
How do you calculate bottom hole pressure?
bottomhole pressure. 1. n. [Drilling] The pressure, usually measured in pounds per square inch (psi), at the bottom of the hole. This pressure may be calculated in a static, fluid-filled wellbore with the equation: BHP = MW * Depth * 0.052. where. BHP is the bottomhole pressure in pounds per square inch.
What is the formula to calculate pressure?
Pressure definition. Our pressure calculator uses the straightforward pressure formula below: p = F / A. where. p is the pressure, F is the force, A is the area of the surface. This pressure definition relates to the force which is applied perpendicularly to the surface of the object. You should remember that pressure is scalar and therefore it ...
What is the normal formation pressure gradient?
FORMATION PRESSURE Dividing this pressure by the true vertical depth gives an average pressure gradient of the formation fluid, normally between 0.433 psi/ft and 0.465 psi/ft.
How should I set the gradient clipping value?
- using a fancy optimizer that can detect directions with a tiny gradient but even smaller curvature. This technique is called the Hessian-free optimization
- not training the connectivity matrix which is the source of the problem (depending on its spectral radius value). ...
- clipping the gradient norm which means make sure at each iteration t
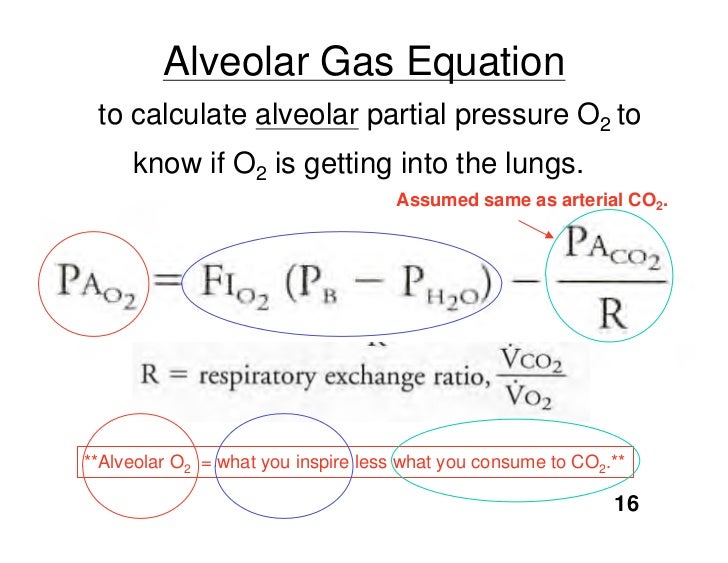
What is the formula of pressure gradient?
Therefore, the pressure gradient is dimensionally represented as [M1 L-2 T-2].
What is the pressure gradient?
A pressure gradient is the rate of change (gradient) of atmospheric (barometric) pressure with regard to horizontal distance at a given point in time. The value is usually expressed in mb per 100 mi. The pressure gradient is a force (P) that acts in a direction from higher toward lower pressure.
How do you calculate pressure gradient on a map?
The pressure gradient is the horizontal change in pressure divided by the horizontal change in distance. On a weather chart, the magnitude of the pressure gradient can be seen by examining the spacing between the contour lines of the map (isobars on the surface map or height contours on the upper air map).
What is pressure and pressure gradient?
Pressure gradient force, is the force produced by differences in barometric pressure between two regions and is responsible for the flow of air from a region of high pressure to a region of low pressure. From: Comprehensive Renewable Energy (Second Edition), 2022.
What is pressure gradient example?
Pressure gradient is how much the atmospheric pressure lowers in an area at a specific time. An example of a pressure gradient is gale force winds turning into a light breeze in a specific city after an hour. The rate of decrease (gradient) of pressure in space at a fixed time.
What are the units for a pressure gradient?
The pressure gradient is a dimensional quantity expressed in units of pascals per metre (Pa/m).
How do you calculate pressure gradient across isobars?
The horizontal pressure gradient force ph= Δp / pΔx, where Δpis the horizontal pressure difference over the distance Δx. The direction of this force and of the pressure difference measurement is locally perpendicular to the lines of equal pressure (isobars) and is directed from high to low pressure.
Is pressure gradient the same as pressure difference?
The pressure gradient force is the force produced when air with different pressures are placed next to each other. Pressure differences occur in the atmosphere due to differences in the density of air.
Is pressure gradient change in pressure?
In terms of the Pressure Gradient Force the gradient is the change in pressure from areas of higher pressure into areas of lower pressure. The more difference between the high and low pressure the stronger the pressure gradient will be resulting in stronger winds.
What is a pressure gradient quizlet?
pressure gradient. the difference between high and low pressure areas. strongest winds.
