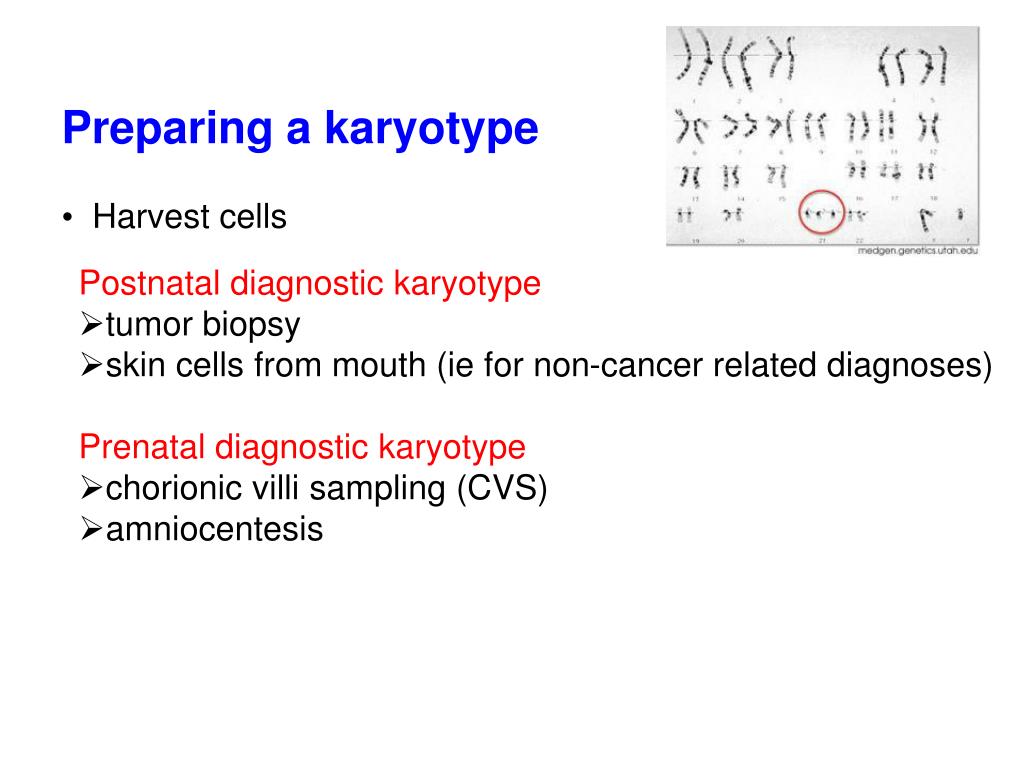
The test is performed by:
- Taking a sample of a person’s cells, culturing them in nutrient-enriched media to promote cell division in vitro. ...
- Isolating the chromosomes from the nucleus of the cells, placing them on a slide, and treating them with a special stain.
- Taking microphotographs of the chromosomes.
What is the most common chromosomal abnormality?
Types chromosomal syndromes
- 1- Turner syndrome or monosomy X. ...
- 2- Patau's syndrome. ...
- 3 - Down Syndrome or Trisomy 21. ...
- Edward's Syndrome. ...
- 5- Fragile X syndrome. ...
- 6- Cri's syndrome Du chat o 5 p. ...
- 7- Wolf Hirschhorn Syndrome. ...
- 8- Klinefelter syndrome or 47 XXY. ...
- 9- Robinow's syndrome. ...
- 10- Double Y syndrome, XYY. ...
Is crossing over a chromosomal abnormality?
Translocation is a chromosomal abnormality. Crossing over is not a chromosomal abnormality. Genetic recombination results in genetic variation among the individuals. It occurs due to various reasons. Crossing over and translocation is two processes which cause genetic variations.
Which chromosomal mutation results in Alagille syndrome?
In more than 90 percent of cases, mutations in the JAG1 gene cause Alagille syndrome. Another 7 percent of individuals with Alagille syndrome have small deletions of genetic material on chromosome 20 that include the JAG1 gene. A few people with Alagille syndrome have mutations in a different gene, called NOTCH2.
Is Turner syndrome a chromosomal abnormality?
