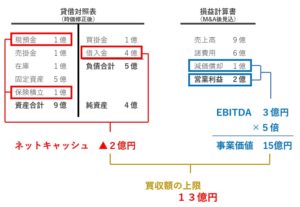
At their simplest, the two metrics can be calculated using the following formulas:
- Enterprise Value (EV) = Equity Value + Net Debt
- EBITDA = EBIT + Depreciation & Amortization
How do you get EV EBITDA multiples?
What is the Formula for the EBITDA Multiple? To Determine the Enterprise Value and EBITDA: Enterprise Value = (market capitalization + value of debt + minority interest + preferred shares) – (cash and cash equivalents) EBITDA = Earnings Before Tax + Interest + Depreciation + Amortization.
How do you calculate EV multiples?
It is computed by dividing enterprise value by EBITDA. The enterprise multiple takes into account a company's debt and cash levels in addition to its stock price and relates that value to the firm's cash profitability. Enterprise multiples can vary depending on the industry.
How do you use EV EBITDA multiple to value a company?
The EV/EBITDA ratio is calculated by dividing EV by EBITDA to achieve an earnings multiple that is more comprehensive than the P/E ratio. The EV/EBITDA ratio compares a company's enterprise value to its earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization.
How do you calculate EV EBITDA price?
With the EV / EBITDA multiple you can multiply by the company's own EBITDA to find the enterprise value of the company. Then you can subtract the net debt of the company to find the equity value of the business. After that point you can divide by shares outstanding to find the equity value per share.
What is EV EBITDA multiple?
The EV/EBITDA Multiple compares the total value of a company's operations (EV) relative to its earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA). In practice, the EV/EBITDA multiple is frequently used in relative valuation to compare different companies in the same (or similar) sector.
What is a normal EV EBITDA multiple?
The EV/EBITDA Multiple The enterprise-value-to-EBITDA ratio is calculated by dividing EV by EBITDA or earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. Typically, EV/EBITDA values below 10 are seen as healthy.
What does 10X EBITDA mean?
Related Definitions 10X LTM EBITDA means, as of the specified date, the product of (i) 10.0 multiplied by (ii) the EBITDA for the twelve months ended as of the last day of the month immediately preceding the measurement date.
Why EV EBITDA is better than P E?
EV/EBITDA takes a more holistic picture of the company and covers the equity and the debt components of the capital structure. P/E ratio works well for manufacturing companies and companies where the business model is matured. EV/EBITDA works better in case of service companies and where the gestation is too long.
Is a high or low EV EBITDA better?
As a general rule, a company with a high EV/EBITDA ratio may be overvalued at its current stock price. Conversely, a company with a low EV/EBITDA ratio may have too low a share price and would provide relative value for an investor.
What is a good EBITDA multiple for acquisition?
Investors can compare the multiples of various companies and estimate how much they really need to pay to acquire this company. As a practice, it is seen that the lower the value of the EBITDA multiplies by industry, the cheaper is the acquisition cost of the company. Usually, any value below 10 is considered good.
What is a good EBITDA ratio?
What is a good EBITDA? An EBITDA over 10 is considered good. Over the last several years, the EBITDA has ranged between 11 and 14 for the S&P 500. You may also look at other businesses in your industry and their reported EBITDA as a way to see how your company is measuring up.
What is a good EBITDA by industry?
One of the most common metrics for business valuation is EBITDA multiples....EBITDA Multiples By Industry.IndustryEBITDA Average MultipleRetail, general14.70Retail, food8.89Utilities, excluding water12.74Homebuilding10.5210 more rows•Sep 9, 2021
How is EV calculated?
The enterprise value of a company shows how much money would be needed to buy that company. EV is calculated by adding market capitalization and total debt, then subtracting all cash and cash equivalents.
How do you calculate share price from EV sales multiple?
EV to Sales Ratio is the valuation metric used to understand the company's total valuation compared to its sale. It is calculated by dividing the enterprise value (Current Market Cap + Debt + Minority Interest + preferred shares – cash) by its annual sales.
How do you calculate EV revenue growth?
