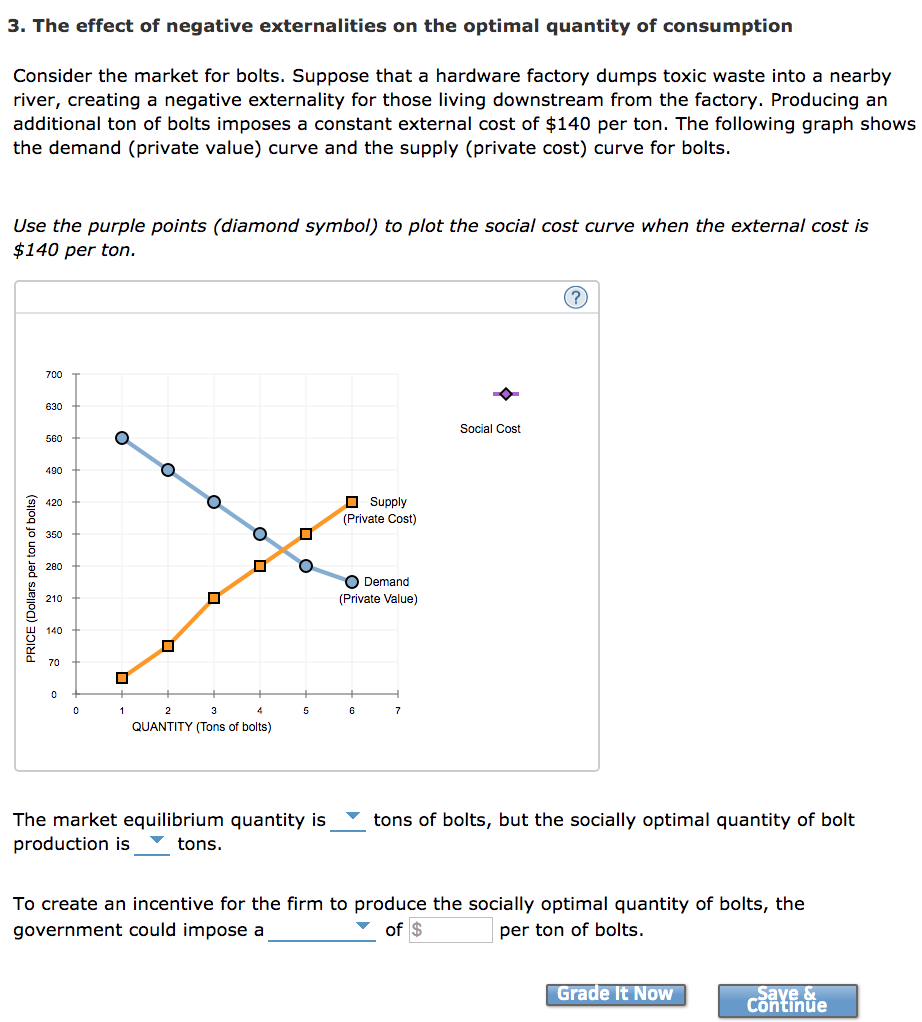
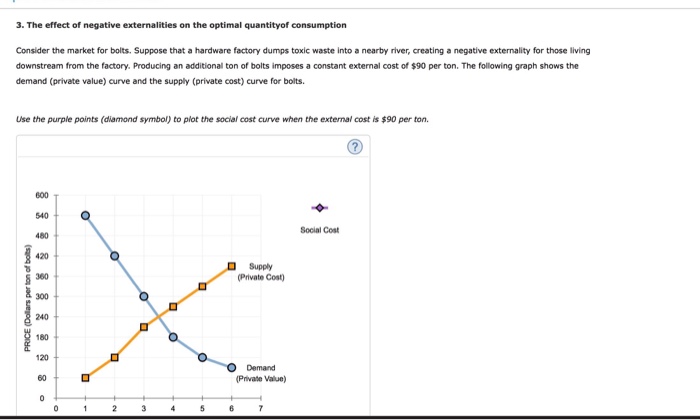
- The market surplus at Q1 is equal to (total private benefits – total private costs), in this case, a+b+e. ...
- The social surplus at Q1 is equal to total social benefits – total social costs. ...
- The market surplus at Q2 is equal to area a+b. ...
- The social surplus at Q2 is equal to area a [(a+b+c) – (b+c)].
What are the consequences of negative externalities?
Implications of negative externalities. If goods or services have negative externalities, then we will get market failure. This is because individuals fail to take into account the costs to other people. To achieve a more socially efficient outcome, the government could try to tax the good with negative externalities.
What are some examples of negative externalities of consumption?
Examples of negative externalities of consumption. Consuming alcohol leads to an increase in drunkenness, increased risk of car accidents and social disorder. Consuming loud music late at night keeps your neighbours awake. Consuming cigarettes causes passive smoking to others in the vacinity.
Who introduced the concept of externalities in the Economics of Welfare?
