
How do you calculate direct variation?
x ∝ y. If a proportionality constant is put, then the direct variation formula is given as, x = ky. Or, x/y = k. Here, “k” is the constant of proportionality. This equation represents that when two directly proportional quantities are divided, the resultant value is always a constant.
How to calculate direct materials used in production?
- Calculate beginning direct materials inventory. Beginning direct material inventory refers to the unused raw material at the start of the month or year.
- Add direct material purchases. Add direct material purchases made during the month. ...
- Determine ending direct material inventory. ...
- Calculate direct material used. ...
What would the direct materials price variance be?
The direct material price variance is the difference between the actual price paid to acquire a direct materials item and its budgeted price, multiplied by the actual number of units acquired. This information is needed to monitor the costs incurred to produce goods. The formula follows:
How to compute the direct labor price variance?
Process of Labor Rate Variance Calculation
- Calculate actual cost The company can get this figure from their actual payment to the workers. It is the actual hour multiply by actual rate.
- Calculate the standard cost of the actual hour We calculate this by using the actual hour at the standard rate per hour. ...
- Calculate variance
What is the formula for direct materials cost variance?
It is the difference between the standard cost of material specified for the output achieved and the actual cost of materials used. = (SP × SQ) – (AP × AQ).
What is the formula for calculating direct materials?
Direct materials. Add the total cost of materials purchases in the period to the cost of beginning inventory, and subtract the cost of ending inventory. The result is the cost of direct materials incurred during the period.
How do you calculate direct materials efficiency variance?
To calculate a direct materials efficiency variance, the formula is (actual quantity used × standard price) − (standard quantity allowed × standard price).
How do you calculate direct materials from raw materials?
The cost of raw materials purchased can therefore be calculated as follows: Raw Materials Purchased = (Ending Inventory – Beginning Inventory) + Cost of Goods Sold. A direct material purchases budget determines the quantity of material purchased within a production period.
What is direct material with examples?
Direct material is the physical items built into a product. For example, the direct materials for a baker include flour, eggs, yeast, sugar, oil, and water. The direct materials concept is used in cost accounting, where this cost is separately classified in several types of financial analysis.
What are the two direct materials variances?
There are two components to a direct materials variance, the direct materials price variance and the direct materials quantity variance, which both compare the actual price or amount used to the standard amount.
What is the direct material variance for price and usage?
The correct answer is b. Unfavorable usage, but favorable price.
What does the direct materials usage variance measure?
What is the Direct Material Usage Variance? The direct material usage variance is the difference between the actual and expected unit quantity needed to manufacture a product. The variance is used in a standard costing system, usually in conjunction with the purchase price variance.
What is the formula of material cost?
And low value means that the cost is 10% of the total....EOQ: Formula-based method.Total costPurchase value of raw material + associated costAssociated costOrdering cost + carrying cost
How do you calculate direct materials budget?
To work this out in units, just apply another simple formula: Budgeted production level during the period x. Units of direct material required per unit = Direct material in units necessary for production.
How do you calculate direct material ending inventory?
The basic formula for calculating ending inventory is: Beginning inventory + net purchases – COGS = ending inventory.
How do you calculate beginning direct materials inventory?
The beginning inventory formula is simple:Beginning inventory = Cost of goods sold + Ending inventory – Purchases.COGS = (Previous accounting period beginning inventory + previous accounting period purchases) – previous accounting period ending inventory.More items...•
What's the difference between raw materials and direct materials?
Direct materials are a type of raw material. Direct materials are the raw materials that end up in your final product, but not all raw materials ha...
What are indirect materials?
Indirect materials refer to materials consumed during the manufacturing process. Glue, nails, and gas are considered indirect materials.
What are examples of direct materials?
Direct materials are the basis of any finished product. Direct materials include:
How to calculate direct material price variance?
To calculate the variance, we multiply the actual purchase volume by the standard and actual price difference.
What is direct material price variation?
Direct Material Price Variance (DMPV) shows the amount by which the total cost of raw materials has deviated from the planned cost as a result of a price change over a period.