EV to Revenue Multiple Formula EV (Enterprise Value) = Equity Value + All Debt + Preferred Shares – Cash and Equivalents. Revenue = Total Annual Revenue.
What is enterprise value formula?
It includes both the current share price (market capitalization) and the cost to pay off debt (net debt, or debt minus cash). Combining these two figures helps establish the company's enterprise value, indicating the neighborhood you need to be in to buy the company. Enterprise Value = Market Cap + Debt - Cash.
What Is The Formula For The EBITDA Multiple?
Formula:EBITDA Multiple = Enterprise Value / EBITDA To Determine the Enterprise Value and EBITDA: 1. Enterprise Value = (market capitalization + va...
What Is Enterprise Value?
Enterprise value is the total value of a company, including common shares equity or market capitalization, short-term and long-term debts, minority...
Historical vs Forecast EBITDA
It’s important to pay close attention to what time period the EBITDA you’re using if from. In order for the EBITDA multiple to be comparable betwee...
How Important Is The EBITDA Multiple?
One of the important features of the EBITDA multiple is its inclusion of both debt and equity, resulting in a more fulsome representation of the to...
How to calculate EV to EBITDA?
EV to EBITDA Multiple is a vital valuation metric used for measuring the value of the company with an objective of comparing its valuation with similar stocks in the sector and it is calculated by dividing the enterprise value (Current Market Cap + Debt + Minority Interest + preferred shares – cash) by EBITDA (earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization) of the company.
What is EV to EBITDA?
EV to EBITDA can be further subdivided into Investment Banking#N#Investment Banking Investment banking is a specialized banking stream that facilitates the business entities, government and other organizations in generating capital through debts and equity, reorganization, mergers and acquisition, etc. read more#N#Analysis.
What is the difference between EBITDA and EV?
EV (which is the sum of market capitalization, preferred shares, minority shares, debt minus cash) to EBITDA is the ratio between enterprise value and Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization that helps the investor in the valuation of the company at a very subtle level by allowing the investor to compare a certain company to the parallel company in the industry as a whole , or other comparative industries.
What is EBITDA in accounting?
EBITDA or earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization is a measure used to get a representation of an organization’s financial performance. With the help of this, we can find out the potential of a particular firm in terms of the profit its operations can make.
How to forward EV to EBITDA?
Likewise, the Forward EV to EBITDA formula = Enterprise Value / EBITDA over the next 12 months.
How to calculate enterprise value?
Theoretically, the calculated enterprise value#N#Calculated Enterprise Value The Enterprise Value Formula is an economic measure that reflects the entire value of the organization, including secured and unsecured creditors, equity and preference shareholders, and is more commonly employed in acquiring other businesses or merging two or more businesses to achieve synergy. Enterprise value Formula = Market Capitalization + Preferred stock + Outstanding Debt + Minority Interest – Cash & Cash Equivalents read more#N#can be considered as the price or value at which the company is bought by an investor. In such a case, the buyer will have to take up the debt of the organization, too, as his responsibility. In other words, it is said that the particular value will be pocketed by him too.
Why is EV better than market capitalization?
The value calculated as the Enterprise Value is considered better than market capitalization because it is calculated by adding more vital components to the value of market capitalization. The added components used in the EV calculation are debt, preferred interest, minority interest.
What is EBITDA multiple?
What is the EBITDA Multiple? The EBITDA multiple is a financial ratio that compares a company’s Enterprise Value. Enterprise Value (EV) Enterprise Value, or Firm Value, is the entire value of a firm equal to its equity value, plus net debt, plus any minority interest. to its annual EBITDA. EBITDA EBITDA or Earnings Before Interest, Tax, ...
What is EV in accounting?
Enterprise Value (EV) Enterprise Value, or Firm Value, is the entire value of a firm equal to its equity value, plus net debt, plus any minority interest.
What is EBITDA before interest?
EBITDA EBITDA or Earnings Before Interest, Tax, Depreciation, Amortization is a company's profits before any of these net deductions are made. EBITDA focuses on the operating decisions of a business because it looks at the business’ profitability from core operations before the impact of capital structure.
Why is EBITDA multiple important?