Arthur Pigou 1920 introduced the concept of externalities in The Economics of Welfare. Pigou used the example of alcohol having external costs, such as creating more demand for police and health care.
How to solve negative externality problem?
Another way to solve the negative externality problem is to simply tax the producer the amount of the negative externality. This adds to the producers marginal cost and will cause them to reduce output.
What is negative externality?
A negative externality occurs when an individual or firm making a decision does not have to pay the full cost of the decision. If a good has a negative externality, then the cost to society is greater than the cost consumer is paying for it.
What are some examples of negative externalities?
These can include decisions that result in costs to other individuals: sitting on the end of a row so that others have to climb over you, littering, painting your house an ugly color in a nice neighborhood, not showering, cutting in line, etc.
Why are negative externalities important?
Since consumers make a decision based on where their marginal cost equals their marginal benefit, and since they don't take into account the cost of the negative externality, negative externalities result in market inefficiencies unless proper action is taken.
What are the methods used to measure externalities?
For measuring externalities, economists may use quantitative methods (cost of damages, cost of control), qualitative methods (qualitative treatment) or hybrid methods (weighting and ranking).
What are the two quantitative methods used by economists to assess externalities?
The two prominent quantitative methods used by economists to assess externalities are cost of damages and cost of control. For example, in the case of an oil spill, the cost of damages method puts a number to the cost of cleanup necessary to clear the pollution and restore the habitat to its original state.
Why do economists use equilibrium models?
An economist may use equilibrium models to succinctly measure externalities as a deadweight loss or gain. This occurs as a result of differences between social and individual marginal cost or benefit curves. However, going from theory to practice creates problems with estimating the effect of externalities since they are sometimes unknown.
Is externality hard to estimate?
Estimating externalities in practice is much harder than in theory since marginal cost and marginal benefit curves are not fully observed very often and since the process of estimating can be met with challenging statistical issues. Sometimes, the full extent of the externalities' effect is not known. The two prominent quantitative methods used by economists to assess externalities are cost of damages and cost of control.
What is the effect of a market exchange on a third party who is outside or “external” to
The effect of a market exchange on a third party who is outside or “external” to the exchange is called an externality. Because externalities that occur in market transactions affect other parties beyond those involved, they are sometimes called spillovers .Externalities can be negative or positive.
What does it mean to leave the market unregulated?
This means that there is an opportunity for government intervention to make society better off.
What is a negative externality?
A negative externality is something that impacts a person or people who are uninvolved in a situation. For example, if you're playing loud music while driving through your neighborhood late at night, you may wake up your neighbors. This can cause them to lose sleep, which might lead to negative health effects.
Types of negative externality
The two primary types of negative externalities are production and consumption, meaning that companies overproduce goods or that consumers overconsume goods. Review these types of negative externalities and how they work:
Negative externality examples
It can be helpful to view examples of negative externalities so you can gain a better understanding of what they look like and how they may impact the community, environment and economy around you. You can review these examples of negative externalities:
Methods for overcoming negative externalities
There are several methods people and the government may employ to help overcome negative externalities that may harmfully affect populations. These methods usually include the following:
What happens if a good has a negative externality?
If a good has a negative externality, without a tax, there will be over-consumption (Q1 where D=S) because people ignore the external costs. 1. Diagram – Taxes on Negative Externalities. A tax should be placed on the good equal to the external marginal cost. It means that consumers will end up paying the full social marginal cost.
Why are negative externalities taxed?
28 July 2019 by Tejvan Pettinger. Taxes on negative externalities are intended to make consumers/producers pay the full social cost of the good. This reduces consumption and creates a more socially efficient outcome. If a good has a negative externality, without a tax, there will be over-consumption ...
What would happen if demand was inelastic?
If demand is inelastic, then higher taxes will not reduce demand much. For example, it is hard to solve the problem of congestion at rush hour, if there are no alternatives to driving. Taxes will cause inequality. A tax on cigarettes takes a higher percentage of income from those on low-income.
Can taxation create unintended consequences?
For example, with a new tax on disposing of rubbish, there has been an increase in fly-tipping (illegal dumping of rubbish) Therefore, taxes can create unintended consequences. May be difficult to decide who is causing pollution.
Negative Production Externalities
Remedies For Negative Externalities
- One of the solutions to negative externalities is to impose taxesto change people’s behavior. The taxes can be imposed to reduce the harmful effects of certain externalities such as air pollution, smoking, and drinking alcohol. An effective tax will equal the cost of the externality, and it is imposed with the goal of discouraging activities that cause such harmful effects. Also, since mos…
More Resources
- Thank you for reading CFI’s guide to Negative Externalities. To keep advancing your career, the additional CFI resources below will be useful: 1. Environmental Liability 2. Greenwashing 3. Network Effect 4. Pigouvian Tax
Measuring Externalities in Theory
Measuring Externalities in Reality
The Bottom Line