
Head of Clinical Department: Neurology, Universitas Academic Hospital, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein, South Africa.
- Step 1. Check ocular alignment using a torch Check the alignment of the eyes. This is performed by comparing the light reflex from the cornea of both eyes. Hold a torch 1 metre in front of the eyes and look for the light reflex on the cornea (Hirschberg test). ...
- Step 2. Check for abnormal head posture
What tests are done to check ocular alignment?
There are different tests to perform to check ocular alignment. A cover test will be performed as an evaluation for ocular misalignment or strabismus. The cover test will be performed by asking the patient to seat at a fixed distance while wearing their best correction for refractive error.
How do you test for occlusion?
This test involves covering one eye and holding the occluder for several seconds to suspend fusion, then shifting the occluder to the other eye and rapidly alternating back and forth without allowing the patient to become binocular and being careful to always keep one eye occluded.
What is a cover test for eyes?
The cover test is a test done on most patients during an eye exam to test the alignment of their eyes. It takes about 10 seconds to do. Thanks to Dr. Kaise... The cover test is a test done on most patients during an eye exam to test the alignment of their eyes. It takes about 10 seconds to do.
What are eye alignment problems?
Eye alignment problems can vary from crossed eyes, misaligned eyes, or wall eyes. In order to fully understand what eye alignment problems are, we need to begin by properly defining the term.
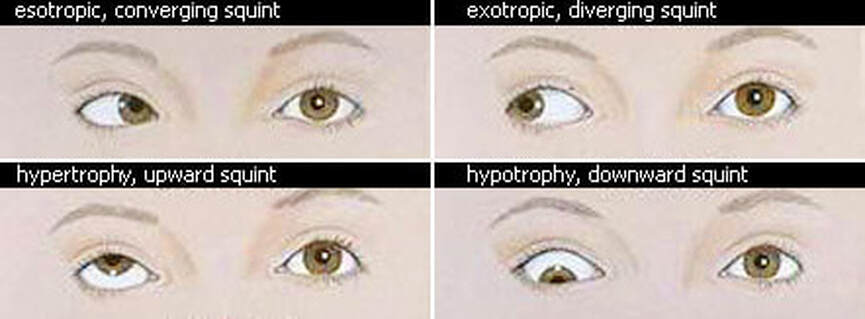
Why is it important to assess ocular alignment?
People wonder what is the importance of assessing ocular alignment. The assessment is essential to know if there are problems such as crossed eyes or misaligned eyes. Early detection is important so it can be corrected as early as possible. There are different tests to perform to check ocular alignment.
Which eye is preferred in the setting of a heterotropia?
The uncovered eye is the preferred eye in the setting of a heterotropia.
How does an alternate cover test work?
The alternate cover test measures the full deviation which brings out any phoria present in addition to the tropia that is determined in the single cover test by suspending binocular fusion. The test is usually performed after a single cover test. The test covers one eye and holding the occluder for several seconds and then shifts it to the other eye. Rapid alternation is done back and forth without making the patient binocular.
What is a cover test?
A cover test will be performed as an evaluation for ocular misalignment or strabismus. The cover test will be performed by asking the patient to seat at a fixed distance while wearing their best correction for refractive error. The patient needs to place their head in a straight position. Ask the patient to avoid tilting or turning their head around.
Why do my eyes point in different directions?
However, the eyes of someone with strabismus may point in different directions. This could be due to family history, a refractive error, or other medical conditions.
What does it mean when your eyes are crossed?
No one in the medical world will diagnose a patient with crossed eyes as having an eye alignment problem. Instead, they might say that you have a condition called strabismus. Strabismus is a condition in which both eyes do not look at the same place at the same time, usually developed in infants and young children.
Why do young adults have one eye vision impairment?
As previously mentioned, it is caused by any condition that renders the eyes ability to focus properly. Typically, it is developed due to strabismus that has not been diagnosed in children.
What is the difference between lazy eye and crossed eye?
For example, crossed eyes is commonly referred to as strabismus, while a lazy eye is medically referred to as amblyopia. As such, we must learn the definition of both ...
Can glasses help with strabismus?
Prescribed glasses are usually adequate enough to treat strabismus in children. If the case of strabismus has developed into amblyopia, further treatment is required. Amblyopia is treated by placing a patch over the better eye to train the brain to use the weaker eye.
How to perform cover test for ocular misalignment?
The following is a brief instructional video tutorial on the appropriate method to perform a cover test in the evaluation of a patient for ocular misalignment or strabismus. The patient should be seated and asked to fixate at distance on an accommodative target. The patient should be wearing their best correction for their refractive error. If the patient is adopting an alternate head position such as a chin up, chin down, face turn or head tilt, they should be placed into a forced primary or straight head position.
What does it mean when your eye shifts out?
If the unoccluded eye shifts out, or laterally, in a nasal to temporal fashion when the opposite eye is occluded – this means that there is an esotropia. If the unoccluded eye shifts down when the opposite eye is occluded – this means that there is a hypertropia. If the unoccluded eye shifts up when the opposite eye is occluded – this means ...
How to determine angle of deviation?
The full angle of deviation can be determined by performing an alternate prism cover test. This test is performed by placing prism of varying strength that is oriented in the appropriate direction for the deviation over the non-fixating eye while performing the alternate cover test until there is no longer a shift in fixation in either eye. This is when the deviation has been neutralized. For an eso deviation, a base out prism should be used. For an exo deviation, a base in prism should be used. For a hyper deviation, a base down prism should be used. For a hypo deviation, a base up prism should be used. Horizontal prism and vertical prisms can be stacked over the same eye, but two prisms that are oriented in the same direction cannot be used over the same eye. This test can be performed in all 9 cardinal gaze positions and head tilts if the clinical situation dictates. This is done by adjusting the patient's head position while asking them to maintain fixation on the distance accommodative target. This same test can also be performed at near, by having the patient fixate on an accomodative near target. Again, making sure they are in their best correction for near.
How to determine if a patient has vertical deviation?
The Parks-Bielschowski 3-step test is a helpful test in determining the etiology of a vertical deviation with or without any horizontal deviation. This test is performed in a similar fashion as the alternate prism cover test. The deviation is first measured in primary gaze. The deviation is then measured in both lateral gazes by turning the patient's head the left while maintaining fixation on the same target to simulate right gaze and similarly with the head turned to the right to simulate left gaze. The deviation is then measured with the face pointed straight ahead, but the head tilted to both the right and left.
What is the eye under the occluder?
The eye under the occluder is observed as the occluder is removed and placed over the fellow eye in order to determine the direction of deviation. If there is an outward, or lateral, refixation in the nasal to temporal direction – this represents an eso deviation. If there is an inward, or medial, refixation in a temporal to nasal fashion – this ...
