How do you calculate workload?
- Choose the output you're measuring.
- Select a period of time to measure.
- Measure the amount of output over this time period for each of your employees.
- Now you need an input figure.
- Divide the output by the input to arrive at a per-hour figure (or other time period).
How to easily calculate work hours?
Time Card Calculator. Use this free timesheet calculator to easily produce a work hours timesheet for any given week. You can then use the resulting time card for payroll purposes. Times are calculated in hours and minutes (e.g 42:30), as well as in decimal notation (42.5 hours). The time card calculator supports lunch breaks.
How to measure workload in the organization?
- All outcomes need to be precisely defined and clearly prioritized. Often, when an organization implements a new initiative, it will state myriad outcomes that it hopes will occur. ...
- When an outcome changes, is it clearly good or bad? This seems straightforward, but in fact things can get quite tricky. ...
- Be aware of unintended consequences. ...
How do you calculate work Index from workload factor?
- T = Temperature in Celsius
- Tg = Globe Thermometer Temperature (in Celsius) - this is measured by a thermometer placed in a special black globe to estimate solar radiation without the effects of the light ...
- Tw = Wet-bulb Temperature (in Celsius)
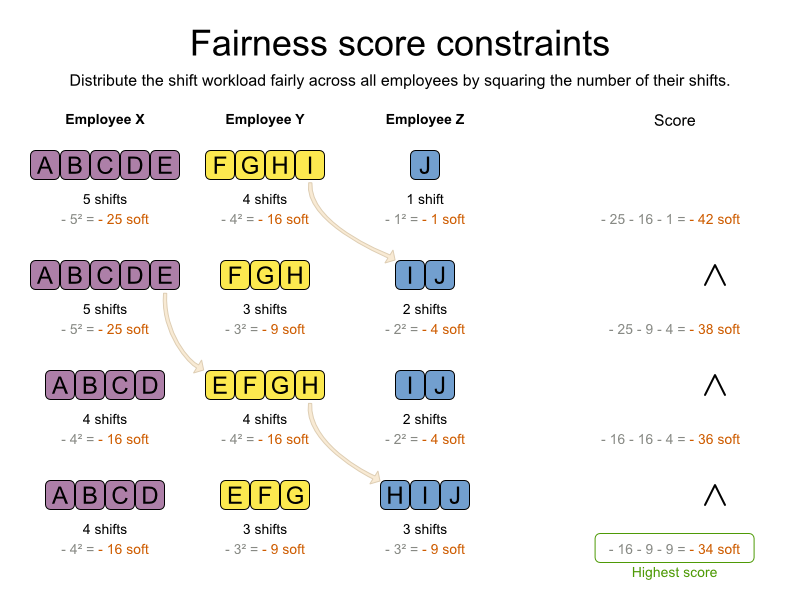
How to divide the workload?
- Be overly rigid about your workload delegation strategy; when projects crop up and priorities shift, you need to be flexible.
- Burn out your top performer. Before you lean on her more, identify the projects that can go on the backburner.
- Beat around the bush with an employee who’s not pulling his weight. Be direct about your expectations.

How do you measure employee workload?
Tips for effective workload managementTake time for planning. ... Get to know your resource availability. ... Estimate tasks and set achievable deadlines. ... Allocate tasks fairly and evenly. ... Split tasks into subtasks & make to-do lists. ... Plan your capacity. ... Draw task dependencies. ... Measure utilization rates.More items...•
How do you do a workload analysis?
Here are several top tips for conducting workload analysis:Assess Each Team's Task and Capability. ... List Individual Workload and Divide the Resources. ... Be Communicative and Flexible about Workload. ... Calculate the Team's Average Outputs. ... Evaluate the Team Structure. ... Use Management Tools. ... Automated Data Entry. ... Issue tracker.More items...
What is standard workload?
Commonly referred to as the SWF (pronounced “swiff”), the Standard Workload Formula is a standardized and objective way to assign, measure, and monitor the workload of academic staff. All aspects of workload monitoring and assignment are covered by Article 11 of the Academic Collective Agreement.
What is workload work?
Workload is the amount of work an individual has to do. There is a distinction between the actual amount of work and the individual's perception of the workload. Workload can also be classified as quantitative (the amount of work to be done) or qualitative (the difficulty of the work).
What is workload capacity?
Workload capacity: ability of our cognitive processing mechanisms to respond to the changes in task demands that influence the workload. These include changes to the number of subtasks within a task, items in a visual or memory search display, and manipulated features in a visual processing task.
What is HR workload analysis?
Workload Analysis is a method used to determine the time, effort, and resources needed by an organization in identifying the actual needs of Human Resources (HR) in quality and quantity in accordance with the goals and strategies of the organization.
How do you calculate aggregate workload?
For example, to find the aggregate workload on workstation A, we would take the demand for product X (50/week) and multiply it by the number of units that each unit of product X requires on workstation A (20 units) to get the total amount of capacity per week that product X requires of workstation A.
How is faculty workload calculated?
