How to check the position of an NG tube
- 1. Aspiration of gastric contents Before removing the guide wire, aspirate from the NG tube and check for gastric pH a pH of between 0 and 5 confirms placement of NG tube If pH confirmed, remove guide wire and tape tube in place ...
- 2. Check an NG tube position on chest X-Ray
How do you position an NG tube in a patient?
Two approaches can be used by nurses to ensure that the tube is properly positioned: Ask the patient to hum or talk (coughing or choking indicates proper tube placement); aspiration stomach contents with an irrigation syringe; chest X-ray; lower the open end of the NG tube into a cup of water bubbles indicate proper tube placement.
How do you check the placement of a nasogastric tube?
Methods Used to Check Correct Placement of Nasogastric (NG) Tube. Nurses can check the placement of the patient’s NG tube by using one of the following methods: Chest X-ray – This method offer one of the best ways to check the placement of the NG tube.
What are the different methods of NG tube testing?
Syringe test – This method is not uses very often anymore. The syringe test or “whoosh test” checks the placement of the tube by using a stethoscope to listen for the whooshing sound as a syringe instills a 30cc air bolus in to the patient’s stomach. pH test – This method aspires the NG tube and checks the content by using pH paper.
How can you tell if a NG tube is in the stomach?
Always aspirate a tiny amount of stomach contents to be sure the NG tube is in the stomach. The best technique to confirm placement is via an X-ray study. What is the purpose of checking gastric residual? Measure gastric residual volume to assess the pace of gastric emptying in a patient who receives tube feedings to prevent aspiration.
How do you confirm placement of nasogastric tube?
Auscultation is most often used at the bedside to check for appropriate placement of a nasogastric tube. Sound generated by air blown through the tube is used to determine tube placement in the gastrointestinal tract.
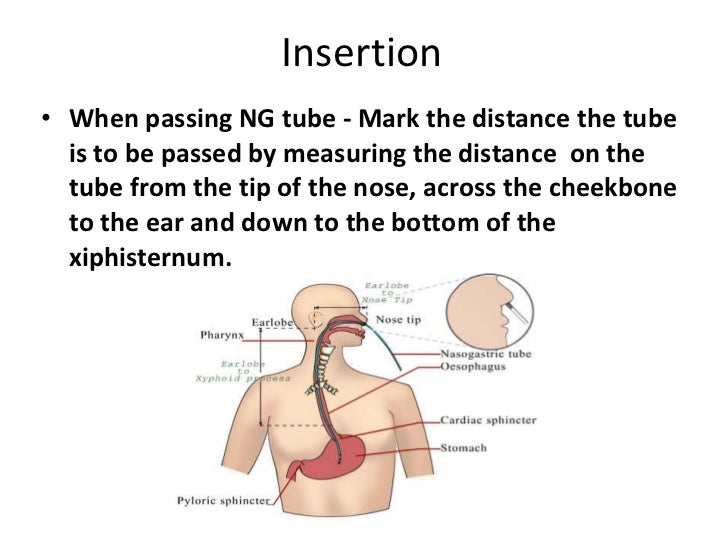
How do you measure NG tube ATI?
Determine the length of the tube to be inserted by measuring the nasogastric tube from the tip of the patient's ear lobe to the tip of the nose, then to the xiphoid process.
What should the nurse do to verify nasogastric NG tube placement select all that apply?
Nurses can verify the placement of the tube by performing two of the following methods: ask the patient to hum or talk ( coughing or choking means the tube is properly placed); use an irrigation syringe to aspire gastric contents; chest X-ray; lower the open end of the NG tube into a cup of water ( bubbles indicate ...
What is normal nasogastric tube output?
The average daily nasogastric output was 440 +/- 283 mL (range 68-1565).
What is the NEX measurement?
The most common methods of measurement are the direct distance from nose to earlobe to xiphisternum (NEX), measuring from the nose to the earlobe to a point halfway between the xiphisternum and the umbilicus (NEMU), an age related height based (ARHB) equation and a weight based method.
How do you measure a baby's NG tube?
Hold the end of the tube with the holes at your child's nostril and begin measuring from the holes. Measure the feeding tube from the nostril to the base of the ear lobe, then to about half way between the base of the chest bone and the umbilicus, or "belly button".
How do you measure OGT?
Measure length of the OG tube from the tip of the patient's nose to the earlobe and then to the xiphisternum. 3. Mark the desired length of the tube with a piece of tape. 4.
