
How do you calculate heat loss from walls and Windows?
Total wall heat loss is determined by adding together the loss from the walls, windows, doors and ceiling: (walls) 321.44 + (window) 273 + (door) 147 + (ceiling) 5,565 = (Total Wall Heat Loss) 6,306.44 BTUH. The total heat loss is arrived at by adding the air infiltration heat loss to this figure:
How to estimate heat loss of a new boiler?
This is to be used as an estimation. A detailed heat loss should be provided before a new boiler is installed. Measure the total length of all outside walls for the house. Calculate gross wall area by multiplying total length by height of the walls. Measure the window and door area. Select proper H.M.
How do you calculate the heat load of a house?
A typical heat load calculation consists of surface heat loss calculation and heat loss due to air infiltration. Both should be done separately for every room in the house, so having a floor plan with dimensions of all walls, floors, ceiling, as well as doors and windows is a good place to start.
What is the formula for heat loss?
The term “heat loss” commonly refers to the thermal transfer of an object to its ambient environment. For example a wall is at a temperature above the ambient temperature. The formula for calculating heat loss of a system through conduction (Fourier's Law), expressed in BTU/hour is: Q =(U)(A)(ΔT) Q = (U) (A) (Δ T)
What is the formula for calculating heat loss?
The general heat loss formula is: Q=U*A*ΔT, or in plain words, the heat loss of an area of size A is determined by the U value of the materials and the difference in temperature between inside and out (that is the difference in temperature of the two surfaces, not the two air temperatures, which might not be quite the ...
How do you calculate heat loss per hour?
Now, heat loss, BTUs per hour, is equal to area times ΔT divided by R-value.
How do you calculate heat loss in a boiler?
Divide the total number of BTUs by the number of heating degree days. The result is a measure of how many BTUs your home lost per Heating-Degree-Day. Now divide that result by 24 to obtain the number of BTUs your home loses per heating-degree-hour.
How do I calculate heat loss in my basement?
For the floor, the average heat loss per square foot is estimated from Table I1 and multiplied by the floor area. The re- sulting two values may then be added together and multiplied by the appro- priate design temperature difference to give the maximum rate of heat loss from that portion of the basement be- low grade.
What is the average heat loss of a house?
Give or take, about 25% of the heat produced by your boiler will escape through the roof of your home. About 35% of the heat will escape through the walls and through gaps, in and around windows and doors, and about 10% of heat will disappear through the floor.
What is heat loss measured in?
BTUsAs mentioned above, heat loss is measured in kWs or BTUs and is a function of heat transfer rates. Heat transfer rates in walls, floors and roofs are measured in U values. The U value is the overall heat transfer co-efficient and indicates how well parts of the building transfer heat.
How do you calculate heat loss through insulated pipes?
Heat Loss from Insulated PipeAir Side Heat Transfer Coefficient, h. AIR ... h_radiation. Heat transfer coefficient due to radiation is calculated using following relation. ... h_convection. Convective heat transfer coefficient comprises of forced and free convection. ... Overall Heat Transfer Coefficient, U. ... Bare Pipe.
How do you calculate heat loss and heat gain?
Heat and Changes of State. The discussion above and the accompanying equation (Q = m•C•∆T) relates the heat gained or lost by an object to the resulting temperature changes of that object.
Can I do my own Manual J calculation?
The Manual J is a very long process, but it gets you very accurate sizing of your space. But if you're only doing a single project, paying for a whole Manual J program can be unnecessarily expensive. Fortunately, you can use a free program called Cool Calc, which will make your heat load calculation much easier.
How do you calculate HVAC load?
To calculate the estimated HVAC load for a house with 2,500 square feet, 12 windows, and 3 exterior doors occupied by 4 people, simply plug it into this formula: 2,500 x 25 = 62,500 base BTU. 4 people x 400 = 1,600. 12 windows x 1,000 = 12,000.
How do I calculate my home heating requirements?
The calculation is as follows:Floor's area: 12*6.5=78 square metres.Volume: 78*3.2=249.6 cubic metres.The value of required thermal power: 249.6*40W=9984 watts.Four windows will add another 400 watts, and two doors will add another 400. ... Since it is a house, we use a heating coefficient of 1.5: 10.784*1.5=16,176 watts.More items...•
How do you calculate heat loss in a garage?
