To calculate the interest payment on a bond, look at the bond’s face value and the coupon rate, or interest rate, at the time it was issued. The coupon rate may also be called the face, nominal, or contractual interest rate. Multiply the bond’s face value by the coupon interest rate to get the annual interest paid.
How do you calculate annual interest on a bond?
Part 2 Part 2 of 2: Calculating Interest Payment on a Bond
- Look at the bond's face value. It is typically $1,000 or a multiple of that amount. ...
- Find the bond's "coupon" (interest) rate at the time it was issued. The rate is stated in the bond's paperwork.
- Multiply the bond's face value by the coupon interest rate. ...
- Calculate how much each bond payment is. ...
- Find the monthly interest. ...
How to calculate interest expenses on a payable bond?
- Calculate the debt premium or discount
- Add any debt issuance costs to the existing discount / Subtract any debt issuance costs from the existing premium
- Calculate the adjusted present value
- Compute the effective interest rate using the adjusted present value
- Multiply the effective interest rate by the carrying value of the instrument
What is the effective interest rate for a bond?
The effective interest rate method uses the market interest rate at the time that the bond was issued. In our example, the market interest rate on January 1, 2020 was 4% per semiannual period for 10 semiannual periods.
How much interest is on a bond?
Calculate how much each bond payment is. Interest is typically paid twice a year. This information is stated when you purchase the bond. If a bond pays interest twice a year, the annual payment would be divided by two. In this case, every six months you can expect $25.
How do you calculate annual interest paid on a bond?
If you want to calculate the annual coupon payment for a bond, all you have to do is multiply the bond's face value by its annual coupon rate. That means if you have a bond with a face value of $1000 and an annual coupon rate of 10%, then the annual coupon payment is 10% of $1000, which is $100.
How do I calculate the interest on a bond?
A simple answer for traditional bonds To figure out the total interest paid, you take the face value of the bond, multiply it by the coupon interest rate, and then multiply that by the number of years corresponding to the term of the bond.
What is the formula for annual interest?
The formula and calculations are as follows: Effective annual interest rate = (1 + (nominal rate / number of compounding periods)) ^ (number of compounding periods) - 1. For investment A, this would be: 10.47% = (1 + (10% / 12)) ^ 12 - 1.
What is annual bond interest?
If an investor purchases a bond with a face value of $1000 that matures in five years with a 10% annual coupon rate, the bond pays 10%, or $100, in interest annually. If interest rates rise above 10%, the bond's price will fall if the investor decides to sell it.
Is bond interest paid annually?
Most bonds pay interest semi-annually, which means bondholders receive two payments each year. 1 So with a $1,000 face value bond that has a 10% semi-annual coupon, you would receive $50 (5% x $1,000) twice per year for the next 10 years.
How do I calculate interest on a bond in Excel?
Select the cell you will place the calculated price at, type the formula =PV(B20/2,B22,B19*B23/2,B19), and press the Enter key. Note: In above formula, B20 is the annual interest rate, B22 is the number of actual periods, B19*B23/2 gets the coupon, B19 is the face value, and you can change them as you need.
How do you convert monthly interest rate to annual?
Convert a Monthly Interest Rate to Annual To calculate monthly interest from APR or annual interest, simply multiply the interest for the month by 12. If you paid $6.70 in interest per month, your annual interest is $80.40.
How do I calculate interest rate on a calculator?
r and t are in the same units of time.Calculate Interest, solve for I. I = Prt.Calculate Principal Amount, solve for P. P = I / rt.Calculate rate of interest in decimal, solve for r. r = I / Pt.Calculate rate of interest in percent. R = r * 100.Calculate time, solve for t. t = I / Pr.
What is the current interest rate on bonds?
US 10-Year Government Bond Interest Rate is at 3.52%, compared to 2.90% last month and 1.37% last year.
Is bond yield the same as interest rate?
Yield is the annual net profit that an investor earns on an investment. The interest rate is the percentage charged by a lender for a loan. The yield on new investments in debt of any kind reflects interest rates at the time they are issued.
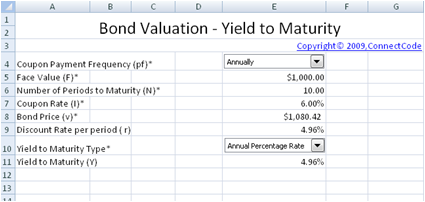
How do you calculate the yield to maturity of a bond?