Faculty workload is calculated by assigning values to lectures and labs separately. Values are also assigned to courses based on the number of students enrolled. FTE is based on credit contact hours taught, (L or B), or number of students enrolled, (N, S, A, or R).
How do you calculate workload in a call center?
Calculating Workload It's simply the number of forecast calls for an hour multiplied by the average handle time of a call.
What is the example of workload?
Term used to describe a collection of things that need to be done. For example, a person may have a high workload, meaning they have a long to-do list. Another example is a server with many tasks to be processed, usually due to a high volume of traffic.
What is included in workload?
Definition of workload 1 : the amount of work or of working time expected or assigned students with a heavy workload. 2 : the amount of work performed or capable of being performed (as by a mechanical device) usually within a specific period.
What is the current workload?
Current Workload means the absorptive capacity of the Applicant to do additional works other than those currently undertaken.
How to calculate basic workload?
The formula: task x time (to perform task) x frequency = basic workload. This is a fairly simple way to calculate the basic workload of most facilities.
What are the three variables that determine the workload of a cleaning company?
When calculating workload, consider three important variables: task, time and frequency of labor. By formulating workload based on these principles, cleaning managers can better track and improve cleaning efficiency.
How to calculate target intensity?
Target intensity using this method is calculated by the VO2R formula: Target VO2 = (intensity fraction) (VO2peak – VO2rest) + VO2rest. The next step in accurate and valid exercise prescriptions for these patients is to accurately measure resting VO2 as well as VO2peak.
How to find power?
To find power, divide the amount of work by the time it takes to do the work. Remember that work is measured in joules. Power is often measured in joules of work per second. The unit of measurement for power is the (W).
How many hours can an employee work in a week?
There is no law on the books that says what constitutes full-time work. Only that 40 hours per week is the maximum an employee can work before they stray into overtime territory. This provides a lot of flexibility to the employer, who can set up a work schedule that benefits both the employee and the business.
When did the federal government start limiting how many hours an employee can work?
In 1940, the federal government passed the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) to set limits on how many hours employees could work each week.
How many hours can a business work full time?
Some businesses, though, have adopted lower numbers like 36, 32, and even 30 hours per week as full-time. There is no law on the books that says what constitutes full-time work.
Why is time worked required by the IRS?
The record of time worked can also be demanded and referenced by the IRS to ensure compliance with local, state, and federal labor laws. Because of this, it’s essential that you do your best to keep accurate records.
How many hours can you work part time?
If you set 40 hours as full-time, part-time is simply any number less than that. You could set it as 20 hours, 24 hours, all the way up to 39 hours.
How many hours does a SWF work?
Each of these factors are represented on a weekly basis, which total up and provide the total number of workload hours per week. A faculty member may work up to 44 hours per week.
What is attributed hours for preparation?
Attributed Hours for Preparation represent the number of hours spent preparing for classroom activities. This calculation is based on how many times the faculty member has taught the course in the past, how many sections they are teaching at once, etc. Please see Table 1 below for the ratios of TCHs to Prep Hours. As you can see, the more experienced a teacher is at delivering a specific course, the fewer hours they will receive for preparation. Table 2 provides definitions of each of the Prep Factors.
How many hours are attributed to complementary functions?
The standard allotment for all faculty members is six hours per week, but this may be increased depending on additional tasks assigned by the manager, e.g. coordinator’s duties.
How many hours per week is a faculty member required to work?
It also means that no faculty member’s workload will exceed 47 hours per week, regardless of voluntary agreements.
How to calculate hours worked?
Follow these steps to calculate worked hours: 1. Determine the start and the end time. If you're using a manual method, like a physical timesheet, you'll need to determine the times your team members clocked in and out each day of the pay period. Example: An employee started working at 7:45 a.m. and finished at 5 p.m.
How to find total hours?
To find the total hours, subtract the time the employee clocked in from when they clocked out. Example: 17 - 7.75 = 9.25. 5. Subtract the unpaid time taken for breaks. You may need to subtract time when an employee takes an unpaid break, such as going to a doctor's appointment.
What is the maximum amount of hours an employee can work in a certain period?
Full time is the maximum time an employee can work in a certain period. The Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) is a federal regulation that sets an upper limit on the number of hours employees can work every week. The FLSA states the maximum amount that employees can work per week is 40 hours, and additional hours are considered overtime.
How many hours can you work in FLSA?
The FLSA states the maximum amount that employees can work per week is 40 hours, and additional hours are considered overtime. Employers can set different amounts for full time as long as it doesn't exceed 40 hours per week. For example, a company could consider 32 hours per week full time for its employees.
What is workload measurement?
Some workload measurement techniques focus on objectively measuring aspects of the operators’ performance. Performance measures of workload all have a common characteristic: they consider only the task being performed or the work being produced by the human operator.
How many approaches to workload measurement have been proposed?
Four basic approaches to measuring workload have been proposed. We will overview each of these basic approaches, review their advantages and disadvantages, and demonstrate the use of a particular workload measurement technique that uses each approach.
What is workload directed research?