Multiply the area of the garage by the Btu/hr per sq. ft.
How do you calculate heat loss per room?
The formula is: Room volume x Delta T x Air Changes per Hour x . 018.
How do you calculate heat loss per unit length?
0:5215:28Determine the rate of heat loss from the steam per unit length of pipeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd inside temperature is high that is 320. And outside is by degree Celsius. So inside is going toMoreAnd inside temperature is high that is 320. And outside is by degree Celsius. So inside is going to be 1851.
How do you calculate heat loss in joules?
Multiply the change in temperature by the specific heat capacity and the mass of your object. This will give you the heat lost or gained in joules. Example: If 10 kilograms of water are heated from 10 degrees Celsius to 50 degrees Celsius, how much energy (in joules) did they absorb?
How do you calculate heat loss per meter of pipe?
Heat loss from steel pipes at various temperature difference between pipes and ambient air:1 kW (kJ/s) = 102.0 kpm/s = 859.9 kcal/h = 3,413 Btu/h = 1.360 hk = 1.341 hp = 738 ft lb/s = 1,000 J/s = 3.6x106 J/h.1 m (metre) = 3.2808 ft = 39.37 in = 1.0936 yd = 6.214x10-4 mile.
How to calculate heat loss in a wall?
The heat loss in the wall is measured in BTUs and the formula is U value x Wall area x Delta T. In our example, this would be: .07 x 164 x 28 = 321.44 BTUH (British Thermal Units per Hour). This is the amount of heat that is escaping through the exterior walls based on the amount of insulation in them. The other interior surface calculation is for the ceiling. Typical ceiling insulation will be an R-19 which has a U value of .53. This results in a loss of 5,565 BTU per hour.
How to calculate window heat loss?
The formula would look like this: .25 x 21 (3’x7’) x 28 = 147 BTU loss per hour through a single door. A 3’x5’ window with a U value of .65 would lose 273 BTUs per hour.
How many BTU per hour is 6,306.44?
6,306.44 + 6,048 = 12,354.44 BTU per hour loss that must be supplied from the heating system to maintain an interior temperature of 68 degrees.
How to calculate heat loss from air infiltration?
The formula is: Room volume x Delta T x Air Changes per Hour x .018. In our example, we will assume the room is 25 ’x 15’ x 8’ high. This gives us a room volume of 3,000 cubic feet. Plugging this into the formula we see: 3,000 x 28 x 4 x .018 = 6,048 BTUH.
What is floor heating?
Floor heating is the modern heating solution – creating the perfect temperature, making you feel warm and comfortable from the moment you enter the room.
How to prepare for an energy audit?
It is recommended that a contractor or systems designer be utilized for the final audit, however, you can prepare for an energy audit by sealing up the obvious leaks around windows and doors and addressing areas where insulation is needed.
Step 1 – Calculate Delta T (Design Temperature)
Delta T is a difference between indoor design temperature (T1) and outdoor design temperature (T2), where indoor design temperature is typically 68-72F depending on your preference, and outdoor design temperature is a typical low during the heating season.
Step 2 – Calculate surface area
If the calculation is done for an outside wall, with windows and doors, the calculations for the window and door heat loss should be done separately.
Step 5 – Calculate total wall heat loss
Follow the steps 1 through 4 to calculate heat loss separately for windows, doors, and ceiling.
How to find heating degree days?
To determine the heating degree days over the billing period find a weather station near you on degreedays.net and download a spread sheet spanning the dates, sum the dates of the bill, and divide by the fuel use.
What is the worst case for heat loss?