What is the standard price of raw materials?
The standard price of raw materials is $4 per unit and the actual purchase quantity is 500 units. If the direct material price variance is $1000 adverse, what is the actual selling price of the raw material?
Why is material price variance favorable?
The material price variance in this example is favorable because the company was able to get the materials at a lower cost compared to the budget.
How to simplify DMPV?
We can simplify the DMPV formula by multiplying the actual purchase quantity by the price difference, as shown below.
What is the left side of the DMPV formula?
The left side of the DMPV formula estimates what the actual quantity of direct materials purchased should cost according to the standard price allowed in the budget. The right side of the formula calculates what the direct materials actually cost during the period.
Why is the price of materials lower?
The lower price of materials is at the expense of lower quality. This is likely when there is an increase in customer returns, refund claims, quality control rejects, customer complaints, and an adverse material usage variance.
How to calculate variance?
Variance calculation should always be calculated by taking the planned or budgeted amount and subtracting the actual/forecasted value. Thus a positive number is favorable and a negative number is unfavorable.
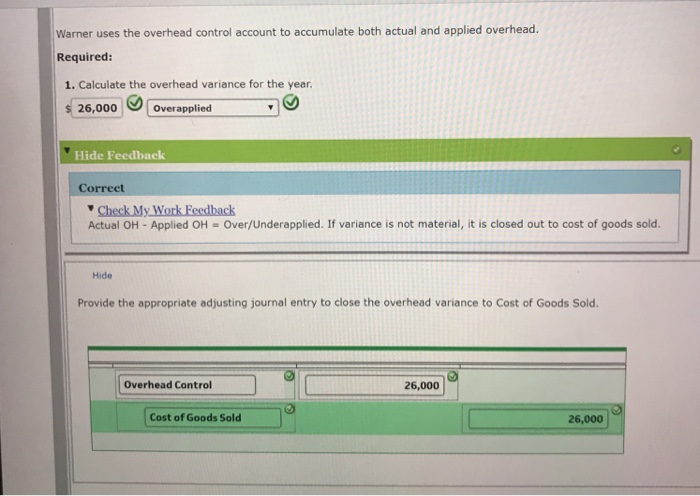
How to calculate variance in fixed overhead?
Fixed overhead expenditure variance is calculated by subtracting the actual fixed overhead cost from the budgeted fixed overhead cost. It can be favorable when the budgeted fixed overhead is less than the actual fixed overhead or adverse when the actual costs are more than the budgeted. In budgeting (or management accounting in general), a variance is the difference between a budgeted, planned, or standard cost and the actual amount incurred/sold. Variance analysis, also described as analysis of variance or ANOVA, involves assessing the difference between two figures.
What is cost variance?
This is the difference between the actual and budgeted number of units sold, multiplied by the budgeted contribution margin. This measure is used to determine the impact on the overall sales margin of differences in the expected mix of units sold.
What is fixed overhead spending variance?
The fixed overhead spending variance is the difference between the actual amount of fixed overhead and the budgeted amount of fixed overhead. If the company spent more than it should have (according to the standard, which is set by management) on fixed overhead, then the fixed overhead spending variance is unfavorable.
How to calculate variable overhead efficiency?
Variable overhead efficiency variance is calculated by subtracting the standard budgeted hours from the actual hours incurred, and then multiplying the result with the standard variable overhead rate. A favorable variance results when the actual hours used are less than the budgeted while an adverse variance results from use of more hours than the budgeted. This is the difference between the budgeted fixed overhead expenditure and the actual fixed overhead incurred. It arises due to changes in the cost of fixed overhead during the period.
What is spending variance?
A spending variance is the difference between the actual and expected (or budgeted) amount of an expense. The spending variance for fixed overhead is known as the fixed overhead spending variance, and is the actual expense incurred minus the budgeted expense.
What is unfavorable budget variance?
Unfavorable budget variances refer to the negative difference between actual revenues and what was budgeted. This usually happens when revenue is lower than expected or when expenses are higher than expected.
What is direct material usage variance?