The workload directed research project surveyed the available literature on: workload measurement techniques; and, the effects of workload on operator performance. Two sets of findings were generated. The first set provided practitioners with a collection of simple-to-use workload measurement techniques along with characterizations of the kinds of tasks each technique has been shown reliably to address. The second set provided practitioners with the guidance needed to design for appropriate kinds and amounts of workload across all tasks for which the operator is responsible. The criterion for inclusion into the EndNote™ reference list database limited the articles to those that were peer reviewed, long standing and accepted in the field, applicable to a relevant range of conditions in a select domain of interest, with parallels being drawn in an attempt to identify analogous “extreme” environments to those in space. Research points towards no one, single approach to determine the suitability of workload in various operational contexts. Different workload evaluations are needed at different phases of the development cycle. The Workload toolbox and the Primer can assist in the selection decision of how and when to use a select set of workload measurement tools.
How does workload affect human performance?
Humans who are overburdened with work tend to hurry their performance, commit more errors, yield poor accuracy, become frustrated, uncomfortable, and fatigued, and have poor awareness of their surroundings. Interestingly, humans who are underworked can exhibit many of the same symptoms. Low workload has been linked to high error rates, frustration, fatigue, and poor awareness of surroundings as they become bored, as their attention drifts, and as complacency sets in. From all we have learned, it seems that humans do their best when their skills are exercised and their abilities challenged, are neither bored nor overburdened, and when periods of work and rest are equitably mixed together.
What are some practical questions to ask about workload?
The most practical questions to ask and answer about workload are those that involve comparing the workload experienced by humans when performing several different tasks. In this way, the biases and limitations that apply when measuring workload for one task consistent ly apply to all tasks that are being compared .
Why is it important to compare workloads?
Because of the limitations inherent in all workload measurement techniques, a more practical goal in assessing workload might be to compare the workload measures obtained for one task or design with those obtained for other tasks and designs. The reason for this is simple: even if operators think differently about workload, have different skill levels, use different strategies, load onto scales differently, or experience different physiological responses, it is likely that they will carry these same differences from task to task and design to design. For example, if an operator consistently provides an average workload rating of 60 for Task A and an average workload rating of 40 for Task B, then we are on more solid ground in concluding that operator is experiencing higher workload on Task A. There is a long history of using a single workload measurement technique for making these kinds of workload assessments and design decisions based on them.
Is there a workload measurement scale?
There is no workload measurement scale or technique that offers the same reliability as the scales used to measure height, weight, pressure, or other physical quantities. Similarly, our efforts to rigorously quantify the point at which human operators reach their workload “boiling point” fall far short of those that quantify similarly important states of physical matter.
How to create a workload plan?
For a workload plan, you must first know your resources and the business priorities to map teams against needs, which is a constantly reviewed and adjustable process. You should have a resource management software that identifies the team’s availability and hours, then analyze the work being done. Use this data to create a workload plan for the future to optimize productivity and balance workload across your entire team. You can use a project management software equipped with workload management tools to help you with this process.
What Is Workload Management?
Workload management is the process of assigning tasks to keep the team working while monitoring their progress over the course of the project. It provides a framework of what tasks need to be done and who on the team is supposed to be working on those tasks.
What is a workload tracker?
A workload tracker will give you the information you need to help you answer these questions. The better you know the strengths and work patterns of your team the easier it will be to figure out how to improve productivity and interpret what your timesheet system is telling you.
How to find out who is working on which tasks?
The fastest way to find the answer is to use task management, capacity planning, or resource management features from your project management software to show you who is working on which tasks. In ProjectManager.com you’ll find that on the Workload management tool tab.
Why is workload management important?
Workload management should be a priority for project managers because it overlaps with other important project management processes such as capacity planning, task management and project scheduling. Managing your team’s workload can be overwhelming, especially in big projects, but you can use workload management software to help you keep track of all your employees.
Why is it important to plan for workload?
Workload planning is a way to keep your teams busy and productive. It’s a strategic way to distribute the work throughout your team. This boosts performance. Planning workload isn’t only about getting the job done, but reducing team stress, burnout and errors.
How to manage your team's workload?
You can manage your team’s workload better if you know when they are going to be around. Talk to them about upcoming holidays and include those in your workload planning so you don’t assign them work while they are away. Equally, check in with your team to make sure your knowledge of their skills is up-to-date.
How to use observation and estimate?
I prefer observation for those frequently occurring tasks, such as daily maintenance, as it gives you a more accurate value and can help better familiarize yourself with the task (s). Estimates are typically used with tasks that happen infrequently or are sporadic. You can also blend observation with estimation by having staff members perform self-observation. Provide staff with a data-collection sheet and have them record what task (s) they were performing and how long it took. You may not get many timings, but it will influence your estimates to a more accurate value. A side benefit is it may also catch a few tasks you may have missed.
What is direct effort bucketed into?
At a high level, direct effort can be bucketed into pre-analytic, analytic, and post-analytic tasks. In our example, all eight tests are instrument based, so once the test is loaded on the instrument, it is hands off.
