quantitative Risk Analysis
There are three recognized risk assessment computations: SLE, ALE, and ARO. Let's look at them in a little more detail.
What is quantitative risk analysis?
Quantitative risk analysis uses relevant, verifiable data to predict the probability of certain risk outcomes and their estimated monetary cost.
How is annual loss expectancy calculated?
Here is an overview of how to calculate ALE. Each term is explained in further detail below.
Why is ALE important?
Calculating ALE as part of a quantitative risk assessment is essential for making informed business decisions. While the process can be confusing and arduous at times, reliably determining risks and accurately calculating potential losses will provide valuable information to help you make smart business decisions. With ALE as a risk assessment tool in your pocket, you can more effectively perform cost-benefit analysis and determine if employing specific countermeasures are worth the investment.
What is annual loss expectancy?
Annual loss expectancy is a calculation that helps you to determine the expected monetary loss for an asset due to a particule risk over a single year. You can calculate ALE as a part of your business’s quantitative cost-benefit analysis for any given investment or project idea.
Why is quantitative risk assessment important?
Quantitative risk assessment helps you make smart, data-informed decisions for your business. You should perform a quantitative risk analysis when you need to:
How to calculate SLE?
Calculate the SLE by multiplying the AV by the EF , which yields an SLE of $56,250.
What is exposure factor?
Exposure factor — This is the percentage of the value of a given asset that gets lost as a result of a specific incident. If you expect to lose a quarter of the value of an asset in an incident, then your EF for that asset is 0.25 (25%). Remember that you can only calculate the EF in relation to a specific risk, such as a security breach or natural disaster. Also keep in mind that a loss can exceed the value of a given asset; in such cases, the EF would be greater than 1.0 (more than 100%).
What is the SLE of a $100,000 asset?
Suppose that an asset is valued at $100,000, and the Exposure Factor (EF) for this asset is 25%. The single loss expectancy (SLE) then, is 25% * $100,000, or $25,000.
What is the ALE of an ARO of 3?
For an ARO of 3, the equation is: ALE = 3 * $25,000. Therefore: ALE = $75,000
How to calculate the expected present value of ARO?
Then, you can follow the steps to calculate the expected present value of the ARO: 1. Estimate the timing of the future retirement costs (cash flows), along with their respective amounts. 2.
What are the rules for ARO?
Governing Rules for AROs. ARO calculations are governed by the Financial Accounting Standards Board’s Rule 143. The rule essentially states that a company has a legal obligation to remove the asset, and there are certain calculation rules for an accountant to follow.
Why should a company periodically review its AROs?
A company should periodically review its AROs to account for upward or downward liability revisions. During the review, the company should use an updated discount rate that reflects current market conditions. Follow the steps below to assist in the recognition of any additional costs an ARO’s undertaken since original recognition:
What is an ARO?
What is an Asset Retirement Obligation (ARO)? An asset retirement obligation (ARO) is a legal obligation that is associated with the retirement of a tangible, long-term asset. It is generally applicable when a company is responsible for removing equipment or cleaning up hazardous materials at some agreed-upon future date.
How to acquire rough estimate?
If you are seeking a rough estimate, you can usually acquire it by accounting only for inflation. For example, if you hold a 40-year lease on a piece of land, the cost of the ARO today is $10,000, and you expect inflation to run at 2% per year, then:
When to write down ARO?
An individual will usually carry out a subsequent measure of an ARO when a portion of the liability must be paid before the asset retires. If there is no expense associated with retiring the asset, then they can write down the ARO to 0.
When must a company realize the ARO?
A company must realize the ARO for a long-term asset at the point an obligating event takes place, so their financial statements accurately reflect the company’s value.