Turner syndrome is due to a chromosomal abnormality in which all or part of one of the X chromosomes is missing or altered. While most people have 46 chromosomes, people with TS usually have 45 in some or all cells. The chromosomal abnormality is often present in just some cells, in which case it is known as TS with mosaicism.
How early can you detect chromosomal abnormalities?
The earliest you can have tests for chromosomal anomalies is about 10-12 weeks of pregnancy. These different kinds of tests can be screening tests or diagnostic tests. Antenatal screening tests work out the chance or risk of your baby having certain chromosomal anomalies or other conditions that can cause disability.
How do they test for chromosomal abnormalities in pregnancy?
The maternal blood screen is a simple blood test. It measures the levels of two proteins, human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) and pregnancy associated plasma protein A (PAPP-A). If the protein levels are abnormally high or low, there could be a chromosomal disorder in the baby.
What are three tests used to detect chromosomal abnormalities?
Diagnostic Tests. Amniocentesis, chorionic villus sampling (CVS) and ultrasound are the three primary procedures for diagnostic testing. Amniocentesis — Amniocentesis is used most commonly to identify chromosomal problems such as Down syndrome.
Can you see chromosomal abnormalities on ultrasound?
Abstract. The use of prenatal ultrasound has proven efficacious for the prenatal diagnosis of chromosomal abnormalities. The first sonographic sign of Down syndrome, the thickened nuchal fold, was first described in 1985.
Who is at high risk for chromosomal abnormalities?
A woman age 35 years or older is at higher risk of having a baby with a chromosomal abnormality. This is because errors in meiosis may be more likely to happen as a result of the aging process. Women are born with all of their eggs already in their ovaries. The eggs begin to mature during puberty.
What are the 4 main causes of birth defects?
Researchers think that most birth defects are caused by a complex mix of factors, which can include:Genetics. ... Chromosomal problems. ... Exposures to medicines, chemicals, or other toxic substances. ... Infections during pregnancy. ... Lack of certain nutrients.
How can you prevent chromosomal abnormalities during pregnancy?
Taking a daily prenatal vitamin that contains 400 micrograms of folic acid for three months before becoming pregnant. Eating a healthful diet that contains foods that have folic acid, such as breakfast cereals, grain products, leafy greens, oranges and orange juice, and peanuts. Reaching or maintaining a healthy weight.
What are the chances of having a baby with chromosomal abnormalities?
What are the chances of your baby having a chromosomal condition? As you get older, there's a greater chance of having a baby with certain chromosomal conditions, like Down syndrome. For example, at age 35, your chances of having a baby with a chromosomal condition are 1 in 192. At age 40, your chances are 1 in 66.
Can you have a healthy pregnant after chromosomal abnormalities?
While parents who carry chromosomal rearrangements are at increased risk to have further miscarriages or babies born with health problems, they can also produce healthy children.
How accurate is 12 week scan for Down's syndrome?
12-Week Screening Test Accuracy The first-trimester screening's detection rate is approximately 96% for pregnancies in which the baby has Down syndrome and is somewhat higher for pregnancies with trisomy 13 or trisomy 18.
What are the most common chromosomal abnormalities?
Some of the most common chromosomal abnormalities include:Down's syndrome or trisomy 21.Edward's syndrome or trisomy 18.Patau syndrome or trisomy 13.Cri du chat syndrome or 5p minus syndrome (partial deletion of short arm of chromosome 5)Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome or deletion 4p syndrome.More items...
What is more accurate a blood test or ultrasound for gender?
Expectant mothers can determine the sex of their babies by undergoing an ultrasound test. Most pregnant women use this method as it gives a more accurate result. In addition, specialists, such as sonographers, radiologists, and obstetricians, perform the test making it safer compared to other baby gender test options.
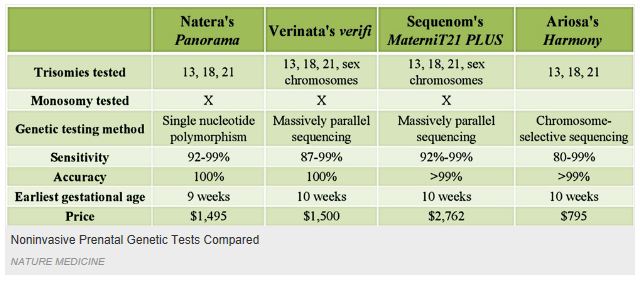
How accurate are blood tests for chromosomal abnormalities?