Yield to Maturity = [Annual Interest + {(FV-Price)/Maturity}] / [(FV+Price)/2]Annual Interest = Annual Interest Payout by the Bond.FV = Face Value of the Bond.Price = Current Market Price of the Bond.Maturity = Time to Maturity i.e. number of years till Maturity of the Bond.
How long do you have to hold an I bond?
You must own the bond for at least 5 years to receive all of the interest. You can cash out an I Bond after one year, but if you withdraw it before 5 years, you'll forfeit 3 months of interest.
What will the I bond rate be in May 2022?
9.62%May 2, 2022. Effective today, Series EE savings bonds issued May 2022 through October 2022 will earn an annual fixed rate of . 10% and Series I savings bonds will earn a composite rate of 9.62%, a portion of which is indexed to inflation every six months.
Are bonds a good investment?
Bonds tend to be considered safer than other financial assets like stocks and, barring an issuer defaulting on their debt, you can rely on the income. There is a wide variety of types of bonds, with different payment timelines and minimum investments. Most bonds offer fixed coupon rates.
Is there a downside to I bonds?
Another disadvantage is I bonds can't be purchased and held in a traditional or Roth IRA. The I bonds have to be held in a taxable account. A final disadvantage of I bonds is there is an interest penalty if the bonds are redeemed in the first five years.
Why do bonds go up and down?
This is because the value of your bond can change over time, and yield is the bond's annual coupon payment as a percent of its current value. Sometimes bond prices go up and down, meaning the price of your bond can change from what your face value is.
How to find out how much money you will receive each year?
By multiplying the bond's face value by its coupon interest rate, you can figure out what the dollar amount of that interest rate is each year. For example, if the bond's face value is $1000, and the interest rate is 5%, by multiplying 5% by $1000, you can find out exactly how much money you will receive each year.
What happens if you hold a bond for a long time and do not sell it?
Keep in mind that if you hold the bond until maturity and do not sell, you will receive back your principal, regardless of what happens to the price of the bond during the term.
What is a coupon on a bond?
Coupon. A coupon can be thought of as a bond's interest payment. A bond's coupon is typically expressed as a percentage of the bond's face value. For example, you may see a 5% coupon on a bond with a face value of $1000. In this case, the coupon would be $50 (0.05 multiplied by $1000).
What is bonding?
Learn what a bond is. Purchasing a bond can be thought of as purchasing debt, or, alternatively stated, loaning money to a company. The bond itself simply represents this debt. Like any loaned money, a bond entitles you to receive interest payments at fixed intervals for a specific time frame, at the end of which you will receive your initial amount back. .
Why do bonds have to be called?
Be aware that a bond may be "called" (or paid off before its maturity date). This tends to happen when current interest rates are lower than the rates prevailing at the time the bond was issued. The issuing company may decide to pay off the current bond and issue a new one at the lower rate to save themselves money on interest payments. The calling of a bond can be disruptive to a bondholder's plans for cash flow and will usually diminish the holder's income.
Why do bond prices change?
The reason bond market prices change is due to fluctuations in the market. For example, if long term interest rates rise from 5% (the coupon rate also) when the bond was purchased, the market price of a $1000 bond will fall to $500.
Why are bonds low?
Bonds have a low but stable return. This is mainly because you run little risk with bonds. Because of the perfect relationship between stable return and low risk, it is often an important part of most portfolios. However, there are a few pitfalls in the yield on bonds. For example, it is important to calculate the effective return instead ...
What is option B in savings account?
This time you buy the bond on the free market at a price of 102%. This will be option A. Option B is a 2-year savings account deposit. The return on this savings account is 3%.
How much interest do you get after 5 years?
So after 5 years you have received a total of 150 dollar in interest. When the term of 5 years has been reached, you get back the nominal value of the bond, which is 1,000 dollar. In total, you therefore received 1,150 dollar and spent 1,000 dollar. This is a profit of 150 dollar.
What is effective return?
The effective return takes into account a number of additional issues compared to the previous calculation. The price is included in this calculation. In addition, “hidden” losses must be taken into account. There are hidden losses when, for example, you can earn more money with an alternative investment (with the same or less risk).