Direct Material Usage Variance measures efficiency in material or material consumption by comparing standard material used for actual production units with actual material usages or consumption.
What happens if a manufacturer uses more direct materials than the standard quantity of materials for the products manufactured?
If a manufacturer uses more direct materials than the standard quantity of materials for the products manufactured, the company will have adverse direct materials usage variance. If the quantity of direct materials used is less than the standard quantity of products manufactured, the company shall have favorable materials usage variance.
What is negative variance?
Negative variance generally means production is not run effectively, and positive variance is normally favorable for management. The direct material usage variance may be divided into mix and yield variances if several materials are mixed in standard proportions.
What is favorable variance?
Favorable usage variance suggests efficient utilization of material resources by the production manager. The various reasons for favorable material usage variance are as follows:
Why is adverse usage variance important?
The various reasons for adverse usage variance are as follows: Using human in manufacturing rather than automated tools which decrease the efficiency and increases the level of error. Ineffective use of skilled labor.
What is direct material price variation?
Direct Material Price Variance is the difference between the actual cost of direct material and the standard cost of quantity purchased or consumed.
What does favorable material price variance mean?
A favorable material price variance suggests cost effective procurement by the company.
What is standard cost basis valuation?
The valuation of stock on standard cost basis implies that the entire effect of any price variance is to be accounted for in the current period. Therefore, the purchase cost of the entire quantity must be compared with the standard cost of the actual quantity.
How to calculate direct materials price variance?
The difference between the actual quantity at standard price and the standard cost is the direct materials quantity variance. To compute the direct materials price variance, subtract the actual cost of direct materials ($297,000) from the actual quantity of direct materials at standard price ($310,500). This difference comes to a $13,500 favorable variance, meaning that the company saves $13,500 by buying direct materials for $9.90 rather than the original standard price of $10.35.
What is direct materials variance?
The direct materials quantity variance refers to the variance that arises from the difference in the expected and actual quantity of materials used in production.
How to estimate how the combination of wages and hours affects total costs?
To estimate how the combination of wages and hours affects total costs, compute the total direct labor variance. As with direct materials, the price and quantity variances add up to the total direct labor variance .
Why is labor variance favorable?
If the actual quantity used is less than the standard quantity, the variance is favorable since the company was able to save on materials. Decreased usage might indicate that the production department is producing lower quality products as a result of trying to reduce the total cost of materials. A direct labor variance is caused by differences in either wage rates or hours worked.
What is the difference between the standard cost of direct materials specified for production and the actual cost of direct materials used in production?
The difference between the standard cost of direct materials specified for production and the actual cost of direct materials used in production is known as Direct Material Cost Variance. Material Cost Variance gives an idea of how much more or less cost has been incurred when compared with the standard cost. Thus, Variance Analysis is an important tool to keep a tab on the deviations from the standard set by a company.
How many units of direct materials were produced in 2012?
During December 2012, 5,000 units of were produced using 8,000 kgs of direct materials. The difference between the total standard cost of the output that has been achieved in a period & the total actual cost which has been incurred in a period is known as total cost variance. On actual output & not on standard or budgeted output, all cost variances are based.
Is variance in dollars?
This is a variance of physical quantity but is also reported in dollars for proper financial measurement. To express this variance in dollars, both actual quantity used and standard quantity allowed are multiplied by standard price per unit of materials.
What is direct material variation?
It is the difference between the standard cost of materials used for the actual output and the actual cost of materials used.
What causes material cost variance?
Direct material cost variance is caused due to the following reasons. 1. Change (increase / decrease) in the price of materials. 2. Change (increase / decrease) in the quantity of materials used. This is happened due to. Change in the mix of more than one type of materials in the process of manufacture. Change (increase / decrease) in the output.
Is variance favorable or negative?
If the standard cost is more than the actual cost, the variance will be favorable and on the other hand if the standard cost is less than the actual cost the variance will be unfavorable or adverse. NOTE: 1. Standard cost has to be calculated with reference to standard quantity for actual output. In such case, the information regarding standard ...