Can nurses place NG tubes?
The process of inserting an NG tube has its risks, but once nurses gain experience in this area, they should be able to insert an NG tube without any level of difficulty.
How to confirm NG tube placement?
Confirmation of safe NG tube placement can be achieved by testing the pH of NG tube aspirate.
What is the assessment of NG tube placement?
The assessment of NG tube placement requires a systemic approach and a willingness to ask for senior assistance if unsure, to prioritise patient safety. The incorrect placement of an NG tube can result in life-threatening complications (e.g. aspiration pneumonia).
Why does a NG tube curl up?
An NG tube can curl up on itself, meaning the tip is placed higher than it should be which can result in reflux and aspiration of NG tube contents. This demonstrates the importance of confirming you can see the NG tube tip clearly.
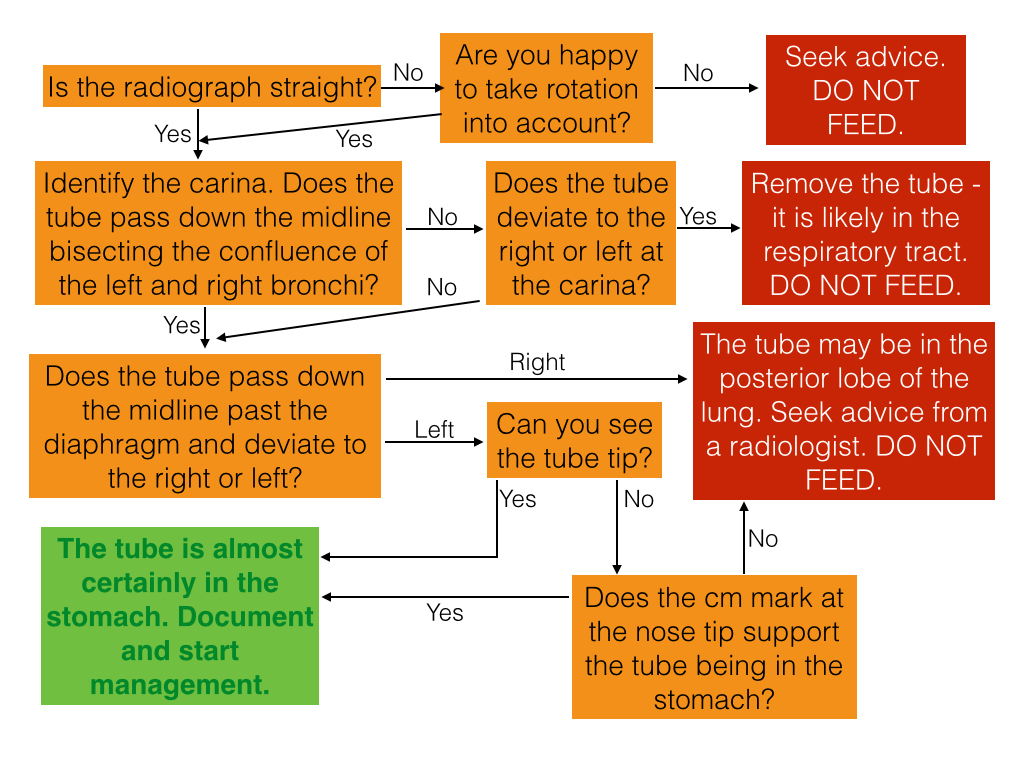
Where is the NG tube positioned?
Incorrect placement of an NG tube. An NG tube can be positioned in the left or right main bronchus but to still appear in the midline (hence why the single criterion of an NG tube appearing in the midline is not satisfactory evidence to confirm safe placement).
What are the landmarks on a chest X-ray?
The annotated chest X-ray below highlights these key anatomical landmarks including: Trachea. Right and left main bronchi.
What is a NG tube?
Drainage of the upper gastrointestinal tract in conditions such as small bowel obstruction ( a larger diameter NG tube – known as a ‘Ryles tube’). When inserting an NG tube for feeding and/or administration of medication you need to confirm the safe placement of the tube prior to its use.
Where should a NG tube be located on a chest X-ray?
To confirm an NG tube is positioned safely, all of the following criteria should be met: The chest X-ray viewing field should include the upper oesophagus and extend to below the diaphragm. The NG tube should remain in the midline down to the level of the diaphragm. The NG tube should bisect the carina.