Is there a pitfalls in yielding bonds?
However, there are a few pitfalls in the yield on bonds. For example, it is important to calculate the effective return instead of blindly using the coupon rate as your effective return. Before we proceed, it is important that you know how a bond is constructed.
Does bond yield equal to yield to maturity?
Technically, yes. Bond yield will equal to yield to maturity if you hold to the bond until its maturity and reinvest at the same rate as the yield to maturity.
What causes bond yields to fall?
There are several factors that can make bond yields fall. For instance, the lower the inflation, the lower the bond yield. The less volatile the market condition, the lower the bond yields.
Can bond yield be negative?
Yes, bond yield can be negative. It happens every now and then, even though it is not common. This situation normally happens when inflation is out of control and the market is unstable.
What does a yield curve mean?
The yield curve is a graph drawn for bond yield against time. It shows the evolution of bond yield with time. If the yield curve is trending upwards, it means that long-term bond yields are higher than short-term bond yields.
What is bond yield?
Bond yield meaning, also often known as the yield to maturity (YTM), is often understood as the rate of return for bond investors, given that the bond investors hold the bond until it matures and reinvest the coupons at an interest rate equal to the the YTM. As bond yield is very volatile and sensitive to the economic climate, it is of the essence that we understand its dynamics and calculation.
Why do bond yields increase?
The more volatile the market conditions, the more uncertainty investors will face. Owing to the higher uncertainty, investors will demand a higher rate of return to compensate for the risks they undertake. Therefore, this is what causes bond yields to rise.
What is frequency in couponing?
frequency - Number of times the coupon is distributed in a year; and
What is a bond?
In finance bonds are often referred to as fixed-income securities as they are a type of investment in which the holder (usually called as the investor) lends money to a bond issuer (usually governmental e.g: foreign governments, municipalities, states or corporate organizations) for a specific period of time while the borrower understands to pay to the investor a fixed interest rate, compounded by the rule negotiated and paid within certain terms. Usually bonds are issued to help such entities finance big or public projects such as utilities, infrastructure, research and development health related.
What is face par value?
Face/par value which is the amount of money the bond holder expects to receive from the issuer at the maturity date as agreed.
What happens if c = r?
IF c = r then the bond should be selling at par value.
What is market interest rate?
Market interest rate represents the return rate similar bonds sold on the market can generate. This figure is used to see whether the bond should be sold at a premium, a discount or at its face valueas explained below.
How to calculate interest on a zero coupon bond?
Just multiply that current value by the periodic interest rate to calculate the interest payment. Interest payments on US Series EE and Series I savings bonds are calculated like zero coupon bonds, with two exceptions. “Electronic” savings bonds sold online are sold at face value, not at a discount. Series I bond interest rates are adjusted each May and November to compensate for inflation, so you need to look on the Treasury Direct website to find the current periodic interest rate before calculating the interest payment.
How to find the value of a zero-coupon bond?
Multiply the initial price of the zero-coupon bond by the periodic interest rate and add the result to the original price to find the value of the bond after the first interest-earning period, called a compounding interval. Suppose a zero-coupon bond with a face value of $1,000 is sold for $500 when issued and earns 8 percent interest compounded semiannually. The periodic rate is 4 percent and the interest earned is 4 percent of $500, or $20. The interest is added to the value of the bond, making it worth $520 after the first six-month compounding interval.
How to find the periodic interest rate?
Once you know how many times each year interest is calculated, divide that number into the annual interest rate to find the periodic interest rate.
What does it mean when you own a bond?
When you own bonds, it means the issuing company or government owes you money. Until the bond matures, you get paid interest. For most bonds, this means you get a nice interest payment, usually twice a year. The interest payment stays the same for the life of the bond. Some bonds work differently.
How does a zero-coupon bond work?
With zero-coupon bonds, you still get interest payments, but the money gets added to the bond, increasing its value and the size of each succeeding interest payment.
Where is W D Adkins?
Based in Atlanta, Georgia, W D Adkins has been writing professionally since 2008. He writes about business, personal finance and careers. Adkins holds master's degrees in history and sociology from Georgia State University. He became a member of the Society of Professional Journalists in 2009.