The test will detect about 93 percent of Down's syndrome cases with a 5 percent false positive rate. It also screens for other chromosome abnormalities and can sometimes detect pregnancies at high risk for complications such as poor growth later in pregnancy.
How can you prevent chromosomal abnormalities during pregnancy?
Taking a daily prenatal vitamin that contains 400 micrograms of folic acid for three months before becoming pregnant. Eating a healthful diet that contains foods that have folic acid, such as breakfast cereals, grain products, leafy greens, oranges and orange juice, and peanuts. Reaching or maintaining a healthy weight.
What is the most accurate screening test for chromosomal abnormalities?
The most accurate is Sequential Integrated Screening test. This test is actually three separate tests integrated to give you a result for fetal chromosomal risk.
What is the best diagnostic test for chromosomal abnormalities?
Chorionic Villus Sampling ( CVS ) and amniocentesis are both diagnostic tests that can confirm whether or not a baby has a chromosome abnormality.
What Are Chromosomal Abnormalities?
Chromosomal abnormalities are differences in the chromosomes that can happen during development. They could be "de novo" (unique to the fetus) or inherited from a parent. Abnormalities are split into two categories: numerical and structural. 3
What is a molar pregnancy?
Molar Pregnancy. In other cases, a chromosomal abnormality may lead to a rare condition called a molar pregnancy. During a molar pregnancy, tissues that were meant to form into a fetus instead become an abnormal growth on the uterus. There are two types of molar pregnancy: 14.
What are the complications of chromosomal abnormalities?
Chromosomal abnormalities can lead to complications during pregnancy. Two such complications are miscarriage and molar pregnancy.
How many miscarriages are caused by chromosomal abnormalities?
Research suggests that chromosomal abnormalities are behind 60% to 70% of first-time miscarriages. In most cases, the error is a random anomaly, and the person will go on to have a healthy subsequent pregnancy. 13
How many chromosomes are in a triad?
Trisomy: There are three chromosomes instead of two.
What is the term for a chromosome that is transferred to another chromosome?
Translocation : One piece of a chromosome is transferred to another. (This could be a Robertsonian translocation, where one chromosome attaches itself to another, or a reciprocal translocation , where two chromosomes are traded.)
What is numerical aneuploidy?
Numerical refers to the fact that there are a different number of chromosomes than expected; there could be more or less. This is also called aneuploidy. Each scenario has a specific term:
What is an unbalanced rearrangement?
Unbalanced rearrangements include deletions, duplications, or insertions of a chromosomal segment. Ring chromosomes can result when a chromosome undergoes two breaks and the broken ends fuse into a circular chromosome. An isochromosome can form when an arm of the chromosome is missing and the remaining arm duplicates.
What is the purpose of prenatal screening?
Prenatal screening and testing can be performed to examine the chromosomes of the fetus and detect some, but not all, types of chromosomal abnormalities. Chromosomal abnormalities can have many different effects, depending on the specific abnormality.
What are the two types of chromosomal abnormalities?
Many types of chromosomal abnormalities exist, but they can be categorized as either numerical or structural. Numerical abnormalities are whole chromosomes either missing from or extra to the normal pair. Structural abnormalities are when part of an individual chromosome is missing, extra, switched to another chromosome, or turned upside down.
How many chromosomes are there in the human body?
Chromosomal Abnormalities. Almost every cell in our body contains 23 pairs of chromosomes, for a total of 46 chromosomes. Half of the chromosomes come from our mother, and the other half come from our father. The first 22 pairs are called autosomes.
What is the 23rd pair?
The 23rd pair consists of the sex chromosomes, X and Y. Females usually have two X chromosomes, and males usually have one X and one Y chromosome in each cell. All of the information that the body needs to grow and develop comes from the chromosomes.
Can chromosomes be abnormal?