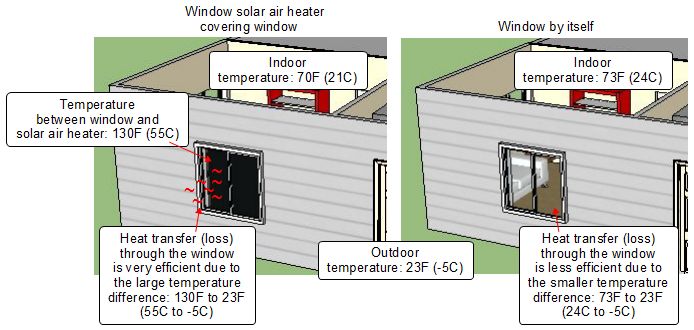
If you’re performing a heat-loss calculation to size heating equipment, you need to perform the calculation for the worst-case condition: namely, the coldest night of the year. (Because the coldest condition usually occurs at night, a heat-loss calculation does not consider solar gain through windows.) The temperature on that night is referred to as the outdoor design temperature. (To be precise, the outdoor design temperature is usually defined as the temperature that is equaled or exceeded for 97.5% of the time during the three coldest months of the year. Other sources define the outdoor design temperature as the temperature that is equaled or exceeded for 99% of the year. As it turns out, most homes will remain comfortable…
What is the 99th percentile of heating design temperature?
If the 99th percentile heating design temp is +7F, that's (65-7=) 58 heating degrees , and the whole house load is about (58 x 650=) 37,700 BTU/hr.
Is 15% oversize on a fuel use calc?
Oversizing the equipment by 15% on a fuel-use calc isn't an efficiency or comfort disaster , even with high-mass boilers, but it tells you just how ridiculously oversized most heating systems are for their actual loads. Oversizing by 15% from Manual-J can sometimes be on the edge not meeting the AFUE tested numbers for cast-iron boilers.
Is shading a heat gain or cooling load factor?
I've yet to meet the heating pro who uses factors in proximity a local lake into a heat load calc. Shading shading is primarily a heat gain/cooling load factor, not a heating load factor. Cooling loads are inherently more difficult to assess without understanding the occupancy duty cycle & plug loads- lots of room for error.
Can a 2 degree delta house be cooled?
It would have to be an awfully big house for a 2 degree delta to add a half ton of cooling load. Cooling loads are driven more by window solar gain, internal heat sorces and air infiltration than outdoor air temperatures. In a related vein, wall insulation R values are relatively inconsequential to cooling loads. Play with a load calc to prove it to yourself.
Can you use historical fuel use data to size a replacement furnace?
It's a useful method; of course, that method can't be used for sizing a furnace for a new home.
What is heat loss?
The term "heat loss" commonly refers to the heat transfer of an object to its ambient environment. This implies that the object in question — a wall, for example — is at a temperature above the ambient temperature (figure 2).
What happens if a pipe is heated?
If enough heat is transferred out of the pipe, the pipe contents may thicken or solidify, resulting in damage to pipes or pumping equipment.
How does heat flow?
Heat flows from one object to another in much the same way as water. Objects of unequal temperatures in a thermal system tend toward thermal equilibrium. The hotter object transfers some of its heat to the colder object until the objects are the same temperature. Heat can be transferred by way of conduction, convection and radiation.
How many BTU is one watt?
Therefore, the equation needs a conversion factor to convert from BTU to watts. One watt equals 3.412 BTU. Modifying the equation yields a new formula:
Can heat loss be ignored?
Therefore, heat loss from radiation can be ignored.
What is heat loss?
The term “heat loss” commonly refers to the thermal transfer of an object to its ambient environment. For example a wall is at a temperature above the ambient temperature. The formula for calculating heat loss of a system through conduction (Fourier's Law), expressed in BTU/hour is:
How much heat loss is in convection?
In most low-to-medium temperature applications, radiation and convection account for about 10% of the heat loss of objects. The formula for calculating heat loss of a system can be calculated by adding in 10%.
What is the transfer of heat through fluids?
Convection is the transfer of heat through fluids (gases or liquids) from a warmer spot to a cooler spot. Place an ice cube in hot coffee and the molecules on top become cooler and dense therefore moving to the bottom.
What are the three types of heat transfer?
Air, water, walls, tanks, and metal are all particles where heat can be transferred or lost. There are 3 types of heat transfer: Conduction, Convection & Radiation which I will cover below. Everything has heat, whether it is hot or cold. It's important to understand the movement of molecules and its relationship to temperature.
Why does an open water tank lose heat?
Open water tanks like plating tanks, di water tanks, hot tubs or swimming pools lose excessive heat due to evaporation. SAVINGS TIP: Cover open water containers with insulation when not in use. The overall heat loss from an open water tank can be expressed as:
How does thermal resistance work?