One of the important features of the EBITDA multiple is its inclusion of both debt and equity, result ing in a more fulsome representation of the total business’ performance. It is used extensively as a valuation technique. , often to find attractive takeover candidates for a merger or acquisition.
What is multiple analysis?
Multiples Analysis The multiples analysis is a valuation technique that utilizes different financial metrics from comparable companies to value a target company.
Why do investors use enterprise multiples?
Investors use a company’s enterprise multiple as a proxy to indicate if a company is overvalued or undervalued. When the value of the ratio is low, it signals that the company is undervalued, and when it is high, it signals that the company is overvalued. Equity research. Equity Research Overview Equity research professionals are responsible ...
Why are cash equivalents not considered?
Cash or cash equivalents are not considered because they can reduce the net cost to a potential buyer by paying back debt. To learn more, read a comparison of Enterprise Value vs Equity Value. Enterprise Value vs Equity Value Enterprise value vs equity value.
What Does the EV/EBITDA Multiple Mean?
The EV/EBITDA Multiple compares the total value of a company’s operations (EV) relative to its earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA). The EV/EBITDA multiple is frequently used in relative valuation to compare across companies in the same (or similar) sector.
What does a low EV to EBITDA ratio mean?
A low EV-to-EBITDA ratio could signal that a stock is potentially undervalued.
What is enterprise value?
The enterprise value represents the debt-inclusive value of a company’s operations (i.e. unlevered) while EBITDA is also a capital structure neutral cash flow metric. The EV / EBITDA multiple is thus widely used to benchmark companies of varying degrees of financial leverage.
Why is EV used in M&A?
And for that reason, EV / EBITDA is frequently used to value potential acquisition targets in M&A because it quantifies the amount of debt that the acquirer must assume (i.e. cash-free, debt-free ).
Is EBITDA an enterprise value multiple?
Since EV / EBITDA is categorized as an enterprise value multiple, you must ensure that both the numerator and denominator represent the same investor groups – which in this case, is ALL investor groups (e.g. common and preferred equity shareholders, debt lenders).
Is EV a valuation multiple?
In certain scenarios, adjusted valuation multiples such as EV / (EBITDA – Capex) can be used instead, which is oftentimes seen in industries like the telecom industry where there is the need to account for capital expenditures due to the sheer degree of impact that capex has on the cash flows of companies in these types of industries.
Is EBITDA the same as enterprise value?
While these two companies are very unlikely to actually be the same, in theory, the enterprise value and EBITDA metrics are each independent of capital structure decisions, thus it makes sense that they would have similar EV / EBITDA multiples.
How is enterprise multiple calculated?
It is computed by dividing enterprise value by EBITDA. The enterprise multiple takes into account a company's debt and cash levels in addition to its stock price and relates that value to the firm's cash profitability. Enterprise multiples can vary depending on the industry.
How much did the enterprise multiple increase?
The increase in the enterprise multiple is largely a result of the near $15 billion increase in market cap, while EBITDA increased just around $500 million. In this example, you can see how the Enterprise Multiple calculation takes into account both the cash the company has on hand and the debt the company is liable for.
What Is Enterprise Multiple?
Enterprise multiple, also known as the EV multiple, is a ratio used to determine the value of a company. The enterprise multiple, which is enterprise value divided by earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), looks at a company the way a potential acquirer would by considering the company's debt. What's considered a "good" or "bad" enterprise multiple will depend on the industry.
Why do investors use enterprise multiples?
Investors mainly use a company's enterprise multiple to determine whether a company is undervalued or overvalued. A low ratio relative to peers or historical averages indicates that a company might be undervalued and a high ratio indicates that the company might be overvalued. An enterprise multiple is useful for transnational comparisons ...
How much is Dollar General's EBITDA?
Dollar General ( DG) generated $3.18 billion in EBITDA for the trailing 12 months (TTM) as of the quarter ending May 1, 2020. The company had $2.67 billion in cash and cash equivalents and $3.97 billion in debt for the same ending quarter. 1
Why is enterprise multiple important?
An enterprise multiple is useful for transnational comparisons because it ignores the distorting effects of individual countries' taxation policies. It's also used to find attractive takeover candidates since enterprise value includes debt and is a better metric than market capitalization for merger and acquisition (M&A) purposes.