What is pressure gradient Class 11?
Pressure gradient helps to determine the direction in which pressure increases most rapidly from a location. The pressure gradient can be measured by finding the difference in pressure between two locations and dividing the difference by the distance between the two locations.
What does pressure gradient mean Class 9?
(a) Pressure Gradient — It is the rate of change of atmospheric pressure between two points on the earth's surface. (b) Winds — Horizontal movements of the air from high pressure to low pressure areas are called winds.
What causes a pressure gradient?
The force actually responsible for causing the movement of air though is the pressure gradient force. Differences in air pressure and the pressure gradient force are caused by the unequal heating of the Earth's surface when incoming solar radiation concentrates at the equator.
How much pressure does a gradient of 0.425 psi/ft at 2000 ft.?
From the previous example, a gradient of 0.425 psi/ft at 2000 ft. resulted in 850 psi pressure.
How to find pressure at a given depth?
To find a pressure at a given depth, simply multiply the VERTICAL depth by the given fluid gradient.
What is the density of pure water?
The density of pure water is 1000 kg/m3. To convert to gradient:
Do you need to calculate specific gravity?
Most of the time you will not be given a fluid gradient or an average specific gravity, you will need to calculate it.
Can we calculate the equivalent fluid column if we know the pressure and the gradient?
Similarly, if we know the pressure and the gradient, we can calculate the equivalent fluid column resulting from that pressure.
The Bernoulli principle and pressure gradients using Doppler measurements
Continuous wave Doppler and pulsed wave Doppler can measure the velocity of erythrocytes as they travel through the heart and vessels. The velocity of erythrocytes ( i.e blood) can be used to estimate pressure gradients (pressure differences) between the atria, ventricles, and connecting vessels.
Disadvantages of the Bernoulli equation
The Bernoulli equation is highly dependent on the precision of the Doppler measurement. The Doppler beam must be parallel to the direction of the blood flow (refer to The Doppler Equation ). Any angle error between the Doppler beam and the blood flow will result in an underestimation of the velocity.
What is the pressure gradient?
The pressure gradient can also be viewed as the pressure drop (i.e., energy loss) that results from a given flow and resistance (i.e., ΔP is the dependent variable), where ΔP=F x R. In other words, ΔP is increased by either an increase in flow or resistance.
How to tell if pressure gradient is dependent or independent?
The pressure gradient can be viewed as the force driving flow ( F), where F = ΔP/R. This relationship is based upon Ohm's Law from physics in which current equals the voltage difference divided by the resistance (I= ΔV/R). Flow is decreased, for example, if there is a decrease in ΔP or an increase in R as shown in the figure below. In this example, ΔP is an independent variable whereas flow is the dependent variable.
Why is the pressure gradient in a valve small?
In contrast, with vascular or valvular stenosis the pressure gradient is increased because of the increased resistance to flow (e.g., by decreased vessel radius or valve cross-sectional area).
What are the factors that determine resistance?
The most important factor, quantitatively and functionally, is the radius of the vessel, or in the case of a heart valve, the orifice area of the opened valve. Resistance is inversely related to the fourth power of the radius (r 4) of a blood vessel.
What happens when stenotic flow increases?
Furthermore, as flow increases across the stenotic lesion (e.g., when cardiac output increases during exercise), the pressure gradient (ΔP) increases further. Increased flow across a heart valve, particularly when it is stenotic, causes a a large increase in velocity that can lead to a significant degree of turbulence, ...
How does this A-a gradient calculator work?
This tool assesses the alveolar - arterial gradient and determines the possible existence and the source of hypoxemia. This gradient is the difference between the alveolar concentration of oxygen and the arterial concentration of oxygen. For your convenience, you can input the pressures required in either mmHg or kPa. The following lines are a guide to how you should use this A-a gradient calculator:
What is the normal range for a pulmonary gradient?
- The normal range is between 5 to 20 mmHg up to middle age and increases as we get older in a rhythm of 1 mmHg for every decade.#N#- It is used to determine whether the source of hypoxemia is intra or extra pulmonary.#N#- A normal gradient accompanied by hypoxemia (low P a O 2) indicates hypoventilation by decreased respiratory drive or neuromuscular impairment or the possibility of a low fraction of oxygen inspired.#N#- The gradient is elevated when the alveolar function is impaired and ventilation issues appear such as in pulmonary embolism or right to left shunt.#N#- An elevated gradient accompanied by hypoxemia indicates V/Q mismatch – ventilation perfusion imbalance that is met in respiratory diseases such as asthma or COPD) or a cardiac right to left shunt, intraalveolar filling such as that in pulmonary edema.