Thermal resistance (R) is a measure of an object's ability to decrease heat transfer by way of conduction through a given thickness of the substance . Mathematically, R is: Calculating Heat Loss from Industrial Systems to determine heat tracing where L is the insulation thickness in inches, k is thermal conductivity, (BTU) (in)/ (ft2) (oF) (hr) As the thickness (L) changes, it affects the R value, or thermal resistance of an insulation. K values are constants that are specific to the physical properties of a given material. They measure thermal conductivity. Here is the Conduction Formula
How does heat loss occur?
Radiation. Radiant heat loss occurs as a result of highly energized molecules transmitting heat by way of waves or particles. For significant heat loss to occur from radiation, the hotter surface must be well above ambient temperature -- much higher than what is observed in typical heat trace applications. Therefore, heat loss from radiation can be ignored.
How much heat loss is convection?
In practical low-to-medium temperature applications, convection and radiation account for about 10 percent of the overall heat loss of a system. By adding 10 percent, the general formula for calculating the heat loss of a system via conduction, convection and radiation can be calculated.
How is heat transferred?
Heat can be transferred by way of conduction, convection and radiation. Conduction. Conduction is defined as transferring heat or electricity through a conducting medium by way of direct contact. The rate of heat transfer is dependent upon how much resistance exists between objects of differing temperatures.
How does heat flow?
Heat flows from one object to another in much the same way as water. Objects of unequal temperatures in a thermal system tend toward thermal equilibrium. The hotter object transfers some of its heat to the colder object until the objects are the same temperature.
What is heat tracing?
Heat tracing is used to maintain process temperatures for piping that must transport substances that solidify at ambient temperatures, as well as for freeze protection and to maintain process fluids at flow temperature. Both electrically heated and steam-heating tracing is used for industrial thermal processes.
What does K mean in insulation?
As the thickness (L) changes, it affects the R value, or thermal resistance of an insulation. K values are constants that are specific to the physical properties of a given material. They measure a material's ability to transfer heat. Some common K values, as measured at room temperature, of materials are 325.300 for steel, 2750.700 for copper, 0.250 for fiberglass and 0.167 for air.
What is flat surface heat loss?
Flat Surface Heat Loss Calculations. The term “heat loss” commonly refers to the heat transfer of an object to its ambient environment. This implies that the object in question -- a wall, for example -- is at a temperature above the ambient temperature (figure 2). Mathematically, the formula for calculating the heat loss of a system through conduction, expressed in BTU/hour is:
What is the mechanism of heat loss?
The other mechanism of heat loss is convection, or heat loss by air movement. In homes, this is principally heat loss by exfiltration and infiltration. Exfiltration is the loss of heated air through building cracks and other openings. Infiltration is the introduction of outside cold air into the building. This air movement also causes discomfort (drafts) to occupants in addition to the heat loss itself.
Why does heat loss occur in winter?
TEMPERATURE difference between the inside and outside of the building is the primary cause of heat loss in the winter months. The greater this difference, the higher the rate of heat loss. Since most buildings are controlled to a constant inside temperature by the occupants, higher heat loss occurs when it is colder outside. This also means that the annual heating bill can be reduced by lowering the setting on the thermostat …. (but only if the occupants agree to it!)
What is thermal zone?
Thermal Zoning is a method of designing and controlling the HVAC system so that occupied areas can be maintained at a different temperature than unoccupied areas using independent setback thermostats.
What is the heat capacity of air?
The heat capacity of air is a physical constant and is .018 Btu per (°F) (cu. ft.). Considering an outside temperature of -20°F and indoor temperature of 70°F, the heat loss due to infiltration will be:
How to calculate R total?
To calculate the "R Total" value of anything that is composed of multiple different materials, just add up the "R" values of each of the components. For example for composite wall (layered construction), the overall thermal resistance is:
Is heat transfer necessary?
Although it is not necessary to understand the physics of heat movement, it is useful to understand it in general terms. Heat transfer is the tendency of heat or energy to move from a warmer space to a cooler space until both spaces are the same temperature. Obviously the greater the difference in temperatures, the greater will be the heat flow. There are three types of heat transfer: