Classification of lipid
- I. Simple lipids: They are further divided into neutral fat and oil and wax. i. Fat and oil: ...
- II. Complex lipids: They are further divided into: Phospholipids ...
- III. Derived lipids: They are the hydrolyzed product of simple and composed lipids with various type of other compounds such as alcohol, ketone, vitamin D, sex-hormone steroid, terpenes, carotenoids. Steroid: ...
What is the largest category of lipids?
Fats make up the largest category of lipids, and also go by the terms triacylglycerols, triglycerides, and glycerolipids. There are several types of fats. Saturated fat is a lipid that exists as a solid substance when it is at room temperature. This is answered comprehensively here. Hereof, what are major lipid classes?
What are the subclasses of lipids?
What are the main subclasses of lipids?
- Triglycerides are also known as triacylglycerols and compose 95% of fat in the foods we eat.
- Phospholipids bring water and fat together and are called emulsifiers.
- Sterols are found in tissues of animals and plants.
What you should know about blood lipids?
Your goal should be:
- Total cholesterol (a measure of HDL, LDL and other lipoproteins) Less than 200 mg/dL
- Triglycerides Less than 150 mg/dL
- LDL (Low-density lipoprotein) Less than 130 mg/dL Less than 100 mg/dL for those with heart or blood vessel disease and for those with diabetes or high total cholesterol
What are some common lipids?
Some common examples of lipids are fats, waxes, soluble vitamins (A,D,E &K), sterols, monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides, phospholipids, etc. The representative images of some of the biologically available lipids are as follows.

How are the lipids classified?
They can be classified as simple lipids, compound lipids, or derived lipids. Simple lipids: esters of fatty acids with alcohols, which include fats, oils, and waxes. Fats are neutral esters of glycerol with saturated or unsaturated fatty acids.
What are the 3 classifications of lipids?
Lipids are important fats that serve different roles in the human body. The three main types of lipids are triacylglycerols (also known as triglycerides), phospholipids, and sterols.
What are the 4 classifications of lipids?
The four main groups of lipids include:Fatty acids (saturated and unsaturated)Glycerides (glycerol-containing lipids)Nonglyceride lipids (sphingolipids, steroids, waxes)Complex lipids (lipoproteins, glycolipids)
What are lipids classify lipids with example?
Lipids are a heterogeneous group of organic compounds that are insoluble in water and soluble in non-polar organic solvents. They naturally occur in most plants, animals, microorganisms and are used as cell membrane components, energy storage molecules, insulation, and hormones.
Who gave the classification of lipids?
In 1815, Henri Braconnot classified lipids (graisses) in two categories, suifs (solid greases or tallow) and huiles (fluid oils). In 1823, Michel Eugène Chevreul developed a more detailed classification, including oils, greases, tallow, waxes, resins, balsams and volatile oils (or essential oils).
What are the characteristics of lipids?
Lipids are fatty, waxy, or oily compounds that are soluble in organic solvents and insoluble in polar solvents such as water. Lipids include: Fats and oils (triglycerides)
What are the 5 classifications of lipids?
Based on this classification system, lipids have been divided into eight categories: fatty acyls, glycerolipids, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids, saccharolipids and polyketides (derived from condensation of ketoacyl subunits); and sterol lipids and prenol lipids (derived from condensation of isoprene subunits) (Fig ...
What are the 4 main functions of lipids?
The Functions of Lipids in the BodyStoring Energy. The excess energy from the food we eat is digested and incorporated into adipose tissue, or fatty tissue. ... Regulating and Signaling. ... Insulating and Protecting. ... Aiding Digestion and Increasing Bioavailability.
What are the 4 classifications of macromolecules?
11.1 Introduction: The Four Major Macromolecules These are the carbohydrates, lipids (or fats), proteins, and nucleic acids. All of the major macromolecule classes are similar, in that, they are large polymers that are assembled from small repeating monomer subunits.
What are lipids?
Lipids are organic compounds that are fatty acids or derivatives of fatty acids, which are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents. For...
How are lipids important to our body?
Lipids play a very important role in our body. They are the structural component of the cell membrane. They help in providing energy and produce ho...
How are lipids digested?
The enzyme lipase breaks down fats into fatty acids and glycerol, which is facilitated by bile in the liver.
What is lipid emulsion?
It refers to an emulsion of lipid for human intravenous use. These are also referred to as intralipids which is the emulsion of soybean oil, glycer...
How are lipids metabolized?
Lipid metabolism involves the oxidation of fatty acids to generate energy to synthesize new lipids from smaller molecules. The metabolism of lipids...
How are lipids released in the blood?
The medium-chain triglycerides with 8-12 carbons are digested and absorbed in the small intestine. Since lipids are insoluble in water, they are ca...
What are the main types of lipids?
There are two major types of lipids- simple lipids and complex lipids. Simple lipids are esters of fatty acids with various alcohols. For eg., fats...
What are lipids made up of?
Lipids are made up of a glycerol molecule attached to three fatty acid molecules. Such a lipid is called triglyceride.
i. Fat and oil
Fat and oil are triglycerides, a triacylglycerol (TAG) in which 3 fatty acids are linked with one glycerol molecule by ester bond.