How to find EV/EBITDA multiple?
The EV/EBITDA multiple for a company can be found by comparing the enterprise value, or EV, to the earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization, or EBITDA.
Why is EV/EBITDA multiple used?
The EV/EBITDA multiple is often used in conjunction with, or instead of, the price-to-earnings, or P/E, ratio. The former is sometimes considered a better valuation tool for potential investors because it is not affected by changes in a company’s capital structure and makes it possible to obtain fair comparisons of companies that have different capital structures. One other advantage of the multiple is it eliminates the effects of noncash expenses that are not typically a major consideration of investors.
What is EV/EBITDA ratio?
The EV/EBITDA ratio is a metric widely used to help investors determine the value of a business. It compares a company’s value, including debt and liabilities, to the its true cash earnings, less noncash expenses. This metric is often used to compare values of companies that operate in the same industry. Lower values can be an indication a company has been undervalued. Generally, analysts interpret any EV/EBITDA value below 10 as positive; however, it is still important to consider the value in relation to EV/EBITDA values of similar firms.
What does it mean when a company's EV/EBITDA is below 10?
Lower values can be an indication a company has been undervalued. Generally, analysts interpret any EV/EBITDA value below 10 as positive; however, it is still important to consider the value in relation to EV/EBITDA values of similar firms.
How to calculate enterprise value?
Enterprise value is calculated as the company's total market capitalization plus debt and preferred shares, minus the company's total cash.
How to calculate EV to EBITDA?
Let’s try to calculate the EV to EBITDA ratio of our example company ABC. There will be three stages of the calculation: 1 Market Cap: To calculate market capitalization, first note down share price (P=1070) and nos of shares outstanding (N=633.93 Cr.). Then multiplying P x N will give the market capitalization. For our example company, the market cap will be Rs.6,78,305 Crore (=1070 x 633.93). 2 EBITDA: Note net profit (PAT), and adding to it the following non-operational expenses: tax, interest, and depreciation will give EBITDA. Our example company has an EBITDA of Rs.62,149 Cr. 3 Enterprise Value (EV): It is calculated by noting the market capitalization and then adding net debt (debt – cash). For our example company, the market cap is Rs.6,78,305, and net debt is Rs.2,21,584 Cr. (=2,30,027-8,443). Hence EV will be 8,99,889 Cr. (=6,78,305+2,21,584).
What is EV multiple?
In this article, we will talk about the EV/EBITDA multiple. It is also known as Enterprise Value (EV) multiple. To get a better understanding of the Enterprise Value, I’ll suggest you kindly read this article.
What is EBITDA in accounting?
EBITDA: Note net profit (PAT), and adding to it the following non-operational expenses: tax, interest, and depreciation will give EBITDA. Our example company has an EBITDA of Rs.62,149 Cr.
Why use EBITDA as a denominator?
EBITDA: The benefit of using EBITDA in the denominator is that it accounts for only operational costs. It is a better representation of the profitability of a business than Net Profit.
How can a company influence the net profit of a company?
It is also possible to influence the net profit of the company by a deferred tax policy. A company may decide to show more net profits than actual by choosing to defer their tax liability in the future. Similarly, net profits can also be lowered by intentionally paying more tax than necessary.
What is the P/E ratio?
P/E ratio mainly estimates the company’s value based on its equity component (shares x market price). While the profit number is estimated by accounting for all operational and non-operation expenses (net profit).
How to calculate market cap?
Market Cap: To calculate market capitalization, first note down share price (P=1070) and nos of shares outstanding (N=633.93 Cr.). Then multiplying P x N will give the market capitalization. For our example company, the market cap will be Rs.6,78,305 Crore (=1070 x 633.93).
What is the EV/EBITDA multiple?
The EV/EBITDA multiple, also known as the enterprise multiple is the ratio between the enterprise value and the EBITDA of a company. The valuation metric compares the debt-included value (the real value) of a company to its cash earnings. Investors and analysts typically use it to compare businesses within the same industry.
What is EV EBITDA?