Prenatal screening and testing can be performed to examine the chromosomes of the fetus and detect some, but not all, types of chromosomal abnormalities.
Is Genetic Alliance a Creative Commons license?
All Genetic Alliance content, except where otherwise noted, is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
What are some examples of chromosomal abnormalities?
Examples of Chromosomal Abnormalities. The most common examples of these chromosomal abnormalities are down syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome, and Turner syndrome. Let us look at these three examples in detail: Down syndrome: This syndrome is a type of trisomy as there is an extra copy of chromosome 21.
What are the symptoms of Turner syndrome?
Turner syndrome: Unlike Klinefelter syndrome, in this chromosomal disorder there is the absence of one X chromosome in females. Hence, decreasing the chromosomes count to 45 (44 + X0). The symptoms include the following: 1 Such females are sterile 2 Have rudimentary ovaries and there is the absence of secondary sexual characters.
What is the term for a loss of chromosomes due to abnormal segregation of genes during cell?
Aneuploidy – It is a condition in which there is a loss or gain of chromosomes due to abnormal segregation of genes during cell division. Polyploidy – It is a condition in which the count of the entire set of chromosomes increases due to the failure of cytokinesis in cell division. It is mostly observed in plants.
What is the name of the disorder that has an extra copy of chromosome 21?
Down syndrome: This syndrome is a type of trisomy as there is an extra copy of chromosome 21. It is named so after the person who discovered this chromosomal disorder – Langdon Down. The symptoms in a person include the following: The person is short and has a small and round head. Physical and mental development is retarded.
What is it called when a chromosome is missing?
In humans, when there is an extra copy of a chromosome in one of the pairs, it is called trisomy and when one of the chromosome from pair is lacking, it is called monosomy .
What is the chromosome count of a broad palm?
Broad palm. Klinefelter syndrome: This genetic disorder arises due to the presence of an additional X chromosome in males. Thus, resulting in a chromosome count of 47 (44 + XXY) instead of 46. Such a person has a masculine physique but has feminine development like the development of breasts.
Can Turner syndrome reproduce?
Such individuals are sterile, i.e.; they cannot reproduce. Turner syndrome: Unlike Klinefelter syndrome, in this chromosomal disorder there is the absence of one X chromosome in females. Hence, decreasing the chromosomes count to 45 (44 + X0). The symptoms include the following:
What to do if your chromosome test shows a normal pregnancy?
And if your test results revealed a chromosomally normal pregnancy or were inconclusive, and you go on to have more miscarriages , you may wish to see a specialist who can test you for other miscarriage causes. If the results of your chromosome testing reveal ...
What can a chromosome test reveal?
What Testing Can Reveal. Based on the number of chromosomes and their structure, a chromosome test can confirm or rule out obvious abnormalities as the cause of a miscarriage. The most common chromosomal cause of miscarriage is trisomy.
What is the treatment for a recurrent miscarriage?
One of these is a procedure known as pre-implantation genetic diagnosis, along with in-vitro fertilization (IVF).
Why do chromosomes have abnormalities?
Most chromosome abnormalities are the result of errors in cell division of the sperm or egg, and most of the time they will not recur in future pregnancies. The exception to this rule is if the results reveal that the baby had an unbalanced translocation, in which case the doctors may recommend you and your partner be tested for a condition called balanced translocation. 3
What are the causes of translocations?
Others include triploidy, monosomy, tetraploidy, or structural malformations such as translocations —all of which usually are caused by sporadic abnormalities in the sperm or egg, rather than inherited from a parent. 2 .
Can you test for chromosomal abnormalities after a miscarriage?
Testing for chromosomal abnormalities after a miscarriage is usually not indicated after a first miscarriage but may be suggested after recurrent pregnancy loss. However, it is up to the pregnant person to decide when and if to do this testing.
Who is Krissi Danielsson?
Krissi Danielsson, MD is a doctor of family medicine and an advocate for those who have experienced miscarriage. Testing for chromosomal abnormalities after a miscarriage is usually not indicated after a first miscarriage but may be suggested after recurrent pregnancy loss.
What is the difference between translocation trisomy 21 and mosaicism?