1. Phospholipid
Glycerophospholipid consists of glycerol in which two fatty acids are linked with -OH group glycerol by ester bond and third -OH group of glycerol is linked with phosphate group which in turn linked with head group substituent.
2. Glycolipids
In glyceroglycolipid, two fatty acids are linked with glycerol by ester bond and their OH group of glycerol is linked with carbohydrate head group.
What are Lipids?
These organic compounds are nonpolar molecules, which are soluble only in nonpolar solvents and insoluble in water because water is a polar molecule. In the human body, these molecules can be synthesized in the liver and are found in oil, butter, whole milk, cheese, fried foods and also in some red meats.
Properties of Lipids
Lipids are a family of organic compounds, composed of fats and oils. These molecules yield high energy and are responsible for different functions within the human body. Listed below are some important characteristics of Lipids.
Lipid Structure
Lipids are the polymers of fatty acids that contain a long, non-polar hydrocarbon chain with a small polar region containing oxygen. The lipid structure is explained in the diagram below:
Classification of Lipids
A nonsaponifiable lipid cannot be disintegrated into smaller molecules through hydrolysis. Nonsaponifiable lipids include cholesterol, prostaglandins, etc
Types of Lipids
Within these two major classes of lipids, there are numerous specific types of lipids important to live, including fatty acids, triglycerides, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids and steroids. These are broadly classified as simple lipids and complex lipids.
Examples of Lipids
There are different types of lipids. Some examples of lipids include butter, ghee, vegetable oil, cheese, cholesterol and other steroids, waxes, phospholipids, and fat-soluble vitamins. All these compounds have similar features, i.e. insoluble in water and soluble in organic solvents, etc.
Frequently Asked Questions
Lipids are organic compounds that are fatty acids or derivatives of fatty acids, which are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents. For eg., natural oil, steroid, waxes.
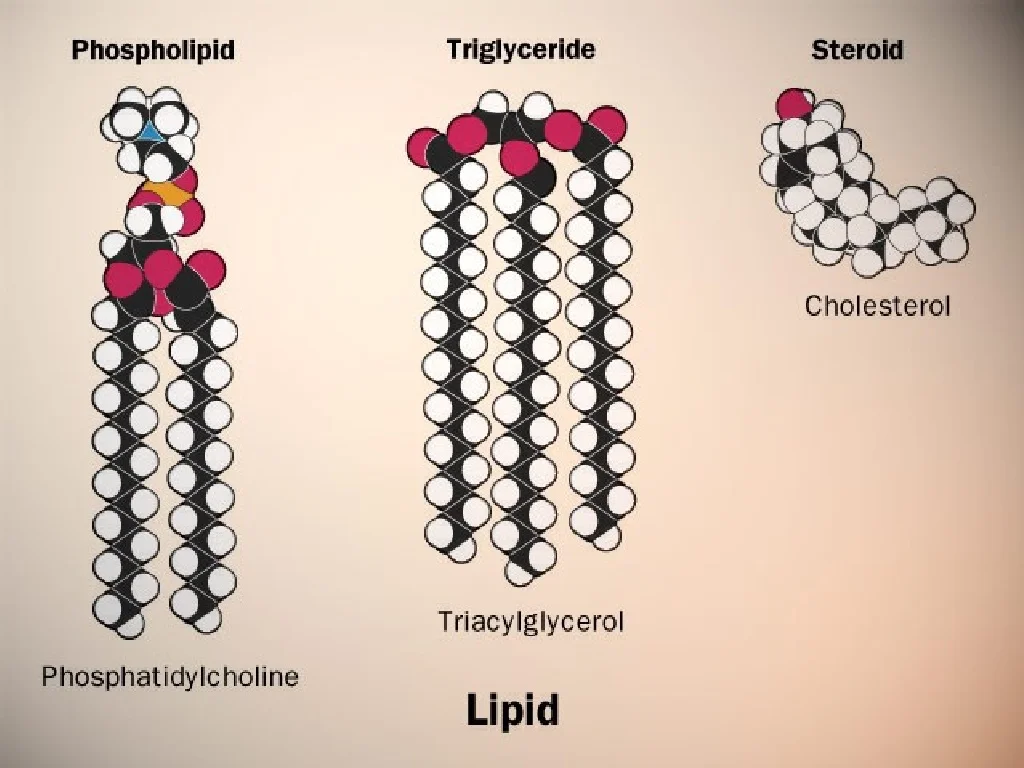
Triglycerides
Triglycerides are lipids you obtain from food sources of fat, such as cooking oils, butter and animal fat. Triglycerides provide insulation that keeps you warm while protecting your internal organs with a layer of padding. They also play a role how your body uses vitamins.
Steroids
Steroids are a type of lipid that includes hormones and cholesterol. Cholesterol is produced by the body and consumed through food, and it plays a role in the production of hormones. Hormones include the sex hormones estrogen and testosterone, as well as your other hormones like adrenaline, cortisol and progesterone.
Phospholipids
Phospholipids are derivatives of triglycerides. They're very similar to them but slightly different on a molecular level. Half of each molecule is water-soluble and the other is not, which causes them to react differently than triglycerides.
Getting Your Lipid Levels Tested
If your blood is too high in triglycerides or cholesterol, you could face a health problem. You may have no specific symptoms that tell you your levels are high, so it's a good idea to get them tested. You can have this done at a clinic through a simple blood test.