The EV EBITDA ratio is a valuation multiple between the enterprise value and the EBITDA of a company. It compares the debt-included value (the real value) of a company to its cash earnings, so it is useful when comparing business with varying degrees of financial leverage.
Why is the EV/EBITDA ratio important?
You'll be surprised to learn that, according to James O'Shaughnessy 's research, stocks with a low enterprise multiple widely outperform the market.
How to compare enterprise multiple with earnings yield?
If you want to compare the enterprise multiple with earnings yield (the price to earnings ratio reciprocal), it could be useful to calculate the EBITDA/Enterprise Value ratio (the enterprise multiple reciprocal).
What is EBITDA in valuation?
EBITDA: Earnings before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization, excluding unusual items. It is a commonly used metric in valuation since it gives analysts a clearer picture of operating profitability when comparing companies with different capital structures. It is equal to:
What is the P/E ratio?
The P/E ratio is equal to a company's market capitalization divided by its net income, so it doesn't consider the company's total value and it isn't appropriate to estimate the value of a company with a high level of depreciation and amortization. Note: If you want to compare the enterprise multiple with earnings yield (the PE ratio reciprocal), ...
When is enterprise multiple useful?
The enterprise multiple functions similarly to the P/E ratio, but it is more useful when comparing business with varying degrees of financial leverage and valuing capital-intensive companies with abnormal levels of depreciation and amortization.
How to Calculate EV to EBITDA Multiple?
The Enterprise multiple is calculated by calculating the enterprise value with the help of the following formula, and then the EBITDA is calculated. Then Enterprise value is divided with the EBITDA value to get the Enterprise Multiple .
What is the EV to EBITDA multiple?
The EV to EBITDA multiple consists of Market capitalization, minority interest, preference shares, debts, and the cash is then deducted with the enterprise value, and thus it is an ideal method to do the comparison.
Why is EBITDA calculated?
The EBITDA is calculated to evaluate the company’s financial strength before clearing the dues of the company. The investors can decide by checking the EBITDA value because it is free from any financial and taxation decisions that manipulate the earnings to a greater extent. Start Your Free Investment Banking Course.
Why is higher EV to EBITDA multiple good?
Higher EV to EBITDA multiple is considered good for the company also for the investors because the investors can get maximum return from that company. Investors use this EV to EBITDA multiple to evaluate whether the company is overvalued as compared to the other company in the industry. It also provides a deep understanding of the earnings, ...
What is enterprise value?
The enterprise value consists of market capitalization, all the minority interest, preference shares, etc. , which will form the value of the company and then the value is divided with the EBITDA to get the Enterprise Value to EBITDA multiple.
Which is better, EV or EBITDA?
The expert analysts have proved that the EV to EBITDA Multiple is better than the Price to earnings ratio. The Price to earnings ratio gives the equity multiple, whereas the EV to EBITDA Multiple helps to find out the entire valuation of the company with respect to market capitalization.
Is it risky to invest in EBITDA multiple?
The earnings should be shown and taken into consideration after paying off all the debts and also it has been seen that some big companies have great incidental cost and thus, in that case, if the decision of investing will be made entirely on the Enterprise Value to EBITDA multiple then it can be very risky.
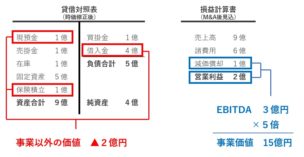
How to Calculate EV/EBITDA Multiple
EV/EBITDA Formula
- The formula for calculating the EV/EBITDA multiple is as follows. The numerator, the enterprise value (EV), calculates the total value of a company’s operations, whereas EBITDA is a widely used proxy for a company’s core (i.e. unlevered) operating cash flows. At their simplest, the two metrics can be calculated using the following formulas: 1. Ente...