Translocation trisomy 21 (2% of cases) is often familial , and commonly involves chromosomes 14 and 21. Mosaicism occur s in about 2% of cases (post-zygotic non-disjunction or more rarely from trisomic rescue). In 1% of cases, the extra chromosome 21 material originates from other rearrangements.
What is the name of the disorder where a person has a pattern of minor and major anomalies?
Trisomy 21, also known as Down syndrome , is a condition characterized by a distinctive pattern of minor and major anomalies associated with excess chromosome 21 material.
What to do if karyotype is not available?
If karyotype not available, check clinical signs on which diagnosis was based.
Why is a karyotype needed?
Karyotype is needed for counselling and for estimating recurrence risk (risk in future pregnancies).
What are the major malformations of Down syndrome?
Major malformations associated with Down syndrome include, among others: heart defects (in about 50%, most notably endocardial cushion defects) vertebral abnormalities. Infants with Down syndrome can present with many other health and developmental issues, such as: intellectual disability of varying degree.
What is a diagnostic test for pregnancy?
A diagnostic test can tell whether a chromosome abnormality is actually present. Anyone who is pregnant can choose to have a diagnostic test, regardless of the risk of chromosomal abnormalities. These tests can count the chromosomes and look for any differences, including those that are less common. The two types of diagnostic tests are chorionic villus sampling (CVS)and amniocentesis. Both types involve taking some tissue or fluid from the uterus (womb). Because of this, there is a small chance that these tests could cause a miscarriage.
What is a screening test for pregnancy?
A screening test estimates the chances of certain chromosome abnormalities in pregnancy. These tests are not invasive and pose no risk to the fetus. The results are based on your age and other factors. Screening tests are used to identify pregnancies that have an increased chance to have a chromosome abnormality, but they do not tell whether one is actually present. If you decide to have screening and your result suggests an increased chance of an abnormality, you will be given information about extra tests that may provide more information. If your results do not suggest an increased chance for an abnormality, extra testing may not be needed. Your doctor or genetic counselor will explain more about what your own results mean. Screening tests have a risk of “false” results. That is, some people who have a pregnancy with a chromosome abnormality will be told their pregnancy is “low-risk.” Others who have a pregnancy with no chromosome abnormality will be told the pregnancy is “high-risk.” The chance for these “false” results depends on the test performed.
How many chromosomes are in a human body?
They contain the instructions for our growth and development. Usually, each person has a total of 46 chromosomes in each cell. The chromosomes come in pairs (23 pairs). Each parent contributes one chromosome to each pair. When a fetus (developing baby) has extra or missing chromosomes, it can lead to medical problems. An extra chromosome (three copies instead of two) is called a trisomy. A missing chromosome (one copy instead of two) is called a monosomy. This type of genetic condition doesn’t usually run in families. It can happen just by chance in any pregnancy.
What is the chance of having a baby with Down syndrome?
For example, a 20-year-old has less than a 1/1000 chance of having a baby with Down syndrome; a 35-year-old has a 1/350 chance of having a baby with Down syndrome; a 40-year-old has about a 1/100 chance of having a baby with Down syndrome. So even though those who are older have a higher chance for these abnormalities, these abnormalities can occur in any pregnancy.
How many babies are affected by genetics?
While most babies are born healthy, approximately 3-5% will be affected with certain birth defects or genetic conditions. In all pregnancies, tests are offered that can tell if the pregnancy may be at high risk for a condition called a chromosome abnormality. Decisions about testing in pregnancy are personal. Some choose not to have any testing done. Others find the information from testing to be helpful. We have made this booklet to give some information on the tests available. We hope that having this information and discussing it with your OB/GYN provider will help you to decide whether this testing makes sense for you and your family.
Does ERA mean a baby has a chromosome abnormality?
This does not mean that a baby has a chromosome abnormality. In fact, for most pregnancies with this type of screening result, additional tests are normal and the baby is healthy. The actual chance of an abnormality depends on many factors and is specific for each pregnancy.
Can a genetic test detect all birth defects?
Remember, there are no tests that can find all birth defects or genetic differences. Even when all results are normal, there is still a small chance for abnormalities that cannot be detected before birth.