How to Interpret Ev to EBITDA Ratio
- Since EV/EBITDA is categorized as an enterprise valuemultiple, you must ensure that both the numerator and denominator represent the same investor groups – which in this case, is ALL investor groups (e.g. common and preferred equity shareholders, debt lenders). In other words, the cash flows must pertain to all providers of capital. For example, interest expensemust NOT b…
Ev to EBITDA Ratio – Industry Benchmarks
- A high EV/EBITDA multiple implies that the company is potentially overvalued, with the reverse being true for a low EV/EBITDA multiple. Generally, the lower the EV-to-EBITDA ratio, the more attractive the company may be as a potential investment. A low EV-to-EBITDA ratio could signal that a stock is potentially undervalued. However, there are no set rules on what determines a lo…
Criticism of Ev to EBITDA Multiple
- For the most part, much of the criticism surrounding the usage of the EV/EBITDA multiple is around the EBITDA metric. To many industry practitioners, EBITDA is not an accurate representation of a company’s true cash flow profile and can be misleading at times, especially for companies that are highly capital intensive. In certain scenarios, adjusted valuation multiple…
Step 1. Operating Assumptions
- In our example exercise, we’ll be assuming three different scenarios for comparability, with the capital intensity of each company as the changing variable. First, let’s begin with the financial data that applies to all companies (i.e. is being kept constant). 1. Enterprise Value (EV):$400m 2. LTM EBIT:$40m For all three companies, the value of the operations is $400m while their operating in…
Step 2. EV/EBITDA Calculation Example
- Using those listed D&A figures, we can add the applicable amount to EBIT to calculate the EBITDA for each company. 1. Company A (Low):EBITDA = $40m + $10m = $50m 2. Company B (Base):EBITDA = $40m + $25m = $65m 3. Company C (High):EBITDA = $40m + $40m = $80m Now, we can calculate the EV/EBITDA multiples for each company on an LTM basis. 1. Compan…
Step 3. Ev to EBITDA Analysis
- So, from our example calculation, we can see just how impactful the non-cash add-back, D&A, can be on the EV/EBITDA valuation multiple of a company. At the EV/EBITlevel, the three companies are all valued at 10.0x, yet the EV/EBITDA multiple shows a different picture. EBITDA is a non-GAAPmeasure, therefore it is imperative to remain consistent in the calculation of EBITDA, as w…
What Is Enterprise Multiple?
- Enterprise multiple, also known as the EV multiple, is a ratio used to determine the value of a company. The enterprise multiple, which is enterprise value divided by earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), looks at a company the way a potential acquirer would by considering the company's debt. What's considered a ...
Formula and Calculation of Enterprise Multiple
- \begin {aligned} &\text {Enterprise Multiple} = \frac { \text {EV} } { \text {EBITDA} } \\ &\textbf {w…
Enterprise multiple, also known as the EV-to-EBITDA multiple, is a ratio used to determine the value of a company. - It is computed by dividing enterprise value by EBITDA.
The enterprise multiple takes into account a company's debt and cash levels in addition to its stock price and relates that value to the firm's cash profitability.
What Enterprise Multiple Can Tell You
- Investors mainly use a company's enterprise multiple to determine whether a company is underv…
An enterprise multiple is useful for transnational comparisons because it ignores the distorting effects of individual countries' taxation policies. It's also used to find attractive takeover candidates since enterprise value includes debt and is a better metric than market capitalizatio… - Enterprise multiples can vary depending on the industry. It is reasonable to expect higher enterpr…
Enterprise value (EV) is a measure of the economic value of a company. It is frequently used to determine the value of the business if it is acquired. It is considered to be a better valuation measure for M&A than a market cap since it includes the debt an acquirer would have to assum…
Example of How to Use Enterprise Multiple
- Dollar General ( DG) generated $3.86 billion in EBITDA for the trailing 12 months (TTM) as of th…
The company's market cap was $56.2 billion as of April 8, 2022. Dollar General's enterprise multiple is 18.2 [ ($56.2 billion + $14.25 billion - $344 million) / $3.86 billion]. At the same time last year, Dollar General's enterprise multiple was 17.4. The increase in the enterprise multiple is larg…
Limitations of Using Enterprise Multiple
- An enterprise multiple is a metric used for finding attractive buyout targets. But, beware of valu…
Investors assume that a stock's past performance is indicative of future returns and when the multiple comes down, they often jump at the opportunity to buy it at a "cheap" value. Knowledge of the industry and company fundamentals can help assess the stock's actual value.